html 文档结构和页面元素三大属性学习总结
1.HTML5 ⽂档结构
| 代码 | 描述 |
|---|---|
<!DOCTYPE html> |
通知浏览器这是⼀个 HTML5 ⽂档,应始终写在第⼀⾏ |
<html>...</html> |
根标签,或叫根元素,整个 hmtl ⽂档内容都必须写到这对标签中 |
<html lang="en"> |
通知搜索引擎 html ⽂档使⽤的编写语⾔,如果是中⽂建议改成:<html lang="zh-CN"> |
<head>...</head> |
供浏览器和搜索引擎使⽤,描述字符编码集,视⼝与⻚⾯标题,⽤户并不感兴趣 |
<meta> |
设置⻚⾯元素数据, 所谓元数据, 就是描述某种特定信息的数据 |
<meta charset="UTF-8"> |
通知浏览器 html ⽂档编写语⾔所属的字符编码集,最流⾏的是UTF-8,已成⾏业标准 |
<meta name="viewport" content="..." /> |
下⾯三⾏是对它的解读 |
name="viewport" |
设置视⼝(即可视区屏幕)如何显示这个⻚⾯, 例如是否允许缩放这个⻚⾯ |
initial-scale=1.0 |
设置⻚⾯初始绽放⽐例,1.0表示原样 1:1 显示,不允许有任何绽放 |
<title> |
显示在浏览器标签上的⽂本, 指定当前⻚⾯的标题, 这个标签对 SEO ⾮常重要 |
<body>...</body> |
⻚⾯主体内容,允许或希望⽤户的内容都应该写到这⾥,⽤户也只对这⾥的内容感兴趣 |
<!-- 注释内容 -> |
注释⽤来描述标签功能或⽤途,它的内容不要出现在显示的⽹⻚中, 只会出现在 html 源代码中 |
2.关于对象
- 请简单描述自己的女朋友
- 姓名:晓丽, 年龄:20,性别:女, 身高:170,体重:80kg
<女朋友 姓名="小丽" 性别="女" 年龄="23">一个将来有可能会成为老婆的女人</女朋友>女朋友/对象用属性来描述: 姓名=”小丽” 性别=”女” 年龄=”23”
2.1.window
浏览器全局对象
2.2.document
代表当前的 html 文档
2.3 浏览器的控制台
控制台:浏览器内置的一个 javascript 解释器,执行器
2.4HTML 文档结构代码示例
<!--文档类型:html5--><!DOCTYPE html><!-- html 根元素 --><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8" /><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" /><title>html页面的文档结构</title><!-- 内联样式表 一个HTML文档可以写多个<style></style> --><style>h2 {font-size: 16px;line-height: 40px;text-align: center;}div {padding-top: 20px;text-align: center;}div h2 {font-weight: bolder;color: sandybrown;}</style><style></style><style></style><style></style><!-- JS文件--></head><!-- 主体内容 --><body><script>1;</script><script>2;</script><script>3;</script><h2>PHP中文网第12期培训班~20200611</h2><div><h2>最常见的结构网站应该使用什么</h2><p>一个主页index.html</p><p>一个图片images 文件夹</p><p>一个样式表styles 文件夹</p><p>一个脚本scripts 文件夹</p></div><script>//javascript的脚本代码//使用console.log()指令将代码执行结果发送到浏览器控制台显示//显示全局对象:windowconsole.log(window);//显示html文档到控制台显示console.log(window.ducument);//显示当前页面urlconsole.log(window.document.url);//省了windowconsole.log(document.url);//文档类型console.log(window.document.doctype);//根元素HTMLconsole.log(window.document.documentElement);//头元素console.log(document.head);//编码console.log(document.charset);//titleconsole.log(document.title);//修改title标题 document.title="123" 用单引号和双引号都可以//如何用js脚本访问HTMLdocument.title = "用js脚本修改HTML文档标题";//主体console.log(document.body);//修改主体背景颜色document.body.style.backgroundColor = "wheat";//样式表cssconsole.log(document.styleSheets);console.log(document.styleSheets[0].type);//js脚本console.log(document.scripts);console.log(document.scripts[0]); //第1个js基本console.log(document.scripts[3]); //第4个js基本//第四个脚本,整好是当前正在被执行的jsconsole.log(document.currentScript);//获取脚本相同,判断返回值trueconsole.log(document.scripts[3] === document.currentScript);console.log(document.h2);</script></body></html>
