一、设置弹性元素的增长因子
实例
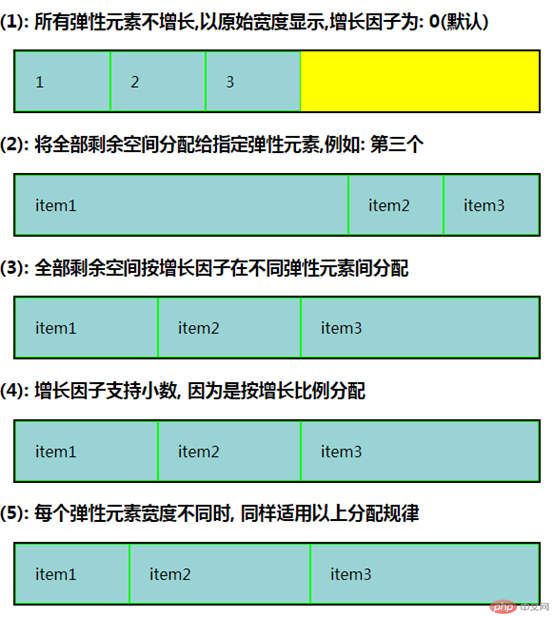
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>设置弹性元素的增长因子</title> <link rel="stylesheet" href="static/css/1.css"> </head> <body> <h3>(1): 所有弹性元素不增长,以原始宽度显示,增长因子为: 0(默认)</h3> <div class="container flex demo1"> <div class="item">1</div> <div class="item">2</div> <div class="item">3</div> </div> <h3>(2): 将全部剩余空间分配给指定弹性元素,例如: 第三个</h3> <div class="container flex demo2"> <span class="item">item1</span> <span class="item">item2</span> <span class="item">item3</span> </div> <h3>(3): 全部剩余空间按增长因子在不同弹性元素间分配</h3> <div class="container flex demo3"> <span class="item">item1</span> <span class="item">item2</span> <span class="item">item3</span> </div> <h3>(4): 增长因子支持小数, 因为是按增长比例分配</h3> <div class="container flex demo4"> <span class="item">item1</span> <span class="item">item2</span> <span class="item">item3</span> </div> <h3>(5): 每个弹性元素宽度不同时, 同样适用以上分配规律</h3> <div class="container flex demo5"> <span class="item">item1</span> <span class="item">item2</span> <span class="item">item3</span> </div> </body> </html>
运行实例 »
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
实例
@import "public.css";
.container{
width: 550px;
}
.item {
width: 100px;
}
.demo1 > .item {
flex-grow: 0;
}
.demo2 > .item:first-of-type {
flex-grow: 1;
}
.demo2 > .item:nth-of-type(2) {
flex-grow: 0;
}
.demo2 > .item:last-of-type {
flex-grow: 0;
}
.demo3 > .item:first-of-type{
flex-grow: 2;
}
.demo3 > .item:nth-of-type(2) {
flex-grow: 2;
}
.demo3 > .item:last-of-type {
flex-grow: 6;
}
.demo4 > .item:first-of-type{
flex-grow: 0.2;
}
.demo4 > .item:nth-of-type(2) {
flex-grow: 0.2;
}
.demo4 > .item:last-of-type {
flex-grow: 0.6;
}
.demo5 > .item:first-of-type{
width: 100px;
flex-grow: 1;
}
.demo5 > .item:nth-of-type(2) {
width: 150px;
flex-grow: 2;
}
.demo5 > .item:last-of-type {
width: 180px;
flex-grow: 3;
}
/*
100+150+180=430
550-430=120
120/6=20
100+20=120
150+20*2=190
180+20*3=210
*/运行实例 »
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
二、设置弹性元素的缩减因子
实例
<body> <h1>flex-shrink: 设置弹性元素的缩减因子</h1> <h3>(1): 所有弹性元素不缩减,以原始宽度显示,缩减因子为: 0</h3> <div class="container flex demo1"> <span class="item">item1</span> <span class="item">item2</span> <span class="item">item3</span> </div> <h3>(2): 所有弹性元素自适应容器宽度且不换行,缩减因子: 1 (默认)</h3> <div class="container flex demo2"> <span class="item">item1</span> <span class="item">item2</span> <span class="item">item3</span> </div> <h3>(3): 当三个弹性元素的缩减因为子不相等时</h3> <div class="container flex demo3"> <span class="item">item1</span> <span class="item">item2</span> <span class="item">item3</span> </div> <h3>(4): 缩减因子也可以是小数,只要大于就可以</h3> <div class="container flex demo4"> <span class="item">item1</span> <span class="item">item2</span> <span class="item">item3</span> </div> <h3>(5): 当每个弹性元素宽度不一样时, 完全是另一道风景线</h3> <div class="container flex demo5"> <span class="item">item1</span> <span class="item">item2</span> <span class="item">item3</span> </div> </body>
运行实例 »
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
实例
@import "public.css";
.container{
width: 550px;
}
.item{
width: 250px;
}
.demo1 > .item{
flex-shrink: 0;
}
.demo2 > .item{
flex-shrink: 1;
}
.demo3 > .item:first-of-type{
flex-shrink: 1;
}
.demo3 > .item:nth-of-type(2){
flex-shrink: 2;
}
.demo3 > .item:last-of-type{
flex-shrink: 3;
}
/*
1+2+3=6
750-550=200
200/6=33.3.
