 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals AI
AI 2022 L4 autonomous driving annual answer sheet, really 'no one' has the last laugh
2022 L4 autonomous driving annual answer sheet, really 'no one' has the last laugh2022 L4 autonomous driving annual answer sheet, really 'no one' has the last laugh
L4 autonomous driving has reached a moment of "big reshuffle" and "big change" this year.
Half of winter. Aurora, the platform-based self-driving star, and Argo, which is backed by Ford and Volkswagen... have all reported news of layoffs or bankruptcy this year, and many companies that previously focused on Robotaxi have switched to assisted driving for passenger cars.
Capital has become extremely cautious about L4’s story. So people say: L4 winter has arrived.
The other half is a flame.
The jewel in the crown is far away, and the leading company has already glimpsed the dawn of the finals and obtained tickets.
Baidu Apollo, Google Waymo, and General Cruise are making rapid progress and making continuous progress.
For example, Waymo and Cruise have continued to make breakthroughs in the scope and duration of their commercial operations in San Francisco and Phoenix; while in China, Baidu Apollo’s Carrot Run has also launched in more than ten cities, with fully driverless operations in Beijing and Wuhan , Chongqing achieved a milestone, and the number of commercial miles and waybills increased rapidly.
how to explain?
It’s actually very simple: in the wave of reshuffle in the autonomous driving industry, only truly “unmanned” people can be the first to see the dawn.
Why is "no one on the ground" so important?
Baidu Apollo, Waymo, and Cruise, the three players that have made the fastest progress in L4 commercialization, all show the same characteristics.
Being backed by giants is just one of them. More importantly, their implementation projects are based on the premise of "no one at all".
For example, in Wuhan, Hubei, you can call a fully unmanned self-driving car through the Luobo Kuaipao App, and the technology behind this comes from Baidu Apollo.
Why is "fully unmanned" the key to the implementation of L4 and above autonomous driving technology?
First of all, from a business perspective, "completely unmanned" is a necessary prerequisite for the initial success of Robotaxi's business model.
For Robotaxi, the biggest challenge to commercialization is cost. The first is the cost of vehicle modifications. In the early days, without reaching pre-installation mass production cooperation with the OEM, it was common for a Robotaxi to cost millions.
In the operational stage, the biggest cost is the safety officer on the vehicle.
The minimum labor cost for an online ride-hailing car driven by an ordinary human driver is about 120,000 yuan a year, and the safety officer is only higher than the driver.
It was difficult for the previous Robotaxi to balance its own costs during the entire operation life cycle
Technically achieving "full unmanned operation" means that labor costs are saved first.
Secondly, the fully unmanned self-driving technology stack must be implemented on pre-installed and mass-produced models, so at the level of the vehicle itself, it also means entering the same cost range as ordinary online ride-hailing.
In addition, "fully unmanned" also means that technology providers have been able to meet the high reliability and safety of autonomous driving travel.
The policy is also more inclined to open operating licenses to such technology providers.
Therefore, the most critical and direct point for the implementation of "fully unmanned" autonomous driving is "lowering costs". The more important and profound influencing factor behind it is the improvement of safety and reliability brought about by the maturity of technology.
The data given by Baidu Apollo is that it has accumulated more than 40 million kilometers of test miles. Robotaxi's successful delivery rate has exceeded 99.99%.
Behind this, there is Apollo’s closed loop of autonomous driving data through L2 and L4, as well as the foundation laid by Baidu’s other accumulation in the AI field.
For example, relying on the thousands of object recognition capabilities of the Wenxin large model, we can greatly expand the semantic recognition data of autonomous driving, especially in the recognition of special vehicles (fire trucks, ambulances), plastic bags and other special-shaped objects. Greatly improve the coverage of long-tail scenarios and improve the reliability of autonomous driving.
In addition, the Apollo self-driving high-precision map has a construction automation rate of 96%. It is based on Baidu Map’s 12 million kilometers of leading road network coverage and massive spatio-temporal data, combined with the driving knowledge accumulated by hundreds of millions of drivers. Build a driving knowledge graph at the entire road network level to improve the comfort of autonomous driving decision-making.
Currently, the commercial operation and testing of Luobo Kuaipao’s fully unmanned self-driving fleet continues to expand the area, increase the volume, and increase the time. It has already landed in Beijing, Chongqing and Wuhan.