- 运行结果

3.元素的三大通用属性
- id:获取页面中的唯一元素
- class:获取页面中的一类元素
- style:设置某个元素的内联样式
- id,class:用在 css,js 中获取一个或多个元素对象
- style:用来设置某个元素的具体样式的
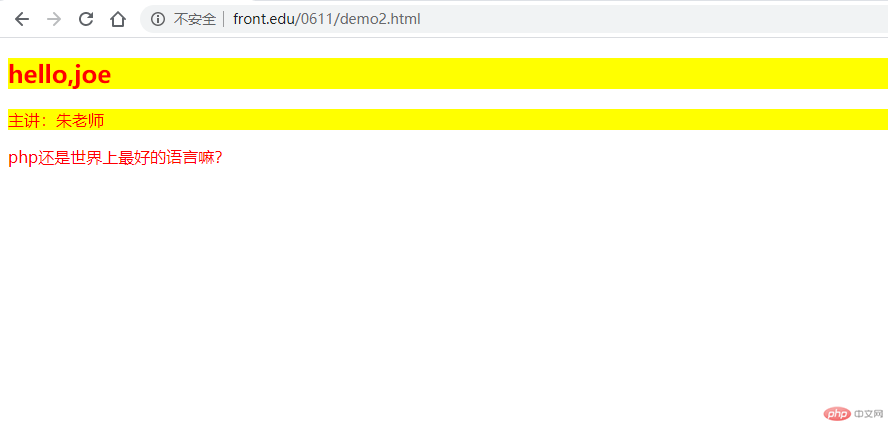
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8" /><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" /><title>元素的三大属性</title><style>/* id获取元素 */#title-id {color: red;}.title-class {color: blue;}/* style属性设置的样式优先级大于class *//* style属性设置的样式:内联样式,仅对当前元素有效 *//* css:层叠样式表 */</style></head><body><!--1. id属性:由用户保证它在当前页面的唯一性,浏览器并不检查,专用于获取唯一元素 --><!--2. class属性:类属性,返回多个具有共同特征的数据集合 --><!--3. style属性:设置当前元素的样式 --><h2 id="title-id" class="title-class bgcolor" style="color: red;">PHP中文网第12期培训班</h2><p id="title-id" class="title-class bgcolor">主讲:朱老师</p><p class="title-class" id="title-id">php还是世界上最好的语言嘛?</p><style>.bgcolor {background-color: yellow;}</style><style>/* 元素、标签选择器 *//* 元素选择器优先级小于类选择器,类选择器又小于id选择器*//* tag < class < id */p {color: violet;}</style><script>//定义一个求和函数let girl = {sum: function (a, b) {return a + b;},};console.log(girl.sum(30, 40));//修改h2标签里面的文本内容document.getElementById("title-id").textContent = "hello,joe";//显示h2标签内容// const h2 = document.getElementById("title-id");// console.log(h2);// h2.style.color = "red";//改变id的title-id元素背景色为黄色// const ele = document.getElementById("title-id");// console.log(ele);// ele.style.backgroundColor = "yellow";//类选择器title-classconst eles = document.getElementsByClassName("title-class");console.log(eles[1]);//标签选择器pconst p = document.getElementsByTagName("p");console.log(p);console.log(p[1]);// 直接使用css选择器来获取:几代前端人的梦想//用title-id拿数据let x = document.querySelector("#title-id");console.log(x);//用.title-class类拿数据//获取满足条件的第一个,只返回一个// let y = document.querySelector(".title-class");//返回全部满足条件全部元素let y = document.querySelectorAll(".title-class");console.log(y);//返回共同有类选择器title-class和bgcolor全部元素let z = document.querySelectorAll(".title-class.bgcolor");console.log(z);</script></body></html>
- 运行结果
4.总结
- 浏览器 window 是全局对象;
- document 代表当前文档;
- 浏览器的控制台:浏览器内置的一个 javascript 解释器,执行器,用命令; console.log()输出到控制台内容;
- 元素的三大属性,元素(标签)选择器优先级小于类选择器,类选择器又小于 id 选择器
- JS 脚本操作页面元素优先级最高 > id > class > tag。

