盒模型
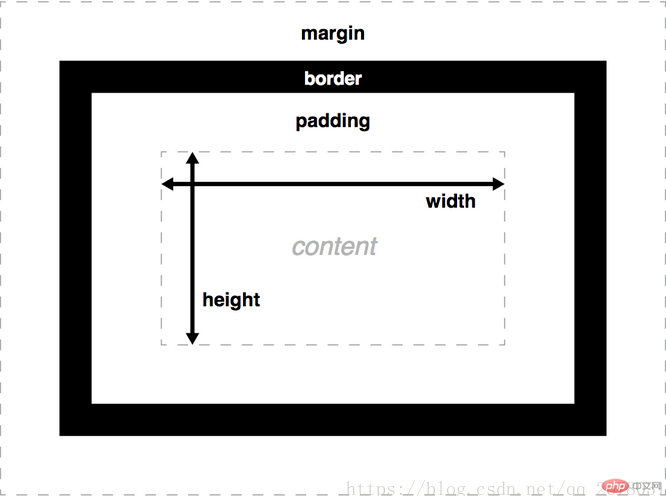
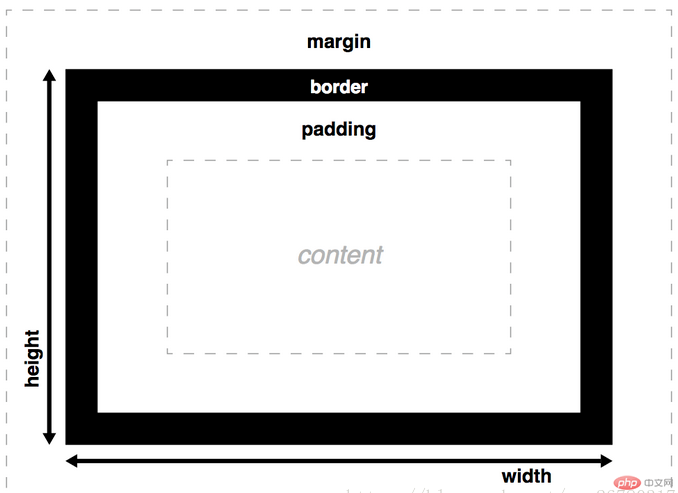
CSS盒模型由内容区(content),内边距(padding),边框(border),外边距(margin)组成。width和height设置内容框(content box)的宽度和高度。
总宽度 = 左外边距 + 左边框 + 左内边距 + 内容区宽度 + 右内边距 + 右边框 + 右外边距
总高度 = 上外边距 + 上边框 + 上内边距 + 内容区高度 + 下内边距 + 下边框 + 下外边距
为方便排版,工作中常常使用box-sizing:border-box样式转化为html盒模型,width=content+padding+border(此时,当width、padding、border设定时,那么content会随着实际的宽度进行自动缩放;)
示例:
width和heigth都为200px,padding为5px,border为1px,在默认情况下,box占用了width+padding+border= 212


使用box-sizing:border-box后,width和heigth仍为200px,content压缩成了188.
 ]
]
<!doctype html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><meta name="viewport"content="width=device-width, user-scalable=no, initial-scale=1.0, maximum-scale=1.0, minimum-scale=1.0"><meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"><title>Document</title><style>* {margin: 0;padding: 0;font-size: 10px;box-sizing: border-box;}.box {border: 1px solid red;height: 20em;width: 20em;padding: 0.5em;margin: 1em;background-color: lightgreen;}</style></head><body><div class="box"></div></body></html>
相对定位position: relative;
相对于元素框在文档流中的原始位置进行定位。元素框仍在文档流中。

<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"><title>Document</title><style>.pos_left {position: relative;left: -30px;}.pos_right {position: relative;right: -30px;}</style></head><body><h3>这是正常位置</h3><h3 class="pos_left">这个位置相对于正常位置向左</h3><h3 class="pos_right">这个位置相对于正常位置向右</h3></body></html>
