PHP 7 exceptions are used for backward compatibility and enhancement of the old assert() function. It enables zero-cost assertions in production environments and provides the ability to throw custom exceptions and errors.
The old version of the API will continue to be maintained for compatibility purposes. assert() is now a language construct that allows the first parameter to be an expression, not just a string to be evaluated or a The boolean to be tested.
assert() configuration
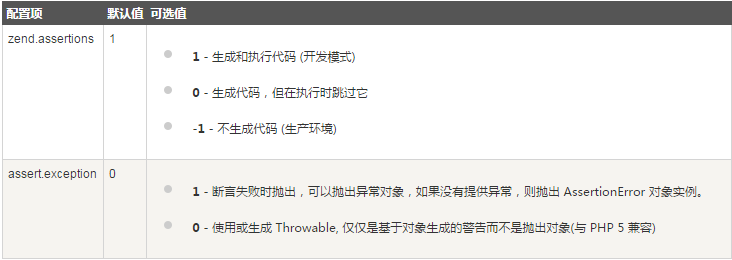
Parameters
- assertion
assertion. In PHP 5, a string for execution or a boolean for testing. In PHP 7, this can be an expression that returns any value, and the result will be used to indicate whether the assertion was successful.
- description
If
assertionfails, the option description will be included in the failure message.- exception
In PHP 7, the second parameter can be a Throwable object instead of a character A string that will be thrown if the assertion fails and assert.exception is enabled.
Example
Set zend.assertions to 0:
Example
<?php
ini_set('zend.assertions', 0);
assert(true == false);
echo 'Hi!';
?>The above program is executed The output result is:
Hi!
Set zend.assertions to 1 and assert.exception to 1:
Example
<?php
ini_set('zend.assertions', 1);
ini_set('assert.exception', 1);
assert(true == false);
echo 'Hi!';
?>The above program execution output The result is:
Fatal error: Uncaught AssertionError: assert(true == false) in -:2
Stack trace:
#0 -(2): assert(false, 'assert(true == ...')
#1 {main}
thrown in - on line 2