 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals AI
AI Stanford 2023 AI Index Report is out! China dominates the top AI conferences, with the Chinese Academy of Sciences ranking first in the world in terms of published papers
Stanford 2023 AI Index Report is out! China dominates the top AI conferences, with the Chinese Academy of Sciences ranking first in the world in terms of published papersToday, Stanford released the 2023 AI Index Report.

It is worth noting that the Stanford AI Index report lists the top ten institutions in the world in terms of "AI paper publication volume", and 9 of them are all from China. , have caught up with MIT.
They are: Chinese Academy of Sciences, Tsinghua University, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Zhejiang University, Harbin Institute of Technology, Beihang University, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Peking University, and MIT.

This year’s report is mainly divided into eight major sections: research and development, technology performance, artificial intelligence technology ethics, economy, education, policy and governance, diversity, and public opinion.
The following content extracts several key points of the report.
The two countries rank first in paper cooperation in the world
From 2010 to 2021, although the pace of cross-border cooperation in AI papers has slowed down, since 2010, the United States The number of artificial intelligence research cooperation with China has increased by approximately 4 times, which is 2.5 times greater than the total number of cooperation between China and the UK.
However, from 2020 to 2021, the total number of cooperation between the two countries only increased by 2.1%, which was the smallest year-on-year growth rate since 2010.
Additionally, the total number of AI papers has more than doubled since 2010. It has increased from 200,000 articles in 2010 to nearly 500,000 articles in 2021 (49,601).

In terms of the types of AI papers published, in 2021, 60% of all published AI papers are journal articles, and 17% are Conference papers, 13% come from repositories.
While journal and repository papers have grown 3-fold and 26.6-fold, respectively, over the past 12 years, the number of conference papers has declined since 2019.

Pattern recognition, machine learning and computer vision are still hot topics in the field of artificial intelligence.

China still leads the way in terms of the total number of papers in journals, conferences and repositories.
The United States still leads in AI conference and repository citations, but these leads are slowly eroding. Despite this, the majority of the world's large language models and multimodal models (54% in 2022) are produced by US institutions.

China dominates the top AI rankings, but the number of citations is lower than that of the United States
China has always maintained its lead in publishing AI journal papers status, 39.8% in 2021, followed by the European Union and the United Kingdom (15.1%), and then the United States (10.0%).

Since 2010, the proportion of citations of Chinese artificial intelligence journal papers has gradually increased, while the EU, UK, and United States have all declined. China, the European Union, the United Kingdom, and the United States account for 65.7% of the total global citations.

So, what is the situation of papers published at the world’s top conferences?
In 2021, China has the largest share of papers published at the top global AI conferences with 26.15%, followed by the European Union and the United Kingdom with 20.29%, and the United States with 17.23 % ranked third.

Judging from the number of citations of top conference papers, although China is highly productive, its number of citations is lower compared to the United States. The number of citations of top conference papers in the United States was 23.9%, and that in China was 22.02%.
It can be seen from the side that China publishes the largest number of papers, but the quality is not as high as that of the United States.

The United States leads the world in submissions to AI paper repositories, with 23.48%. China is the lowest, 11.87%.

9 institutions in China, AI paper publishing catches up with MIT
In 2021, the total number of published papers is among the top ten institutions in the world , China accounts for 9. The total number of papers published by different institutions is as shown below. MIT ranks tenth, publishing 1745 papers.

In terms of the field of computer vision (CV), China’s ten institutions rank among the top ten in the world. They are: Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai Jiaotong University, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Tsinghua University, Zhejiang University, Beihang University, Wuhan University, Beijing Institute of Technology, Harbin Institute of Technology, and Tianjin University.

In the field of natural language processing (NLP), it is different.
The top ten institutions/companies in the world are: Chinese Academy of Sciences, Carnegie Mellon University, Microsoft, Tsinghua University, Carnegie Mellon University-Australia, Google, Peking University , University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Alibaba, Amazon.

The rankings in the field of speech recognition are as follows:

Industry leads academia
Among the important artificial intelligence machine learning systems released in 2022, language systems account for the most, with 23, which is 6 times the number of multi-modal systems.

In terms of paper output, industry is ahead of academia.
Until 2014, most important models were published by academia. Since then, industry has turned around. By 2022, 32 important machine learning models will be born in industry, while only 3 will be in academia.