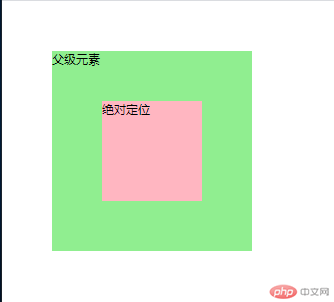
绝对定位position: absolute;
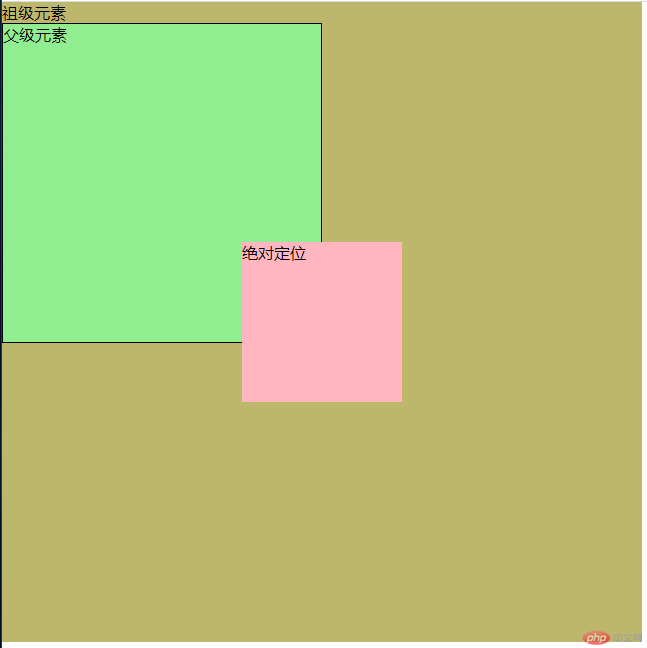
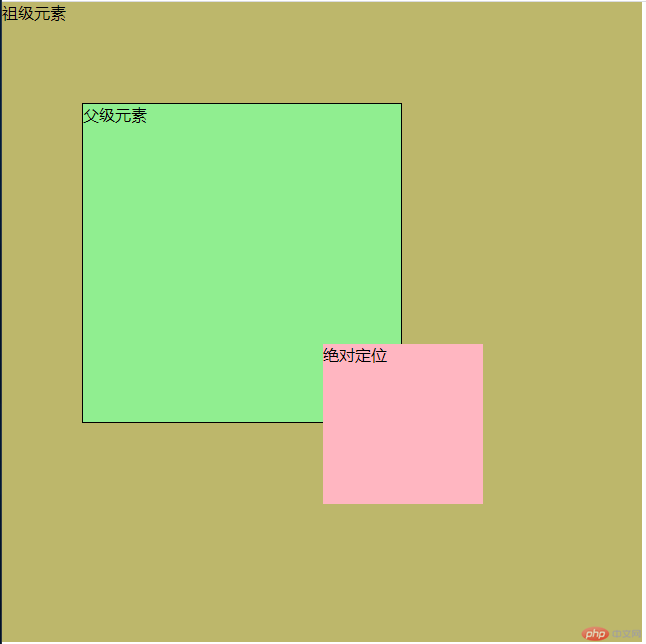
设置为绝对定位的元素框从文档流完全删除,并相对于其包含块定位,包含块可能是文档中的另一个元素或者是初始包含块。元素原先在正常文档流中所占的空间会关闭,就好像该元素原来不存在一样。
示例:
当没有相对定位元素时,从初始html定位。
当有相对定位元素时,从相对定位元素定位。
代码如下:其它代码相同,区别在是否开启position: relative;关闭效果为上图,开启效果如下图。
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"><title>Document</title><style>* {margin: 0;padding: 0;box-sizing: border-box;}.gf {height: 40em;width: 40em;background-color: darkkhaki;}.parent {/* 父级元素相对定位 */position: relative;background-color: lightgreen;height: 20em;width: 20em;top: 5em;left: 5em;border: 1px solid #000000;}.box {/* 子级元素绝对定位 */position: absolute;height: 10em;width: 10em;left: 15em;top: 15em;background-color: lightpink;}</style></head><body><div class="gf">祖级元素<div class="parent">父级元素<div class="box">绝对定位</div></div></div></body></html>
块元素的垂直居中方法
position: absolute;
left: 0;
top: 0;
bottom: 0;
right: 0;
margin: auto;
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"><title>Document</title><style>* {margin: 0;padding: 0;box-sizing: border-box;font-size: 10px;}.parent {/* 父级元素相对定位 */position: relative;background-color: lightgreen;height: 20em;width: 20em;top: 5em;left: 5em;}.box {/* 子级元素绝对定位 */position: absolute;height: 10em;width: 10em;left: 0;top: 0;bottom: 0;right: 0;margin: auto;background-color: lightpink;}</style></head><body><div class="parent">父级元素<div class="box">绝对定位</div></div></body></html>