Take Wuhan Economic Development Zone as an example, covering a total area of more than 130 square kilometers and covering more than 1 million residents. The operation scenarios of the autonomous driving fleet include urban elevated roads and ordinary roads, and the operation period covers day and night. The long-tail scenarios and complex challenges encountered in the process draft are no different from ordinary online ride-hailing private cars.
The accumulation and training of data in real scenarios can directly accelerate Apollo’s technical iteration efficiency, thereby exploring more long-tail scenarios and forming a data closed-loop “flywheel” effect.
Fully unmanned technology has matured, bringing about the initial run-through of the business model and enabling large-scale operations in some cities.
In this process, capable players will further verify and improve the Robotaxi business model, and further expand the scope of implementation, thereby forming a leading advantage.
This is exactly the path that players such as Baidu Apollo and Waymo are currently taking, and it is also the "torch" that allows people to still believe in technology and autonomous driving in the cold winter.
What kind of technology is required?
To achieve the goal of no one landing, the technology behind it needs to be solid and hard enough.
As for Baidu, as the one that has been developing steadily in this industry reshuffle and polarization, and has always been the leader in autonomous driving in China, its technological development can be said to have certain reference significance.
Therefore, we might as well look at this issue from the perspective of Baidu’s autonomous driving technology development path.
Different from other players’ play styles, a very distinctive feature of Baidu’s autonomous driving is its in-depth integration with Wenxin’s large model.
And looking at the entire industry, Baidu is still the first to apply large models in autonomous driving perception.
Specifically, to solve the long-tail data mining problem of autonomous driving, Baidu uses the Wenxin large model - a weakly supervised image and text pre-training model.
Several more typical long-tail data mining problems include:
• Rare vehicle models: such as fire trucks, ambulances, etc., due to their low "appearance rate" on the road, And the shape and shape are irregular, which brings certain challenges to perception and understanding. • Pedestrians in various postures: On the road, there is often not one person appearing on the road. This not only brings challenges to identification, but also brings certain difficulties to subsequent prediction and tracking. • Low objects and elements of traffic and construction: Low objects (such as guardrails on roads, etc.) have always been a very challenging problem to perceive.
Faced with the above inherent problems, with the help of the Wenxin large model's ability to recognize thousands of objects, Baidu's semantic recognition data for autonomous driving can be greatly expanded, achieving exponential improvements in efficiency.
In addition, thanks to the Wenxin Large Model-Autonomous Driving Perception Model with a parameter scale of more than 1 billion, through the large model training of small models, the generalization ability of autonomous driving perception has also been significantly enhanced.