It can be seen that compared with non-profit organizations and academia, building state-of-the-art artificial intelligence systems increasingly requires large amounts of data, Computer capabilities and financial resources, and industry participants certainly have more financial resources to do this.
In 2022, the United States produced the largest number of important machine learning systems, with 16, followed by the United Kingdom (8) and China (3).
Furthermore, the United States has surpassed the United Kingdom and the European Union and China in terms of the total number of significant machine learning systems created since 2002

Looking at the distribution of researchers behind these important AI systems by country, the United States has the largest number of researchers, 285, which is more than twice that of the United Kingdom and nearly six times that of China.

LLMs are getting bigger and bigger, and the computing power is more expensive
Large language and multi-modal models, sometimes called base models , is currently an emerging and increasingly popular type of AI model that is trained on large amounts of data and suitable for various downstream applications.
Large-scale languages and multi-modal models such as ChatGPT, DALL-E 2, and MakeA-Video have demonstrated impressive capabilities and are starting to be widely deployed in the real world.
The country affiliations of the authors of these models were analyzed and the majority of these researchers were from US institutions (54.2%).

The Stanford AI Index report also lays out a timeline for the release of large language and multi-modal models.

#Large language models are getting bigger and more expensive.
The first large-scale language model, GPT-2, was released in 2019, with 1.5 billion parameters and a training cost of about US$50,000. Google PaLM is one of the large language models launched in 2022, with 540 billion parameters and a cost of up to $8 million.

In terms of parameters and training costs, Palm is 360 times larger and 160 times more expensive than GPT-2.
It’s not just PalM, but large language and multimodal models as a whole are getting bigger and more expensive.
For example, Chinchilla, a large-scale language model launched by DeepMind in May 2022, is estimated to cost US$2.1 million, while training of BLOOM costs approximately US$2.3 million.

Over time, the progress of GAN in face generation, the last image was generated by Diffusion-GAN, this model in STL The latest SOTA was obtained on -10.

Last year, with OpenAI’s DALL-E 2, Stability AI’s Stable Diffusion, Midjourney, Meta’s Make-AScene, and Google’s Imagen With the release of the model, the text-to-image generation model has gradually entered the public eye.
As follows, enter the same prompt, "A panda plays the piano on a warm Parisian night", respectively, from three publicly accessible programs: DALL-E 2, Stable Diffusion and Midjourney. Image generated by AI text-to-image system.

Among all recently released text-to-image generation models, Google’s Imagen performs best on the COCO benchmark.
This year, the Google researchers who created Imagen also released DrawBench, a more difficult text-to-image benchmark designed to challenge increasingly powerful text-to-image models.

In addition, the report also introduced that there are some biases in the current generative AI model. For example, when prompting the CEO to DELLE-2, everyone seemed to take crossed arms in a confident pose.

In Midjourney, when prompted to generate "influencers" it generates 4 images of older looking white men .

