CSS float
The attribute involved here is float, and its value can be assigned as:
left: The element floats to the left right: element floats to the right none: no floating inherit: Inherit floating properties from the parent
There is also the clear property: Mainly used to remove floating attributes in all directions (including inherited attributes)
Let’s first create a basic html and CSS file. The following is the basic content:
html:
<div class="qd"></div> <div class="wd"></div> <div class="ed"></div>
CSS
.qd{ width: 100px; height: 100px; background-color: lightskyblue;
}.wd{ width: 100px; height: 100px; background-color: lightseagreen;
}.ed{ width: 100px; height: 100px; background-color: lightsalmon;
}The following is the display effect:
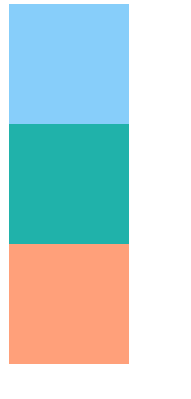
On this basis we all add float Properties, the first two go to the left, the last one to the right, see what the effect will be:
float: left;float: right;
Rendering

Just like a few small things running in a room, you can specify the direction in which they run, and they will run to the border. For testing, we might as well limit a space for them (put all three divs into one div) ).Like this:
<div class="container"> <div class="qd"></div> <div class="wd"></div> <div class="ed"></div> </div>
The next thing you will see is:

But sometimes we don’t need floats, like As shown below, we want to add a sentence below the above effect, and then we directly add a
<div class="text">hello php</div>
in the container. Then we will see

.text{ clear: both;
}Rendering:
