Machine Learning in Retail: Essentials and Ten Key Applications

In recent years, between lockdowns, supply chain disruptions and energy crises, retailers must have felt like dinosaurs trying to avoid a rain of asteroids and avoid extinction.
But unlike those giant prehistoric reptiles, the retail industry can rely on a range of technological innovations to better cope with these challenges in hard times.
And one of the most influential tools is undoubtedly artificial intelligence, including its powerful sub-branch machine learning (ML). Let’s briefly introduce the nature of this technology and explore the key use cases of machine learning in retail.
The role of machine learning in retail
Machine learning in retail relies on self-improving computer algorithms that are used to process data and find recurring patterns and anomalies among variables , and learn independently how this relationship affects or determines industry trends, phenomena and business scenarios.
The self-learning and situational understanding potential of machine learning systems can be used in the retail industry to:
- Identify the underlying dynamics driving retail. For example, machine learning-based data analysis systems are widely adopted in marketing to personalize the shopping experience through recommendation engines and targeted advertising based on customer data, and to predict product demand or other market trends to optimize inventory management. , logistics and pricing strategies.
- Advance cognitive technologies related to artificial intelligence, such as computer vision and natural language processing (NLP), which recognize and learn from visual and linguistic patterns, respectively, to imitate human vision and communication. Retailers often use these tools to collect data from textual and visual sources, power interactive solutions such as chatbots and contextual shopping, or for video surveillance.
10 Machine Learning Use Cases Redefining Retail
How can retailers benefit from the practical capabilities of the above machine learning algorithms? Below are the most relevant machine learning use cases in typical retail scenarios.
1. Targeted Advertising
Although primarily used in e-commerce, targeted marketing is a powerful tool for directing potential customers to online platforms and traditional stores. This involves segmenting users based on a range of behavioral, psychographic, demographic and geographical parameters (such as their purchase and browsing history, age, gender, interests, region, etc.) and targeting them with fully personalized advertising and promotions .
2. Contextual Shopping
A different, more interactive solution is contextual shopping, which grabs users’ attention and directs them to your e-commerce platform . The marketing tool uses machine learning and computer vision to identify and point out products shown in videos and images on social media, while providing a "shortcut" to relevant product pages in online stores.
3. Recommendation engine
Once users log into an online platform, they may get lost in the massive amount of products. Recommendation engines are powerful tools designed to put products in front of your customers that they might actually need.
To provide tailored recommendations, these systems can either employ a content-based filtering approach, which recommends items with similar characteristics to those purchased in the past, or collaborative filtering, which means recommending items with similar purchasing patterns. , personal characteristics and interests of other customers.
4. Dynamic Pricing
Product recommendations and advertising aren’t the only things that change dynamically thanks to machine learning. Today, most online stores and e-commerce platforms constantly adjust prices based on factors such as fluctuations in product demand and supply, competitors' promotion and pricing strategies, broader sales trends, and more.
5. Chatbots
Chatbots and virtual assistants are highly interactive tools powered by machine learning and NLP that provide customers with 24/7 user support (including information on available products and shipping options) while sending reminders, coupons and personalized recommendations to increase sales.
6. Supply Chain Management
Product replenishment and other inventory management operations must not be left to chance. To better match commodity supply and demand, optimize warehouse space utilization, and avoid food spoilage, it’s worth relying on the analytical and predictive capabilities of machine learning algorithms. This means taking into account multiple variables, such as price fluctuations or seasonality-based buying patterns, to predict future sales trends and plan appropriate replenishment plans accordingly.
7. Delivery Optimization
Another aspect of logistics that can be enhanced through machine learning is the delivery of goods. Traffic and weather data collected by a network of IoT sensors and cameras powers a machine learning-driven system that can easily calculate the fastest delivery routes. And, by processing user data, they can recommend appropriate delivery methods to better meet customer needs.
The exemplar of this approach should be the machine learning-based anticipatory shipping technology implemented by Amazon, which allows predicting future deliveries based on customer purchasing patterns and moving products to the warehouse closest to the customer, thus The ability to ship faster and cheaper when customers actually order.
8. Self-driving cars
This implementation of machine learning and computer vision for merchandise delivery is far from perfected and implemented at scale, however, companies like Amazon and Kroger are working on Bet on this technology, we may soon be relying on self-driving cars to speed up the delivery of goods.
9. Video Surveillance
Computer vision systems powered by machine learning can detect thieves. The main difference between these tools and traditional video surveillance solutions is that the latter are based on a rather inaccurate rules-based approach to identifying intruders, which is prone to high numbers of false positives. Machine learning systems, on the other hand, can identify more subtle patterns of behavior and alert managers when something suspicious occurs.
10. Fraud Detection
For online retailers and e-commerce platforms, thieves are more likely to steal money from credit cards than goods off the shelves. Because machine learning algorithms are designed to identify recurring patterns, they can also pinpoint any deviations from the norm, including unusual trading frequencies or inconsistencies in account data, and flag them as suspicious for further inspection.
