1. 实例演示相邻选择器与兄弟选择器,并分析异同
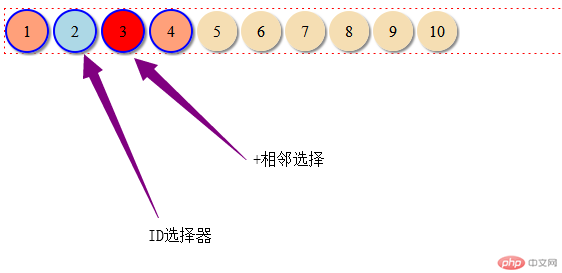
1.1.相邻选择器(相邻选择器分析
+表示相邻的 *通配符所有元素相
邻选择器是某一个小球后面相邻的紧跟的)
ul {
margin: 0;
padding-left: 0;
border: 1px dashed red;
}
ul li {
/*数字前小黑色圆点取消*/
list-style-type: none;
width: 40px;
height: 40px;
background-color: wheat;
/* border: 1px solid black;*/
/*水平和垂直的居中*/
text-align: center;
line-height: 40px;
/*50%相对值*/
border-radius: 50%;
/*将一个块元素转为内联元素*/
display: inline-block;
/*2px和2px左边和右边偏移2个像素边距,1为扩散1个像素 888为阴影*/
box-shadow: 2px 2px 1px #888;
}
/*#id选择器*/
#bg-blue {
background: lightblue;
}
/*class选择器*/
.bg-green {
background-color: lightsalmon;
}
/*属性选择器*/
li[id="bg-blue"] {
border: 2px solid red;
}
/*群组选择器*/
#bg-blue, .bg-green {
border: 2px solid blue;
}
/*相邻选择器分析
+表示相邻的 *
通配符所有元素相
邻选择器是某一个小球后面相邻的紧跟的*/
#bg-blue + * {
background-color: red;
}
实例
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>选择器</title> <link rel="stylesheet" href="static/style1.css"> </head> <body> <ul> <li class="bg-green">1</li> <li