In this regard, Baidu autonomous driving technology expert Wang Jingdong said:
Large models have become the core driving force for improving autonomous driving capabilities.
The "second magic weapon" that enables Baidu's autonomous driving to quickly realize unmanned landing is the Baidu Apollo autonomous driving map.
Different from the navigation maps we usually use, high-precision maps can be said to be indispensable for realizing intelligent driving.
Overall, high-precision maps need to meet three major characteristics.
The first is centimeter-level high precision.
When humans use ordinary navigation maps, they only need to be accurate to 5-10 meters, plus the driver's own judgment.
But smart cars do not have the judgment ability of humans, so an error of 1-2 meters may lead to problems such as line pressing. This is why the accuracy must be kept within the centimeter range. .
The second is the large amount of road information covered.
The information that high-precision maps need to provide to smart cars can go beyond the basic information such as road selection, congestion, and driving time contained in ordinary navigation maps. It also needs to include a large amount of driving assistance information, such as lane width change offset points, diversion areas, circular signs, highway exits, etc.
The most important thing is the accurate three-dimensional representation of the road network, as well as more than 100 road features including how many lanes there are, where the boundary lines are, guardrails, street lights, and even the size of the curbs.
The third is that there will be detours on high-precision maps.
This is because the high-precision map is aimed at smart cars rather than humans. The information it provides is used for the positioning system, perception system and decision-making system of smart cars.
Therefore, when faced with situations such as tunnels, the high-precision map may "detour" because in its eyes, this road does not exist.
It can be seen that in order to achieve a fully unmanned landing, high-precision maps are indispensable, and it is not easy to achieve.
But as the Baidu Apollo self-driving map that has been "on duty", it must have held the above-mentioned difficulties.
It is understood that Baidu’s high-precision construction automation rate has reached 96%, which means that the problem of high application costs can be solved to a greater extent.
At the same time, it also has the ability to generate online maps in real time, and can integrate tear-off sensing data and multi-source maps to protect the safety of autonomous driving.
In terms of decision-making, based on Baidu Maps’ 12 million kilometers of leading road network coverage level massive spatio-temporal data and hundreds of millions of drivers’ driving knowledge data, Baidu has also built a driving knowledge graph at the entire road network level. To improve the comfort of autonomous driving decision-making.
In addition to the algorithm and software levels, Baidu has achieved no-one implementation and has not neglected its efforts in hardware.
It is understood that Baidu’s self-developed AI chip Kunlun Core 2 has completed end-to-end performance adaptation for autonomous driving scenarios, in order to consolidate Baidu’s advantages in the integration of software and hardware for autonomous driving.
Of course, Baidu’s ability to take the lead in autonomous driving is not something that can be achieved overnight. It is actually the result of “ten years of hard work in the field” and continuous technological accumulation.
A set of public data can be seen at a glance:
At present, Baidu Apollo has grown into the world's most active autonomous driving open platform, with more than 210 global ecological partners, 80,000 global developers, 700,000 lines of open source code, and a total test mileage of more than 40 million kilometers; there are 3,477 autonomous driving patents, ranking first in the world for four consecutive years.
The above is the technical strength behind the players who are the first to realize unmanned landing.
The tickets for the finals have been decided
As we mentioned at the beginning, this year the global autonomous driving industry is undergoing a "major reshuffle".
Judging from the self-driving companies that have been exposed to bankruptcy, filing for bankruptcy, and massive layoffs, they seem to have one thing in common - they have failed to achieve the goal of fully autonomous driving.
After all, autonomous driving is not only a competition in technical strength, but also a contest in time and endurance.
Just like you can only see who is swimming naked when the tide recedes, standing at the end of 2022, accelerating the landing of no one has become an inevitable node for "coming ashore" players.
Not only Baidu, the domestic leader in autonomous driving, is doing this, but also leading international players.
Autonomous driving companies such as Waymo and Cruise are accelerating the large-scale commercialization of autonomous driving.
It is understood that San Francisco in the United States has now opened a 24/7 driverless travel service in the entire city. At the same time, Phoenix’s autonomous driving operation area continues to expand to the core urban area.
In addition, the world's first fully driverless taxi-hailing service has been launched from Phoenix Sky Harbor International Airport to the city center, operating 24/7.
Baidu has also recently released a new signal:
In 2023, Baidu Apollo will continue to expand its business scale and plans to launch an additional 200 wireless devices nationwide. We will operate vehicles driven by humans and strive to build the world’s largest driverless operation service area.
It is understood that Baidu’s sixth-generation unmanned vehicle Apollo RT6 (costing only 250,000 yuan), which will be mass-produced this year, will be put into use on Luobo Kuaipao next year.