Using Machine Learning to Overcome Modern Challenges
Artificial intelligence, machine learning and cognitive technologies are proven operational in increasing profits and optimizing costs, personalizing customer experiences, and improving logistics and inventory management efficiency, and ensuring a safe retail environment.
In fact, Fortune Business Insight’s 2020 report highlights that the global retail AI market is expected to reach $31.18 billion by 2028, with machine learning being a core part of it.
From a retail perspective, this will make machine learning a beacon, allowing it to find the right course and dock in a safe port after more than two years of storms. (Compiled by: iothome)
The above is the detailed content of Machine Learning in Retail: Essentials and Ten Key Applications. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
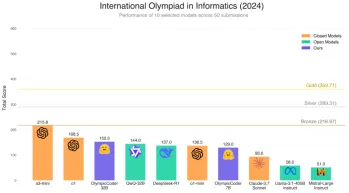 Does Hugging Face's 7B Model OlympicCoder Beat Claude 3.7?Apr 23, 2025 am 11:49 AM
Does Hugging Face's 7B Model OlympicCoder Beat Claude 3.7?Apr 23, 2025 am 11:49 AMHugging Face's OlympicCoder-7B: A Powerful Open-Source Code Reasoning Model The race to develop superior code-focused language models is intensifying, and Hugging Face has joined the competition with a formidable contender: OlympicCoder-7B, a product
 4 New Gemini Features You Can't Afford to MissApr 23, 2025 am 11:48 AM
4 New Gemini Features You Can't Afford to MissApr 23, 2025 am 11:48 AMHow many of you have wished AI could do more than just answer questions? I know I have, and as of late, I’m amazed by how it’s transforming. AI chatbots aren’t just about chatting anymore, they’re about creating, researchin
 Camunda Writes New Score For Agentic AI OrchestrationApr 23, 2025 am 11:46 AM
Camunda Writes New Score For Agentic AI OrchestrationApr 23, 2025 am 11:46 AMAs smart AI begins to be integrated into all levels of enterprise software platforms and applications (we must emphasize that there are both powerful core tools and some less reliable simulation tools), we need a new set of infrastructure capabilities to manage these agents. Camunda, a process orchestration company based in Berlin, Germany, believes it can help smart AI play its due role and align with accurate business goals and rules in the new digital workplace. The company currently offers intelligent orchestration capabilities designed to help organizations model, deploy and manage AI agents. From a practical software engineering perspective, what does this mean? The integration of certainty and non-deterministic processes The company said the key is to allow users (usually data scientists, software)
 Is There Value In A Curated Enterprise AI Experience?Apr 23, 2025 am 11:45 AM
Is There Value In A Curated Enterprise AI Experience?Apr 23, 2025 am 11:45 AMAttending Google Cloud Next '25, I was keen to see how Google would distinguish its AI offerings. Recent announcements regarding Agentspace (discussed here) and the Customer Experience Suite (discussed here) were promising, emphasizing business valu
 How to Find the Best Multilingual Embedding Model for Your RAG?Apr 23, 2025 am 11:44 AM
How to Find the Best Multilingual Embedding Model for Your RAG?Apr 23, 2025 am 11:44 AMSelecting the Optimal Multilingual Embedding Model for Your Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) System In today's interconnected world, building effective multilingual AI systems is paramount. Robust multilingual embedding models are crucial for Re
 Musk: Robotaxis In Austin Need Intervention Every 10,000 MilesApr 23, 2025 am 11:42 AM
Musk: Robotaxis In Austin Need Intervention Every 10,000 MilesApr 23, 2025 am 11:42 AMTesla's Austin Robotaxi Launch: A Closer Look at Musk's Claims Elon Musk recently announced Tesla's upcoming robotaxi launch in Austin, Texas, initially deploying a small fleet of 10-20 vehicles for safety reasons, with plans for rapid expansion. H
 AI's Shocking Pivot: From Work Tool To Digital Therapist And Life CoachApr 23, 2025 am 11:41 AM
AI's Shocking Pivot: From Work Tool To Digital Therapist And Life CoachApr 23, 2025 am 11:41 AMThe way artificial intelligence is applied may be unexpected. Initially, many of us might think it was mainly used for creative and technical tasks, such as writing code and creating content. However, a recent survey reported by Harvard Business Review shows that this is not the case. Most users seek artificial intelligence not just for work, but for support, organization, and even friendship! The report said that the first of AI application cases is treatment and companionship. This shows that its 24/7 availability and the ability to provide anonymous, honest advice and feedback are of great value. On the other hand, marketing tasks (such as writing a blog, creating social media posts, or advertising copy) rank much lower on the popular use list. Why is this? Let's see the results of the research and how it continues to be
 Companies Race Toward AI Agent AdoptionApr 23, 2025 am 11:40 AM
Companies Race Toward AI Agent AdoptionApr 23, 2025 am 11:40 AMThe rise of AI agents is transforming the business landscape. Compared to the cloud revolution, the impact of AI agents is predicted to be exponentially greater, promising to revolutionize knowledge work. The ability to simulate human decision-maki


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

VSCode Windows 64-bit Download
A free and powerful IDE editor launched by Microsoft

MinGW - Minimalist GNU for Windows
This project is in the process of being migrated to osdn.net/projects/mingw, you can continue to follow us there. MinGW: A native Windows port of the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC), freely distributable import libraries and header files for building native Windows applications; includes extensions to the MSVC runtime to support C99 functionality. All MinGW software can run on 64-bit Windows platforms.

mPDF
mPDF is a PHP library that can generate PDF files from UTF-8 encoded HTML. The original author, Ian Back, wrote mPDF to output PDF files "on the fly" from his website and handle different languages. It is slower than original scripts like HTML2FPDF and produces larger files when using Unicode fonts, but supports CSS styles etc. and has a lot of enhancements. Supports almost all languages, including RTL (Arabic and Hebrew) and CJK (Chinese, Japanese and Korean). Supports nested block-level elements (such as P, DIV),

PhpStorm Mac version
The latest (2018.2.1) professional PHP integrated development tool

SublimeText3 English version
Recommended: Win version, supports code prompts!