id="bg-blue">2</li> <li class="bg-green">3</li> <li class="bg-green">4</li> <li>5</li> <li>6</li> <li>7</li> <li>8</li> <li>9</li> <li>10</li> </ul> </body> </html>
运行实例 »
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
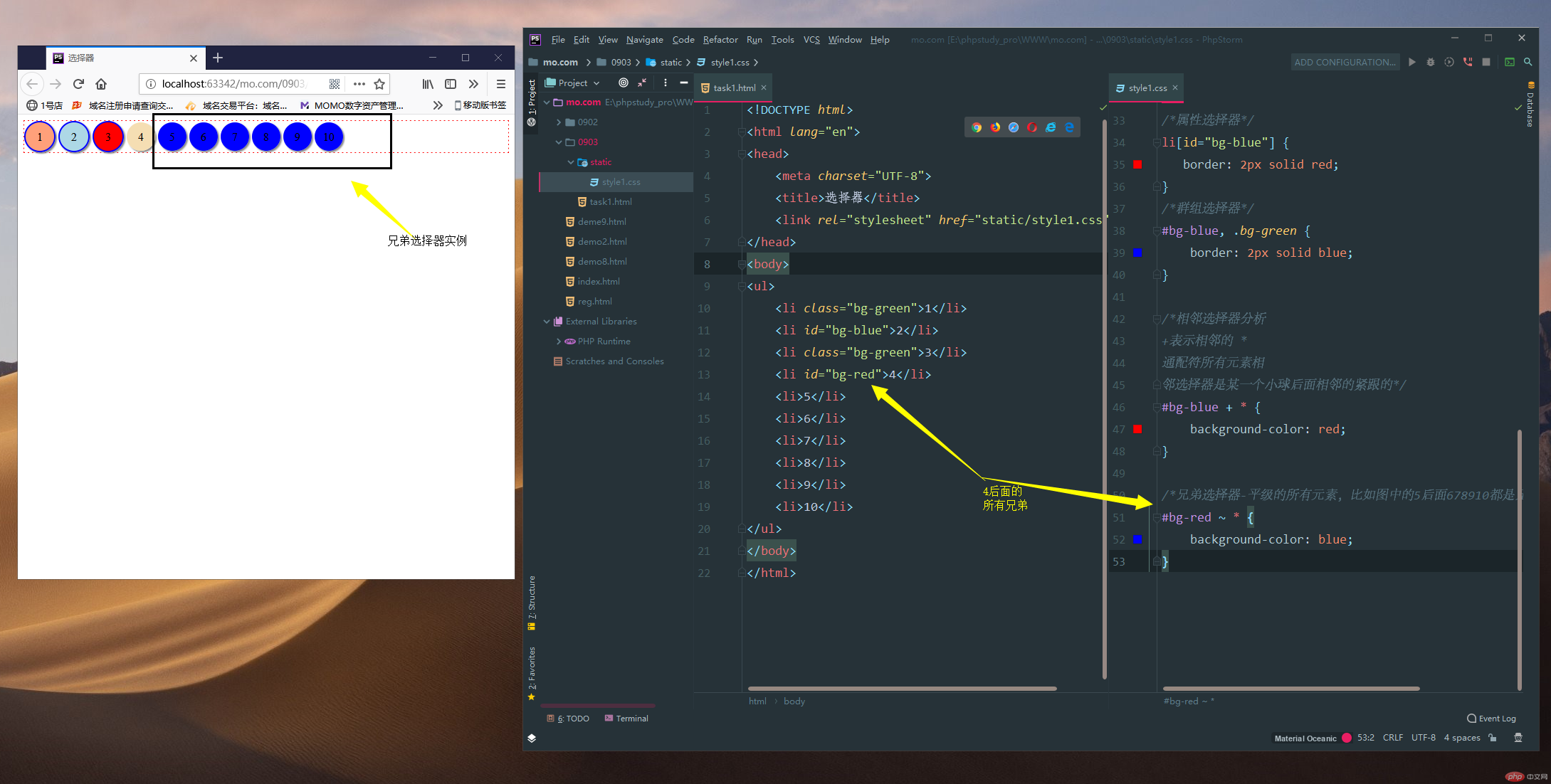
1.2.兄弟选择器(~波浪线表示兄弟选择器,后面的全部选中,兄弟选择器-平级的所有元素,比如图中的5后面678910都是兄弟)
实例
ul {
margin: 0;
padding-left: 0;
border: 1px dashed red;
}
ul li {
/*数字前小黑色圆点取消*/
list-style-type: none;
width: 40px;
height: 40px;
background-color: wheat;
/* border: 1px solid black;*/
/*水平和垂直的居中*/
text-align: center;
line-height: 40px;
/*50%相对值*/
border-radius: 50%;
/*将一个块元素转为内联元素*/
display: inline-block;
/*2px和2px左边和右边偏移2个像素边距,1为扩散1个像素 888为阴影*/
box-shadow: 2px 2px 1px #888;
}
/*#id选择器*/
#bg-blue {
background: lightblue;
}
/*class选择器*/
.bg-green {
background-color: lightsalmon;
}
/*属性选择器*/
li[id="bg-blue"] {
border: 2px solid red;
}
/*群组选择器*/
#bg-blue, .bg-green {
border: 2px solid blue;
}
/*相邻选择器分析
+表示相邻的 *
通配符所有元素相
邻选择器是某一个小球后面相邻的紧跟的*/
#bg-blue + * {
background-color: red;
}
/*兄弟选择器-平级的所有元素,比如图中的5后面678910都是兄弟,用~表示*/
#bg-red ~ * {
background-color: blue;
}运行实例 »
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
实例
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>选择器</title> <link rel="stylesheet" href="static/style1.css"> </head> <body> <ul> <li class="bg-green">1</li> <li id="bg-blue">2</li> <li class="bg-green">3</li> <li id="bg-red">4</li> <li>5</li> <li>6</li> <li>7</li> <li>8</li> <li>9</li> <li>10</li> </ul> </body> </html>
运行实例 »
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
2. 实例演示:nth-child() 和 :nth-of-type()选择器,并分析异同
异同关注点不相同,如果关注点是位置则用nth-child
既关注位置,有关注类型,则用nth-of-type
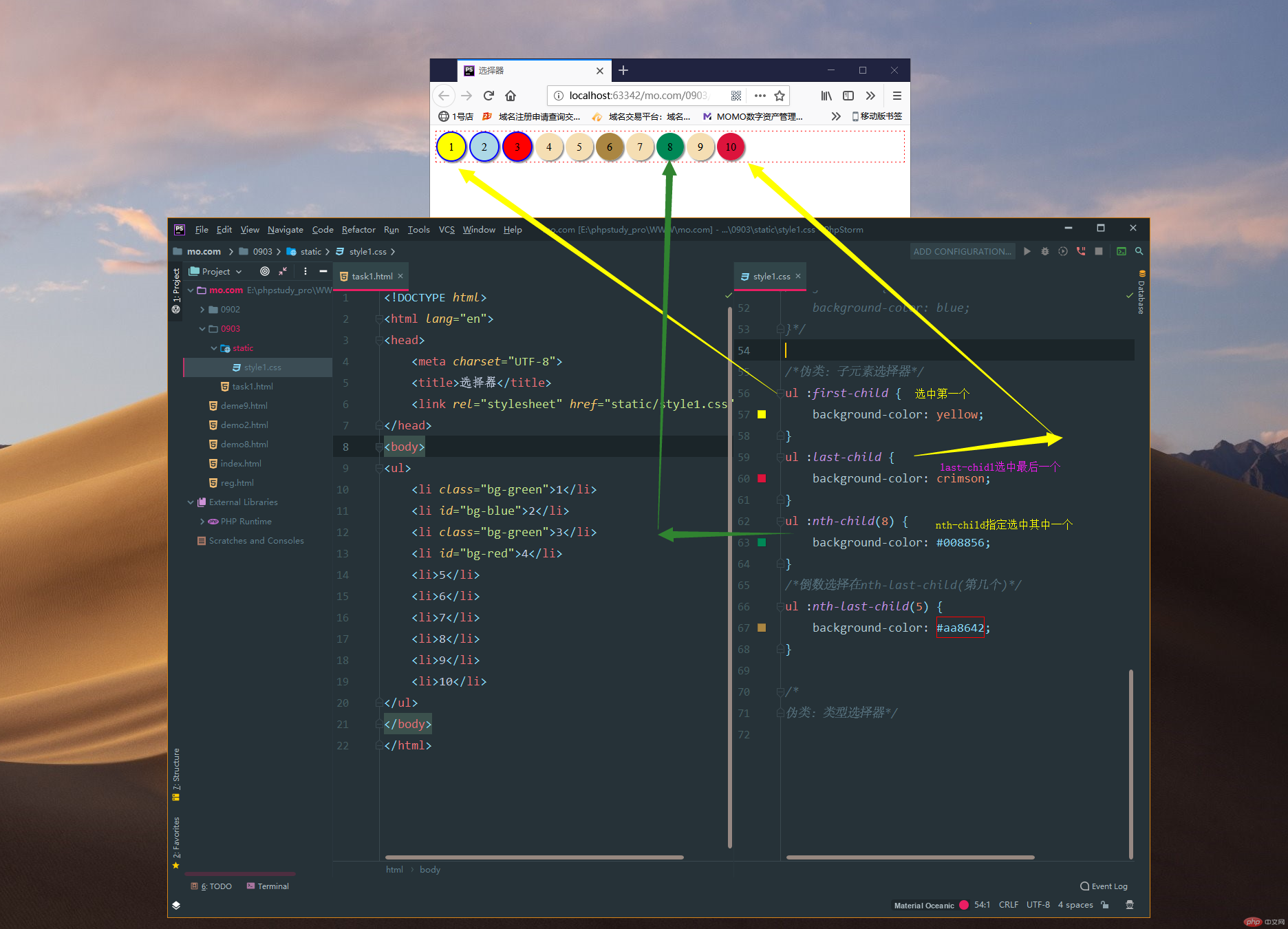
2.1.nth-child(直接选中其中一个,索引由几开始)
实例
/*伪类:子元素选择器*/
ul :first-child {
background-color: yellow;
}
ul :last-child {
background-color: crimson;
}
ul :nth-child(8) {
background-color: #008856;
}
/*倒数选择在nth-last-child(第几个)*/
ul :nth-last-child(5) {
background-color: #875eaa;
}运行实例 »