For the complete report content, please see:
https ://aiindex.stanford.edu/wp-content/uploads/2023/04/HAI_AI-Index_Report_2023.pdf
The above is the detailed content of Stanford 2023 AI Index Report is out! China dominates the top AI conferences, with the Chinese Academy of Sciences ranking first in the world in terms of published papers. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
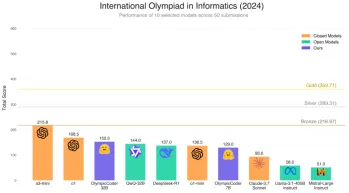 Does Hugging Face's 7B Model OlympicCoder Beat Claude 3.7?Apr 23, 2025 am 11:49 AM
Does Hugging Face's 7B Model OlympicCoder Beat Claude 3.7?Apr 23, 2025 am 11:49 AMHugging Face's OlympicCoder-7B: A Powerful Open-Source Code Reasoning Model The race to develop superior code-focused language models is intensifying, and Hugging Face has joined the competition with a formidable contender: OlympicCoder-7B, a product
 4 New Gemini Features You Can't Afford to MissApr 23, 2025 am 11:48 AM
4 New Gemini Features You Can't Afford to MissApr 23, 2025 am 11:48 AMHow many of you have wished AI could do more than just answer questions? I know I have, and as of late, I’m amazed by how it’s transforming. AI chatbots aren’t just about chatting anymore, they’re about creating, researchin
 Camunda Writes New Score For Agentic AI OrchestrationApr 23, 2025 am 11:46 AM
Camunda Writes New Score For Agentic AI OrchestrationApr 23, 2025 am 11:46 AMAs smart AI begins to be integrated into all levels of enterprise software platforms and applications (we must emphasize that there are both powerful core tools and some less reliable simulation tools), we need a new set of infrastructure capabilities to manage these agents. Camunda, a process orchestration company based in Berlin, Germany, believes it can help smart AI play its due role and align with accurate business goals and rules in the new digital workplace. The company currently offers intelligent orchestration capabilities designed to help organizations model, deploy and manage AI agents. From a practical software engineering perspective, what does this mean? The integration of certainty and non-deterministic processes The company said the key is to allow users (usually data scientists, software)
 Is There Value In A Curated Enterprise AI Experience?Apr 23, 2025 am 11:45 AM
Is There Value In A Curated Enterprise AI Experience?Apr 23, 2025 am 11:45 AMAttending Google Cloud Next '25, I was keen to see how Google would distinguish its AI offerings. Recent announcements regarding Agentspace (discussed here) and the Customer Experience Suite (discussed here) were promising, emphasizing business valu
 How to Find the Best Multilingual Embedding Model for Your RAG?Apr 23, 2025 am 11:44 AM
How to Find the Best Multilingual Embedding Model for Your RAG?Apr 23, 2025 am 11:44 AMSelecting the Optimal Multilingual Embedding Model for Your Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) System In today's interconnected world, building effective multilingual AI systems is paramount. Robust multilingual embedding models are crucial for Re
 Musk: Robotaxis In Austin Need Intervention Every 10,000 MilesApr 23, 2025 am 11:42 AM
Musk: Robotaxis In Austin Need Intervention Every 10,000 MilesApr 23, 2025 am 11:42 AMTesla's Austin Robotaxi Launch: A Closer Look at Musk's Claims Elon Musk recently announced Tesla's upcoming robotaxi launch in Austin, Texas, initially deploying a small fleet of 10-20 vehicles for safety reasons, with plans for rapid expansion. H
 AI's Shocking Pivot: From Work Tool To Digital Therapist And Life CoachApr 23, 2025 am 11:41 AM
AI's Shocking Pivot: From Work Tool To Digital Therapist And Life CoachApr 23, 2025 am 11:41 AMThe way artificial intelligence is applied may be unexpected. Initially, many of us might think it was mainly used for creative and technical tasks, such as writing code and creating content. However, a recent survey reported by Harvard Business Review shows that this is not the case. Most users seek artificial intelligence not just for work, but for support, organization, and even friendship! The report said that the first of AI application cases is treatment and companionship. This shows that its 24/7 availability and the ability to provide anonymous, honest advice and feedback are of great value. On the other hand, marketing tasks (such as writing a blog, creating social media posts, or advertising copy) rank much lower on the popular use list. Why is this? Let's see the results of the research and how it continues to be
 Companies Race Toward AI Agent AdoptionApr 23, 2025 am 11:40 AM
Companies Race Toward AI Agent AdoptionApr 23, 2025 am 11:40 AMThe rise of AI agents is transforming the business landscape. Compared to the cloud revolution, the impact of AI agents is predicted to be exponentially greater, promising to revolutionize knowledge work. The ability to simulate human decision-maki


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

DVWA
Damn Vulnerable Web App (DVWA) is a PHP/MySQL web application that is very vulnerable. Its main goals are to be an aid for security professionals to test their skills and tools in a legal environment, to help web developers better understand the process of securing web applications, and to help teachers/students teach/learn in a classroom environment Web application security. The goal of DVWA is to practice some of the most common web vulnerabilities through a simple and straightforward interface, with varying degrees of difficulty. Please note that this software

MantisBT
Mantis is an easy-to-deploy web-based defect tracking tool designed to aid in product defect tracking. It requires PHP, MySQL and a web server. Check out our demo and hosting services.

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

mPDF
mPDF is a PHP library that can generate PDF files from UTF-8 encoded HTML. The original author, Ian Back, wrote mPDF to output PDF files "on the fly" from his website and handle different languages. It is slower than original scripts like HTML2FPDF and produces larger files when using Unicode fonts, but supports CSS styles etc. and has a lot of enhancements. Supports almost all languages, including RTL (Arabic and Hebrew) and CJK (Chinese, Japanese and Korean). Supports nested block-level elements (such as P, DIV),





