Summary of AJAX content of PHP development basic tutorial
The workflow of AJAX is as follows:
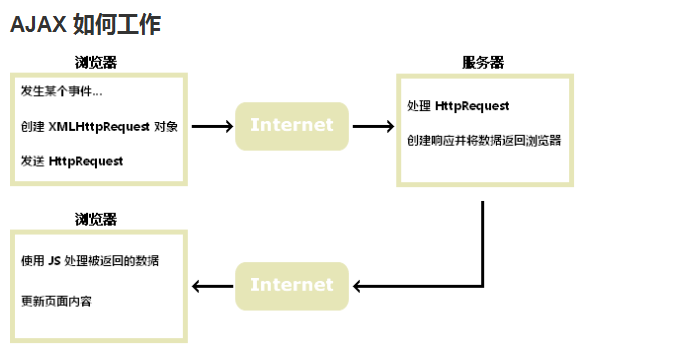
##1. An event occurs: usually oclick event, onchange events, onkeyup events, etc.
Note:
oclick event: Occurs when the object is clicked
onchange event: Occurs when the content of the field changes
onkeyup event: Occurs when the keyboard key is released
#2. Create an XMLHttpRequest object
var xmlhttp;
if (window.XMLHttpRequest)
{// code for IE7+, Firefox, Chrome, Opera, Safari
xmlhttp=new XMLHttpRequest();
}
else
{// code for IE6, IE5
xmlhttp=new ActiveXObject("Microsoft.XMLHTTP");
}##3. Send HttpRequest
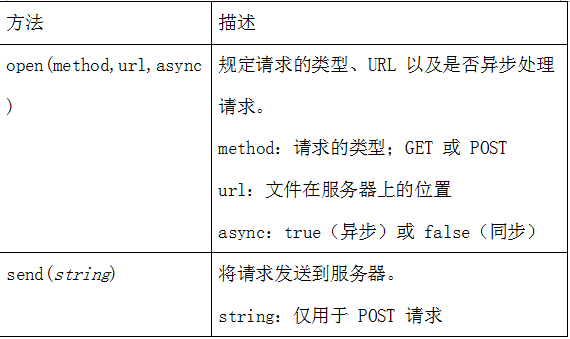
Use the open() and send() methods of the XMLHttpRequest object to send the request to the server
xmlhttp.open("GET","test1.txt",true);
xmlhttp.send();Note: Pay attention to the format of the request, the specific format is as follows
4. Process the HTTPRequest, create a response and return the data to the browser
- When a request is sent to the server, we need to perform some response-based tasks.
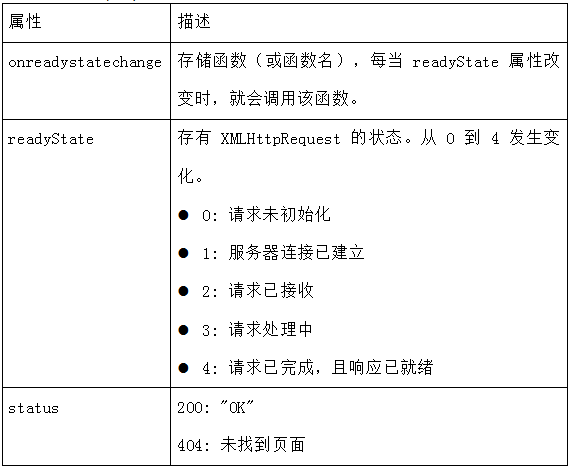
- Whenever readyState changes, the onreadystatechange event will be triggered.
The readyState attribute stores the status information of XMLHttpRequest.
The three important properties of the XMLHttpRequest object are as follows:
 In the onreadystatechange event, we specify when the server responds A task performed when it is ready to be processed.
In the onreadystatechange event, we specify when the server responds A task performed when it is ready to be processed.
when. When readyState is equal to 4 and the status is 200, it means that the response is ready
Note: the onreadystatechange event is triggered 5 times (0 - 4), corresponding to each change in readyState
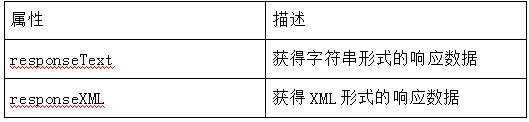
- If you want to get the response from the server, you can use the responseText or responseXML attribute of the XMLHttpRequest object.
 Example:
Example:
xmlhttp.onreadystatechange=function()
{
if (xmlhttp.readyState==4 && xmlhttp.status==200)
{
document.getElementById("myDiv").innerHTML=xmlhttp.responseText;
}
}##5. Use js to process the returned data and update the page
js gets part of the form area through the id, and then Populate it with the data returned by the XMLHttpRequest object.
Next Section