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
实例
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>选择器</title> <link rel="stylesheet" href="static/style1.css"> </head> <body> <ul> <li class="bg-green">1</li> <li id="bg-blue">2</li> <li class="bg-green">3</li> <li id="bg-red">4</li> <li>5</li> <li>6</li> <li>7</li> <li>8</li> <li>9</li> <li>10</li> </ul> </body> </html>
运行实例 »
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
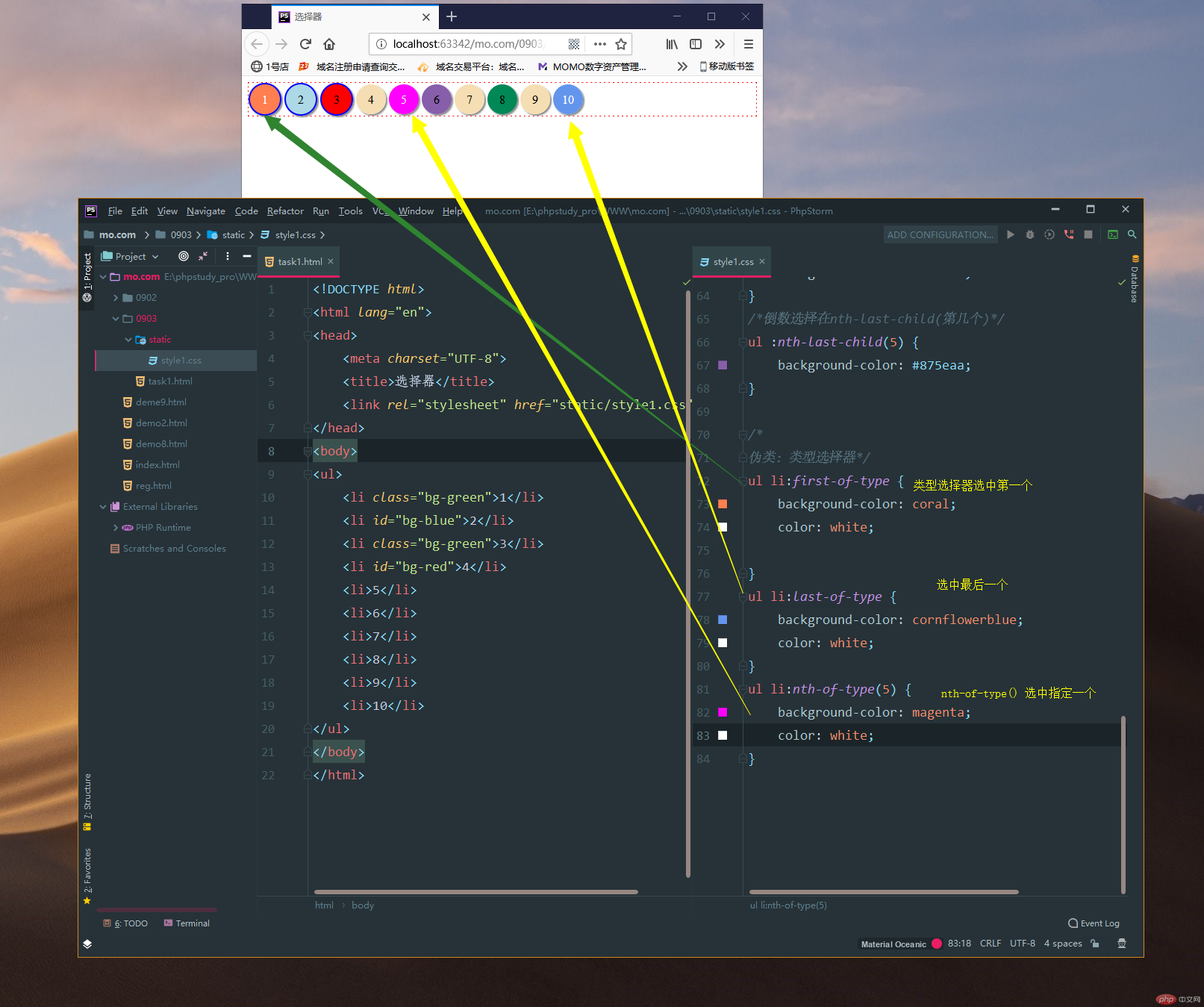
2.2 nth-of-type()选择器(只要是前面指定了这个类型一定要用nth-of-type类型)
实例
/*伪类:类型选择器*/
ul li:first-of-type {
background-color: coral;
color: white;
}
ul li:last-of-type {
background-color: cornflowerblue;
color: white;
}
ul li:nth-of-type(5) {
background-color: magenta;
color: white;
}运行实例 »
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
实例
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>选择器</title> <link rel="stylesheet" href="static/style1.css"> </head> <body> <ul> <li class="bg-green">1</li> <li id="bg-blue">2</li> <li class="bg-green">3</li> <li id="bg-red">4</li> <li>5</li> <li>6</li> <li>7</li> <li>8</li> <li>9</li> <li>10</li> </ul> </body> </html>
