课程:PHP中文网上了第三期的培训(前端部分)
时间:2018年8月16号晚8点
讲师:Peter zhu!
内容:元素对齐、定位、浮动
<!--
1. 固定定位与绝对定位是双胞胎,唯一的区别是定位父级不同.
2. 绝对定位是相对于它最近的有定位属性的父级区块进行定位;
3. 固定定位永远相对于当前的窗口进行定位(body)
-->
实例
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>元素对齐方式</title>
</head>
<body>
<h3>元素对齐方式</h3>
1. 子元素是单行行内元素: 如a, span <br>
a:水平居中: 在父元素应用: text-align: center;
b:垂直居中: 在行内子元素上设置行高与父元素等高: line-height:200px;
<style>
.box1 {
width: 200px;
<!--height: 200px;
background-color: #ffff0a;
<!--text-align: center;
}
.box1 a {-->
<!--line-height: 200px;
}
</style>
<div class="box1">
<a href="">php中文网</a>
</div>
<hr>
2. 子元素是多行的内联文本 <br>
a:水平居中: 在父元素应用: text-align: center;<br>
b:垂直居中: 在父元素: display:table-cell;
<style>
.box2 {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: lightgreen;
text-align: center; /*水平居中*/
display: table-cell;
vertical-align: middle; /*垂直居中*/
}
</style>
<div class="box2">
<span>php中文网</span> <br>
<span>www.php.cn</span>
</div>
<hr>
3.子元素是块元素 <br>
a: 水平居中: 子元素设置左右外边距自动适应容器margin: auto;
b:垂直居中: 在父元素: display:table-cell;
<style>
.box3 {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: lightgreen;
display: table-cell;
vertical-align: middle; /*垂直居中*/
}
.box3 .child {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: lightcoral;
/*margin-left: auto;*/
/*margin-right: auto;*/
margin: auto; /*水平居中*/
}
</style>
<div class="box3">
<div class="child"></div>
</div>
<hr>
4. 子元素是不定宽的块元素
a: 水平居中: 子元素转为行内元素,父级加: text-align:center
b: 垂直居中: 在父元素: display:table-cell;
<style>
.box4 {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: lightblue;
text-align: center; /*水平居中*/
display: table-cell;
vertical-align: bottom; /*位于底部*/
}
ul {
margin: 0;
padding-left: 0;
}
.box4 li {
display: inline; /*将块元素转为行内元素*/
}
</style>
<div class="box4">
<ul>
<li><a href="">1</a></li>
<li><a href="">2</a></li>
<li><a href="">3</a></li>
<li><a href="">4</a></li>
<li><a href="">5</a></li>
</ul>
</div>
</body>
</html>
分割线
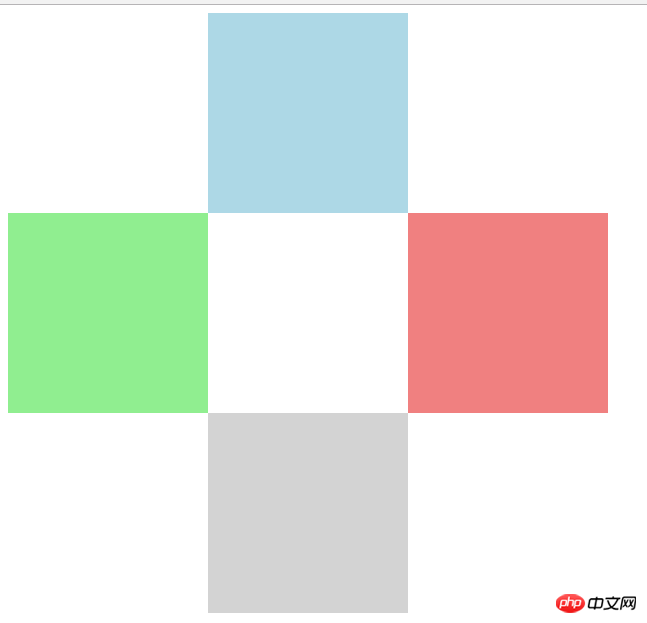
绝对定位
实例
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>绝对定位</title>
<style>
body {
/*margin:0;*/
}
.box {
width: 600px;
height: 600px;
/*background-color: wheat;*/
/*定位父级必须设置定位属性*/
position: relative;
}
.box1 {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: lightblue;
/*绝对定位元素会脱离文档流*/
position: absolute;
top:0;
left: 200px;
}
.box2 {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: lightgreen;
position: absolute;
top:200px;
left:0;
}
.box3 {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: lightcoral;
position: absolute;
top: 200px;
left: 400px;
}
.box4 {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: lightgrey;
position: absolute;
top: 400px;
left: 200px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box">
<div class="box1"></div>
<div class="box2"></div>
<div class="box3"></div>
<div class="box4"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>运行实例 »
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
分割线
固定定位,及页面右下角广告案例
实例
<!doctype html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>固定定位</title>
</head>
<body>
<!--
1. 固定定位与绝对定位是双胞胎,唯一的区别是定位父级不同.