1*33.33=33.33
2*33.33=66.66
3*33.33=99.99
250-33.33=216.67
250-66.66=183.34
250-99.9=150.01
3
*/
.demo4 > .item:first-of-type{
flex-shrink: 0.2;
}
.demo4 > .item:nth-of-type(2){
flex-shrink: 0.2;
}
.demo4 > .item:last-of-type{
flex-shrink: 0.6;
}
/*
0.2+0.2+0.6=1
200*0.2=40
200*0.6=120
250-40=210
250-120=130
*/
.demo5 > .item:first-of-type{
width: 100px;
flex-shrink: 2;
}
.demo5 > .item:nth-of-type(2){
width: 250px;
flex-shrink: 3 ;
}
.demo5 > .item:last-of-type{
width: 300px;
flex-shrink: 5;
}
/*
2+3+5=10
100+250+300=650-550=100
100/((100*2)+(250*3)+(300*5))=0.0408
0.0816 0.1224 0.204
100*0.0816=8.16
250*0.1224=30.6
100*0.3108=61.2
100-8.16=91.84
250-30.6=219.4
300-61.2=238.8
*/运行实例 »
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例

三、设置弹性元素的基准尺寸
实例
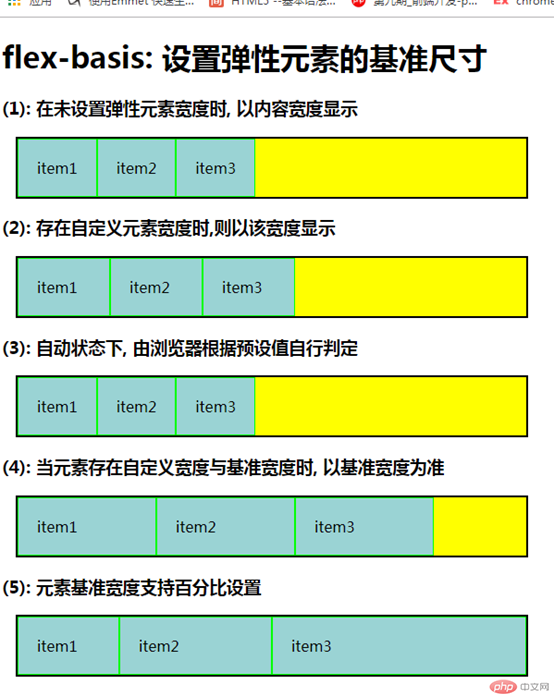
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>设置弹性元素的基准尺寸</title> <link rel="stylesheet" href="static/css/3.css"> </head> <body> <h1>flex-basis: 设置弹性元素的基准尺寸</h1> <h3>(1): 在未设置弹性元素宽度时, 以内容宽度显示</h3> <div class="container flex demo1"> <span class="item">item1</span> <span class="item">item2</span> <span class="item">item3</span> </div> <h3>(2): 存在自定义元素宽度时,则以该宽度显示</h3> <div class="container flex demo2"> <span class="item">item1</span> <span class="item">item2</span> <span class="item">item3</span> </div> <h3>(3): 自动状态下, 由浏览器根据预设值自行判定</h3> <div class="container flex demo3"> <span class="item">item1</span> <span class="item">item2</span> <span class="item">item3</span> </div> <h3>(4): 当元素存在自定义宽度与基准宽度时, 以基准宽度为准 </h3> <div class="container flex demo4"> <span class="item">item1</span> <span class="item">item2</span> <span class="item">item3</span> </div> <h3>(5): 元素基准宽度支持百分比设置 </h3> <div class="container flex demo5"> <span class="item">item1</span> <span class="item">item2</span> <span class="item">item3</span> </div> </body> </html>
运行实例 »
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
实例
@import "public.css";
.container{
width: 550px;
}
.demo1 >.item{
flex-basis: content;
}
.demo2 >.item{
width: 100px;
}
.demo3 >.item{
flex-basis: auto;
}
.demo4 > .item{
width: 100px;
flex-basis: 150px;
}
.demo5 > .item:first-of-type{
flex-basis: 20%;
}
.demo5 > .item:nth-of-type(2){
flex-basis: 30%;
}
.demo5 > .item:last-of-type{
flex-basis: 50%;
}运行实例 »
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
四、简化弹性元素的基本设置
实例
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>简化弹性元素的基本设置</title> <link rel="stylesheet" href="static/css/4.css"> </head> <body> <h1>简化弹性元素的基本设置</h1> <h3>(1): 根据宽度计算,允许缩减适应容器</h3> <div class="container flex demo1"> <span class="item">item1</span> <span class="item">item2</span> <span class="item">item3</span> </div> <h3>(2): 根据宽度计算,元素完全弹性以适应容器</h3> <div class="container flex demo2"> <span class="item">item1</span> <span class="item">item2</span> <span class="item">item3</span> </div> <h3>(3): 元素完全失去弹性, 以原始大小呈现</h3> <div class="container