运行实例 »
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
3. 实例演示:padding 对盒子大小的影响与解决方案, 使用宽度分离或box-sizing
3.1.padding会撑开整个盒子,可以使用border包住,这样在使用padding就撑不开了
box-sizing: border-box; 后面加上一个bordr-box 这样padding可以随便改了。不会撑大。
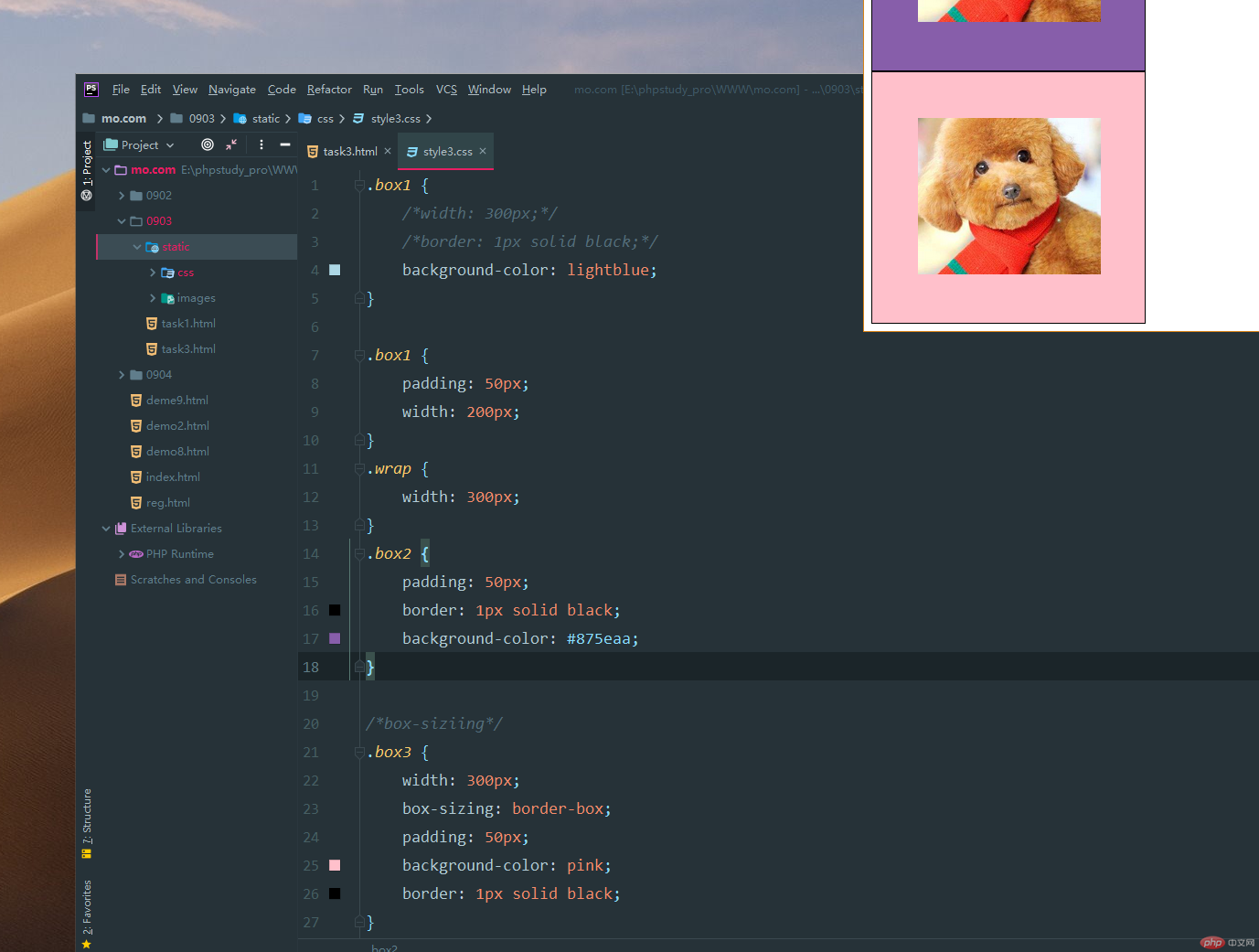
实例
.box1 {
/*width: 300px;*/
/*border: 1px solid black;*/
background-color: lightblue;
}
.box1 {
padding: 50px;
width: 200px;
}
.wrap {
width: 300px;
}
.box2 {
padding: 50px;
border: 1px solid black;
background-color: #875eaa;
}
/*box-siziing*/
.box3 {
width: 300px;
box-sizing: border-box;
padding: 50px;
background-color: pink;
border: 1px solid black;
}运行实例 »
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
实例
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <link rel="stylesheet" href="static/css/style3.css"> <title>padding</title> </head> <body> <!