2. 绝对定位是相对于它最近的有定位属性的父级区块进行定位;
3. 固定定位永远相对于当前的窗口进行定位(body)
-->
<style>
.box1 {
position: fixed;
bottom: 0; /*底部*/
right: 0; /*右边*/
}
.close {
position: absolute;
right: 20px;
top: 10px;
}
</style>
<div class="box1">
<a href="http://php.cn/k.html"><img src="images/ads.jpg" alt="广告"></a>
<span class="close">X</span>
<!--等学到js,再教大家如何关闭掉这个广告-->
<!--<span class="close" onclick="this.parentNode.style.display='none' ">X</span>-->
</div>
</body>
</html>运行实例 »
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例

分割线
浮动
总结:
1. 元素的水平方向浮动,意味着元素只能左右移动而不能上下移动。
2.一个浮动元素会尽量向左或向右移动,直到它的外边缘碰到包含框或另一个浮动框的边框为止。
3.浮动元素之后的元素将围绕它。
4.浮动元素之前的元素将不会受到影响。
5.如果图像是右浮动,下面的文本流将环绕在它左边;
实例
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>浮动的原理与清除浮动</title>
</head>
<body style="border: 1px dashed red">
<style>
.box1 {
width:200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: lightskyblue;
float:left; /*设置左浮动*/
/*下面绿色块看不到了,因为浮动元素脱离了文档流,绿色自动上移占据了原来蓝色块的位置*/
/*如果想看到绿色块,只要将绿色块宽高调整大一点就可以*/
/*得到第一个特点: 浮动元素与绝对定位元素一样,也脱离了文档流*/
}
</style>
<div class="box1"></div>
<!--------------------------------------------------------------------------->
<style>
.box2 {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: lightgreen;
/*float:left; !*设置左浮动*!*/
/*为什么会紧贴着第一个浮动的元素?*/
/*因为第二个色块也脱离了文档流,与第一个是在同一个空间中,所以会挨着顺序排列,大家都上天了都是神仙*/
float: right; /*浮动方向可以调整*/
/*得到第二个特点:
1.浮动元素之前的元素将不会受到影响(关掉.box1的浮动试试看),只对浮动元素后面的元素有影响
2.多个浮动元素只能沿着水平方向排列,一行排不下自动换行
*/
}
</style>
<div class="box2"></div>
<!--------------------------------------------------------------------------->
<style>
.box3 {
width: 900px;
height: 200px;
background-color: lightsalmon;
clear: left; /*清除左边元素的浮云属性*/
clear: right; /*清除右边元素的浮动属性,窗口调整到一定大小才会看到左右区块都回到文档流中*/
clear: both; /* clear: left; clear: right; 的简写 */
}
</style>
<div class="box3"></div>
<!--------------------------------------------------------------------------->
<style>
.text {
/*行内元素,它的宽高由内部文本决定,不支持用户自定义*/
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: yellow;
float: left; /*设置浮动*/
/*浮动使元素脱离了文档流,同时使行内元素也支持了宽高,表现出与块级元素一样的特征*/
/*可以看出该文本块已在不在body中了,脱离了文档流,说明浮动的确仅影响到后面的元素*/
}
</style>
<span class="text">php中文网</span>
<!--
总结:
1. 元素的水平方向浮动,意味着元素只能左右移动而不能上下移动。
2.一个浮动元素会尽量向左或向右移动,直到它的外边缘碰到包含框或另一个浮动框的边框为止。
3.浮动元素之后的元素将围绕它。
4.浮动元素之前的元素将不会受到影响。
5.如果图像是右浮动,下面的文本流将环绕在它左边;
-->
</body>
</html>运行实例 »
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例

分割线
子元素浮动引起的父级区块高度塌陷的解决方案
实例
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>子元素浮动引起的父级区块高度塌陷的解决方案</title>
</head>
<body>
<style>
.box1 {
border: 5px dashed red;
/*
流式布局中,子块高度撑开父块
子块浮动后,脱离文档流,父块失去高度限制,自动折叠,出现高度塌陷
解决方案有三种:
*/
/*方案一:给父级区块加高度,优点是简单,缺点是不能自适应子块高度变化*/
/*height: 400px; !*父块加高度的方案不推荐*!*/
/*方案二:父级区块加:overflow: hidden;(溢出隐藏)*/
/*overflow: hidden; !*部分浏览器可能会存在兼容性,例如IE,可能会出现gun动条*!*/
}
/*方案三: 给父级区块添加伪类元素解决*/
.box1:after {
content: ''; /*添加空内容元素*/
display: block; /*将添加的空元素转为块级元素*/
clear: both; /*清除该空元素前面元素的浮动属性,使之回到文档流中,以撑开父级高度*/
}
.box2 {
height: 400px;
width: 100%;
background-color: lightgreen;
float: left;
}
</style>
<div class="box1">
<div class="box2"></div>
<!--方案四: 添加附加空区块,仅仅用来清除前面元素的浮动属性-->
<!--不推荐,因为后端进行数据绑定时会遇到麻烦:例如循环输出数据,需要对它单独处理-->
<div style="clear: both;"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>运行实例 »
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例