flex demo3"> <span class="item">item1</span> <span class="item">item2</span> <span class="item">item3</span> </div> <h3>(4): 一个数值表示增长因子,其它值默认: flex: 1 1 auto</h3> <div class="container flex demo4"> <span class="item">item1</span> <span class="item">item2</span> <span class="item">item3</span> </div> <h3>(5): 第三个有具体数值时, 以它为计算标准</h3> <div class="container flex demo5"> <span class="item">item1</span> <span class="item">item2</span> <span class="item">item3</span> </div> <h3>(6): 单独设置某一个元素弹性大小 </h3> <div class="container flex demo6"> <span class="item">item1</span> <span class="item">item2</span> <span class="item">item3</span> </div> </body> </html>
运行实例 »
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
实例
@import "public.css";
.container{
width: 550px;
}
.demo1 > .item{
width: 100px;
height: 60px;
flex: initial;
/* flex: 0 1 auto*/
}
.demo2 > .item{
width: 100px;
height: 60px;
flex: auto;
/* flex: 1 1 auto*/
}
.demo3 > .item{
width: 100px;
height: 60px;
flex: none;
/* flex: 0 0 auto*/
}
.demo4 > .item{
width: 100px;
height: 60px;
flex: 1;
/* flex: 1 1 atto*/
}
.demo5 > .item{
width: 100px;
height: 60px;
flex: 1 0 200px;
}
.demo6 > .item{
width: 100px;
height: 60px;
}
.demo6 > .item:last-of-type{
flex: 1 0 0;
/* flex: 1 1 50%;*/
/* flex: 1 0 50%;*/
}运行实例 »
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例

五、单独设置元素在交叉轴上排列方式
实例
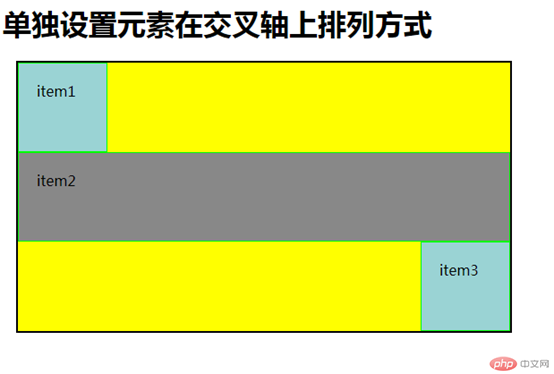
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>单独设置元素在交叉轴上排列方式</title> <link rel="stylesheet" href="static/css/5.css"> </head> <body> <h1>单独设置元素在交叉轴上排列方式</h1> <div class="container flex"> <span class="item">item1</span> <span class="item">item2</span> <span class="item">item3</span> </div> </body> </html>
运行实例 »
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
实例
@import url(public.css);
.container{
width: 550px;
height: 300px;
flex-flow: column nowrap;
align-items: flex-end;
}
/*.item:first-of-type{*/
/* align-self: flex-start;*/
/*}*/
/*.item:nth-of-type(2){*/
/* align-self: flex-end;*/
/*}*/
/*.item:nth-of-type(3){*/
/* align-self: center;*/
/*}*/
/*.item:nth-of-type(4){*/
/* align-self:auto;*/
/*}*/
/*.item:nth-of-type(2){*/
/* background-color: #9ad3d4;*/
/* width: auto;*/
/* align-self: stretch;*/
/*}*/
/*.item:last-of-type{*/
/* align-self: self-start;*/
/*}*/
.item{
width: 100px;
height: 60%;
}
.item:first-of-type{
align-self: flex-start;
}
.item:last-of-type{
align-self: flex-end;
}
.item:nth-of-type(2){
background-color: #888888;
width: auto;
align-self: stretch;
}运行实例 »
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
六、order学习
实例
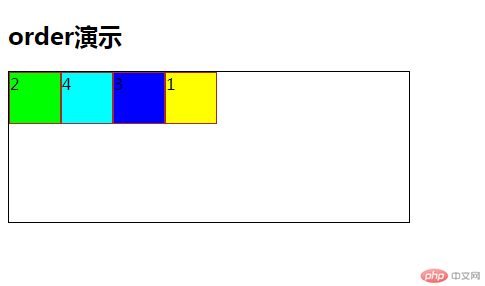
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>order</title> <link rel="stylesheet" href="static/css/6.css"> </head> <body> <h2 >order演示</h2> <div class="main"> <div class=" order1">1</div> <div class=" order2">2</div> <div class=" order3">3</div> <div class=" order4">4</div> </div> </body> </html>