--实例演示:padding 对盒子大小的影响与解决方案, 使用宽度分离或box-sizing--> <!--padding会撑开整个盒子,可以使用border包住,这样在使用padding就撑不开了--> <div class="box1"> <img src="static/images/taidi.png" alt="可爱的小泰迪" width="200"> </div> <div class="wrap"> <div class="box2"> <img src="static/images/taidi.png" alt="可爱的小泰迪" width="200"> </div> </div> <div class="box3"> <img src="static/images/taidi.png" alt="可爱的小泰迪" width="200"> </div> </body> </html>
运行实例 »
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
4. 实例演示: margin中的同级塌陷, 嵌套传递与自动挤压, 并提出解决方案或应用场景
4.1margin中的同级塌陷(垂直方向内,margin值谁大以谁为准 两个盒子同级排列)
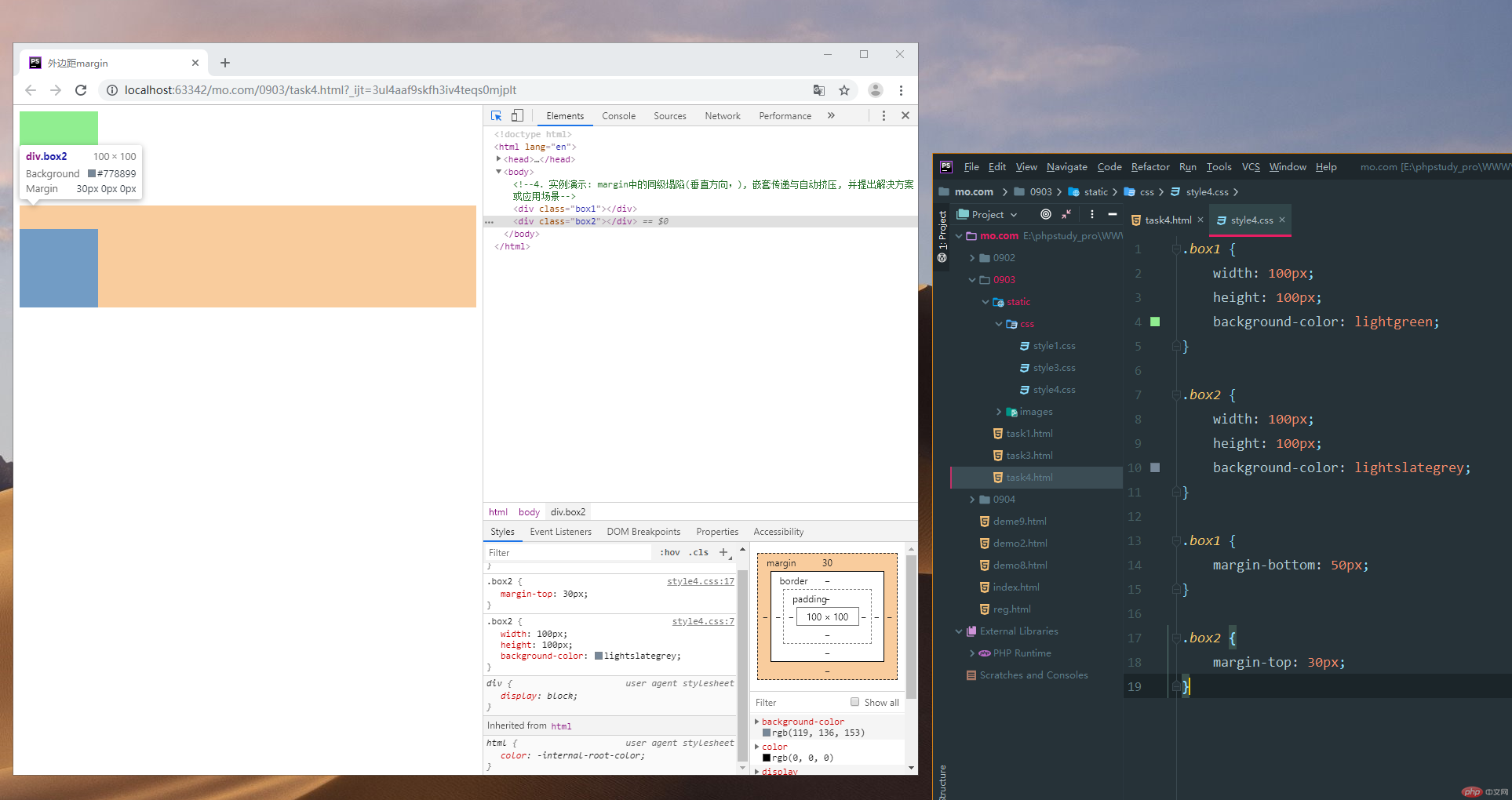
实例
.box1 {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: lightgreen;
}
.box2 {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: lightslategrey;
}
.box1 {
margin-bottom: 50px;
}
.box2 {
margin-top: 30px;
}运行实例 »
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
实例