Generally speaking, Baidu has achieved cost reduction, safety and quality assurance in fully unmanned implementation, and at the same time, it is continuing to accelerate the expansion of scale.
The reason is that what Baidu currently wants to ensure is that each city can run its business model at low cost (gross profit is positive); but if it takes a long-term view, the exponential growth of its operating scale is foreseeable. .
It can be seen that "no one lands on the ground" has become the key for players to enter the autonomous driving finals.
So in this second half of autonomous driving, who can have the last laugh?
Baidu is undoubtedly one of them.
The above is the detailed content of 2022 L4 autonomous driving annual answer sheet, really 'no one' has the last laugh. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
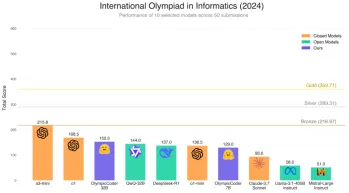 Does Hugging Face's 7B Model OlympicCoder Beat Claude 3.7?Apr 23, 2025 am 11:49 AM
Does Hugging Face's 7B Model OlympicCoder Beat Claude 3.7?Apr 23, 2025 am 11:49 AMHugging Face's OlympicCoder-7B: A Powerful Open-Source Code Reasoning Model The race to develop superior code-focused language models is intensifying, and Hugging Face has joined the competition with a formidable contender: OlympicCoder-7B, a product
 4 New Gemini Features You Can't Afford to MissApr 23, 2025 am 11:48 AM
4 New Gemini Features You Can't Afford to MissApr 23, 2025 am 11:48 AMHow many of you have wished AI could do more than just answer questions? I know I have, and as of late, I’m amazed by how it’s transforming. AI chatbots aren’t just about chatting anymore, they’re about creating, researchin
 Camunda Writes New Score For Agentic AI OrchestrationApr 23, 2025 am 11:46 AM
Camunda Writes New Score For Agentic AI OrchestrationApr 23, 2025 am 11:46 AMAs smart AI begins to be integrated into all levels of enterprise software platforms and applications (we must emphasize that there are both powerful core tools and some less reliable simulation tools), we need a new set of infrastructure capabilities to manage these agents. Camunda, a process orchestration company based in Berlin, Germany, believes it can help smart AI play its due role and align with accurate business goals and rules in the new digital workplace. The company currently offers intelligent orchestration capabilities designed to help organizations model, deploy and manage AI agents. From a practical software engineering perspective, what does this mean? The integration of certainty and non-deterministic processes The company said the key is to allow users (usually data scientists, software)
 Is There Value In A Curated Enterprise AI Experience?Apr 23, 2025 am 11:45 AM
Is There Value In A Curated Enterprise AI Experience?Apr 23, 2025 am 11:45 AMAttending Google Cloud Next '25, I was keen to see how Google would distinguish its AI offerings. Recent announcements regarding Agentspace (discussed here) and the Customer Experience Suite (discussed here) were promising, emphasizing business valu
 How to Find the Best Multilingual Embedding Model for Your RAG?Apr 23, 2025 am 11:44 AM
How to Find the Best Multilingual Embedding Model for Your RAG?Apr 23, 2025 am 11:44 AMSelecting the Optimal Multilingual Embedding Model for Your Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) System In today's interconnected world, building effective multilingual AI systems is paramount. Robust multilingual embedding models are crucial for Re
 Musk: Robotaxis In Austin Need Intervention Every 10,000 MilesApr 23, 2025 am 11:42 AM
Musk: Robotaxis In Austin Need Intervention Every 10,000 MilesApr 23, 2025 am 11:42 AMTesla's Austin Robotaxi Launch: A Closer Look at Musk's Claims Elon Musk recently announced Tesla's upcoming robotaxi launch in Austin, Texas, initially deploying a small fleet of 10-20 vehicles for safety reasons, with plans for rapid expansion. H
 AI's Shocking Pivot: From Work Tool To Digital Therapist And Life CoachApr 23, 2025 am 11:41 AM
AI's Shocking Pivot: From Work Tool To Digital Therapist And Life CoachApr 23, 2025 am 11:41 AMThe way artificial intelligence is applied may be unexpected. Initially, many of us might think it was mainly used for creative and technical tasks, such as writing code and creating content. However, a recent survey reported by Harvard Business Review shows that this is not the case. Most users seek artificial intelligence not just for work, but for support, organization, and even friendship! The report said that the first of AI application cases is treatment and companionship. This shows that its 24/7 availability and the ability to provide anonymous, honest advice and feedback are of great value. On the other hand, marketing tasks (such as writing a blog, creating social media posts, or advertising copy) rank much lower on the popular use list. Why is this? Let's see the results of the research and how it continues to be
 Companies Race Toward AI Agent AdoptionApr 23, 2025 am 11:40 AM
Companies Race Toward AI Agent AdoptionApr 23, 2025 am 11:40 AMThe rise of AI agents is transforming the business landscape. Compared to the cloud revolution, the impact of AI agents is predicted to be exponentially greater, promising to revolutionize knowledge work. The ability to simulate human decision-maki


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

WebStorm Mac version
Useful JavaScript development tools

VSCode Windows 64-bit Download
A free and powerful IDE editor launched by Microsoft

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

MantisBT
Mantis is an easy-to-deploy web-based defect tracking tool designed to aid in product defect tracking. It requires PHP, MySQL and a web server. Check out our demo and hosting services.