运行实例 »
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
实例
.main{
width: 400px;
height: 150px;
border: 1px solid black;
/*display: -webkit-flex;*/
display: flex;
}
.main >div{
width: 50px;
height: 50px;
border: 1px solid brown;
}
.order1{
background-color: yellow;
}
.order2{
background-color: lime;
}
.order3{
background-color: blue;
}
.order4{
background-color: aqua;
}
.order1{
order:4;
}
.order2{
order:1;
}
.order3{
order:3;
}
.order4{
order:2;
}
/*.order1{*/
/* order: initial;*/
/*}*/
/*.order2{*/
/* order: revert;*/
/*}*/
/*.order1{*/
/* order: inherit;*/
/* }*/
/*.order2{*/
/* order: unset;*/
/*}*/运行实例 »
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
实例
*{
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
.body{
height: 100vh;
display: flex;
flex-flow: column nowrap;
}
.header,
.footer{
min-height: 100px;
background-color: lightseagreen;
flex: auto;
text-align: center;
font-size: 1.5rem;
}
.main{
height: 70vh;
background-color: lime;
flex: 1;
text-align: center;
font-size: 1.2rem;
}运行实例 »
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
七、移动端首页
实例
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>移动端首页</title> <link rel="stylesheet" href="static/css/8.css"> </head> <body> <header class="header">头部</header> <main class="main">主体</main> <footer class="footer">底部</footer> </body> </html>
运行实例 »
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例

八、弹性盒子仿写圣杯布局
实例
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>弹性盒子仿写圣杯布局</title> <link rel="stylesheet" href="static/css/9.css"> </head> <body> <header>头部</header> <main> <article> 内容区 </article> <aside class="left">左侧</aside> <aside class="right">右侧</aside> </main> <footer>底部</footer> </body> </html>
运行实例 »
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
实例
*{
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
html,body{
height: 900px;
border: 1px solid black;
}
body{
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
}
header{
flex: 0 0 50px;
border: 1px solid black;
background-color: #9ad3d4;
}
footer{
flex: 0 0 60px;
background-color: #444444;
}
main{
display: flex;
background-color: blue;
flex: 1;
text-align: center;
font-size: 2rem;
}
article{
flex-grow: 1;
order: 2;
background-color: lime;
width: 70%;
}
.right{
order: 3;
background-color: yellow;
width: 15%;
}
.left{
width: 15%;
}运行实例 »
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例

九手写flex属性

十、程序抄写







十一、总结
学习了flex的布局,但是有个问题请答复一下
.demo5 > .item:first-of-type{
width: 100px;
flex-shrink: 2;
}
.demo5 > .item:nth-of-type(2){
width: 250px;
flex-shrink: 3 ;
}
.demo5 > .item:last-of-type{
width: 300px;
flex-shrink: 5;
}
/*
2+3+5=10
100+250+300=650-550=100
100/((100*2)+(250*3)+(300*5))=0.0408
0.0816 0.1224 0.204
100*0.0816=8.16
250*0.1224=30.6
300*0.204=61.2
100-8.16=91.84
250-30.6=219.4
300-61.2=238.8
*/
算法有无问题,我允许后发现对不上
允许后的数字为
94.28
219.27
236.48
请告知我那点计算有误