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>外边距margin</title> <link rel="stylesheet" href="static/css/style4.css"> </head> <body> <!--4. 实例演示: margin中的同级塌陷(垂直方向内,margin值谁大以谁为准 两个盒子同级排列), 嵌套传递 与自动挤压, 并提出解决方案或应用场景--> </body> <div class="box1"></div> <div class="box2"></div> </html>
运行实例 »
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
4.2.嵌套传递:两个块级元素子成父级关系或嵌套关系,子元素margin值会向父元素传递
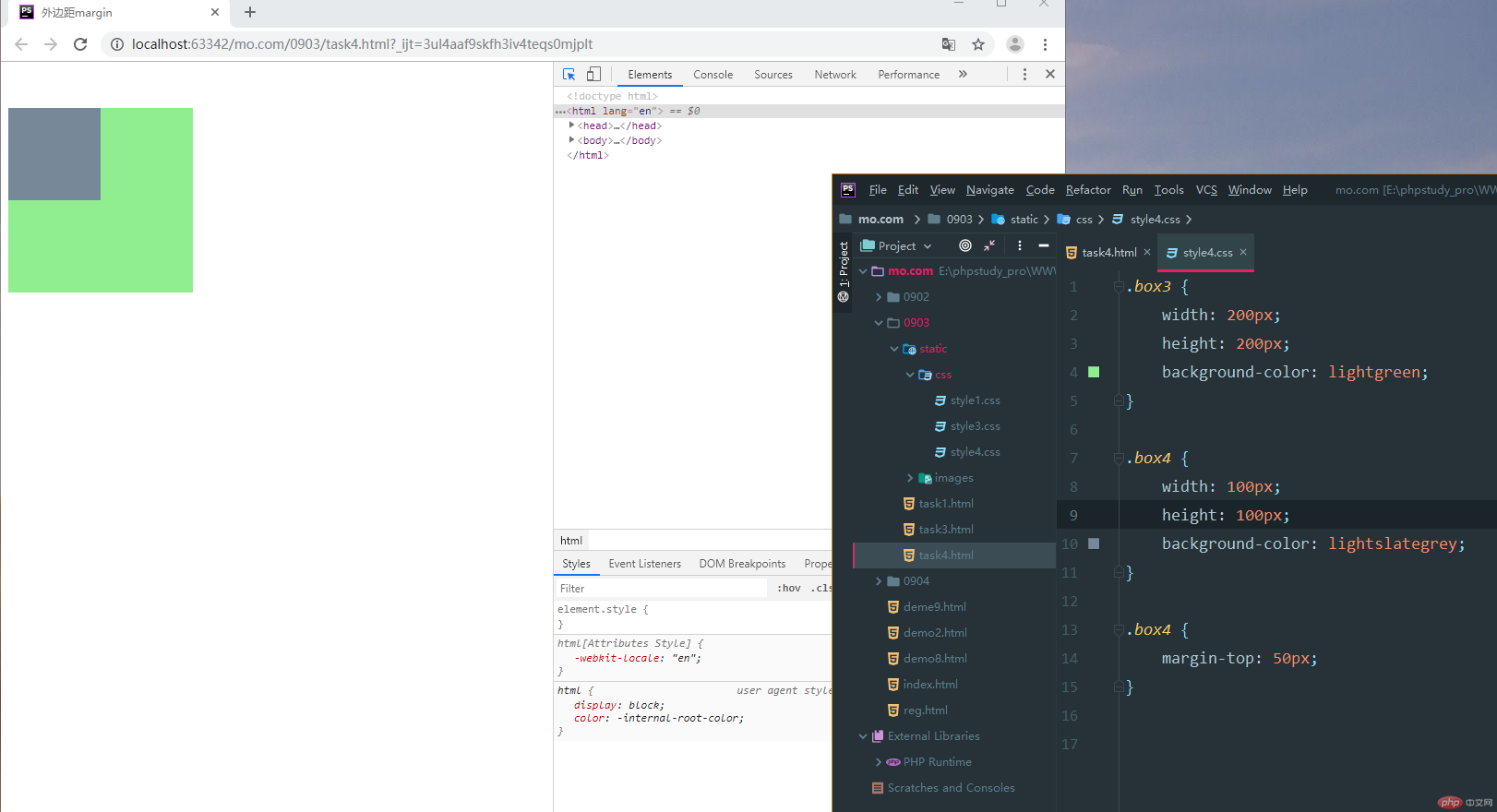
实例
.box3 {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: lightgreen;
}
.box4 {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: lightslategrey;
}
.box4 {
margin-top: 50px;
}运行实例 »
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
实例
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>外边距margin</title> <link rel="stylesheet" href="static/css/style4.css"> </head> <body> <!--4. 实例演示: margin中的同级塌陷(垂直方向内,margin值谁大以谁为准 两个盒子同级排列), 嵌套传递 与自动挤压, 并提出解决方案或应用场景--> </body> <div class="box1"></div> <div class="box2"></div> <!--嵌套传递:两个块级元素子成父级关系或嵌套关系,子元素argin值会向父元素传递--> <div class="box3"> <div class="box4"></div> </div> </html>
运行实例 »
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
4.3.自动挤压:一个元素设定了边距,margin-left,不给值,为auto,则会自动向右边自动挤压,那么right自会向左边 ,left-right都用auto时则会居中 比如为margin: 30px auto: 上下30 左右居中
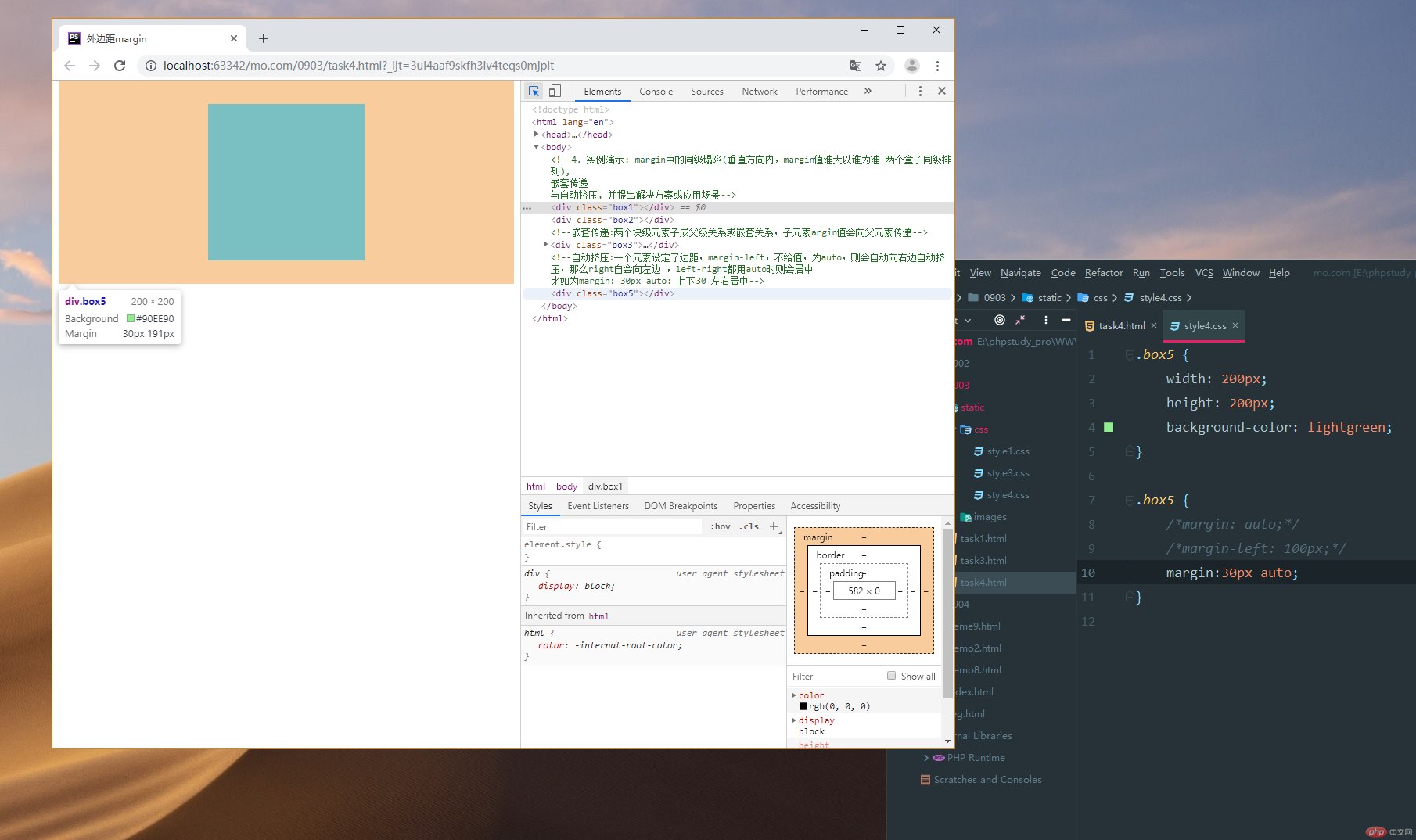
实例
.box5 {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: lightgreen;
}
.box5 {
/*margin: auto;*/
/*margin-left: 100px;*/
margin:30px auto;
}运行实例 »
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
实例
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>外边距margin</title> <link rel="stylesheet" href="static/css/style4.css"> </head> <body> <!--4. 实例演示: margin中的同级塌陷(垂直方向内,margin值谁大以谁为准 两个盒子同级排列), 嵌套传递 与自动挤压, 并提出解决方案或应用场景--> </body> <div class="box1"></div> <div class="box2"></div> <!--嵌套传递:两个块级元素子成父级关系或嵌套关系,子元素argin值会向父元素传递--> <div class="box3"> <div class="box4"></div> </div> <!--自动挤压:一个元素设定了边距,margin-left,不给值,为auto,则会自动向右边自动挤压,那么right自会向左边 ,left-right都用auto时则会居中 比如为margin: 30px auto: 上下30 左右居中--> <div class="box5"></div> </html>
运行实例 »
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例

