| Note:
Use refers to use;
library name is the name of the specific database in the current database system;  # Note: We can use the USE statement to switch the database to be operated at any time # Note: We can use the USE statement to switch the database to be operated at any time
## 4. View tables in the database
# After entering the library, we can see how many data tables in this library.
Category
| Detailed explanation
| Basic syntax
| show tables;
| # Example Example
## Show all the tables under the current database | ##
After using use to enter a database, you can use show tables Example to view the tables of the current database: 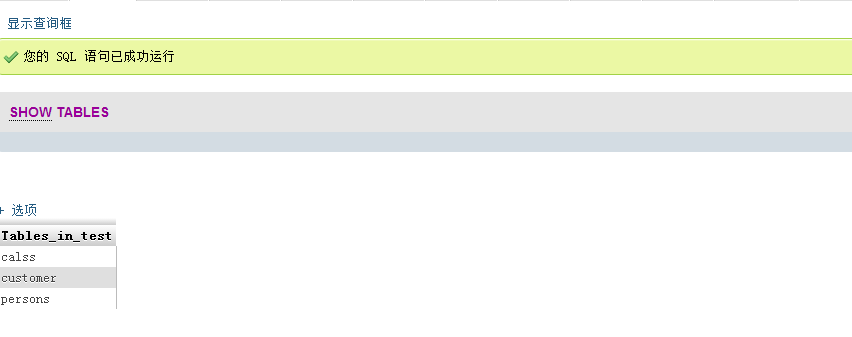
Note: The database must be selected before you can view the table 5. Delete database
##Category
| Detailed explanation
| Basic syntax
| drop database library name;
| Example
| ## drop database liwenkai;
| Example description
| Delete a database, the name of the database is liwenkai | Note:
Drop is Chinese that can be translated as a finger.
## Note: After the database is deleted, all the following data will be deleted, so you must carefully and make a corresponding backup before deleting.
##Q
#1. Create table
##Category
Detailed explanation
##Basic syntax |
create table table name (field name 1 field type,.... field name n field type n); |
Example |
create table user(username varchar(20),password varchar(32)); | ##Example description
| Create a table named user, the first field is username, the field type of the table is varchar, the length is 32 length. The second field is password, the type is also varchar, and the length is also 32 characters.
| Note: In order to better let everyone get started, data types are temporarily outside the scope of our explanation in this chapter. I’m afraid that everyone will focus on one thing and lose another. It is very important to quickly learn the management and operation statements of the database. Data types, fields, character sets, and engines are all knowledge points to understand. . As for field types, you only need to learn int now, which represents integer type. float represents floating point. char and varchar can represent strings. We can add the length after the type, such as: varchar(20).
View table field structure information
Category
| Detailed explanation
| Basic syntax
| desc table name;
| ##Example
| desc emp
| Example description
| View the table structure of the emp table | 2. Delete table
##category
| Detailed explanation
| ##Basic syntax
| Drop table Name;
| # Example
emp; |
| Example description
Delete table emp |
|
Note: Delete the table. Both tables and data will be lost. Do not delete the data before the important table. 3. Specify table engine and character set ## At the end of the creation table, we often use MyISAM or InnoDB engine. When designated by the engine, we can use: ENGINE = InnoDB Speculating Form default character set: DEFAULT CHARSET = UTF8 ## The effect is as follows: Create Table Emp ( Useraaname Varchar (10) Default Null, Password Date Default Null, )
## database field operation
#qian directly uses PHPMYADMIN to create the field in the table # Click the structure:
Fill in the information in each field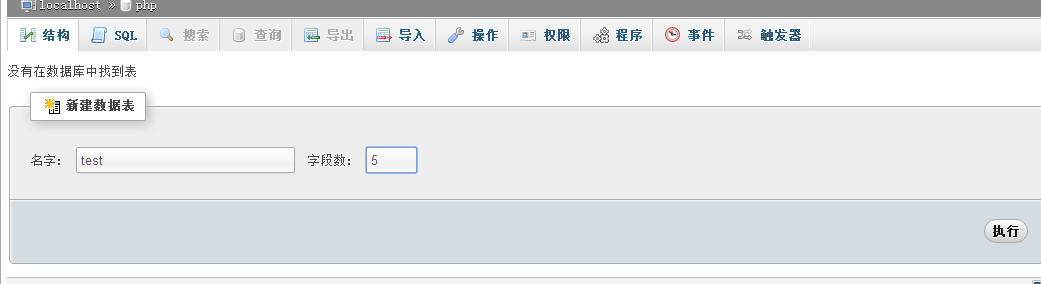
##Click Execute to complete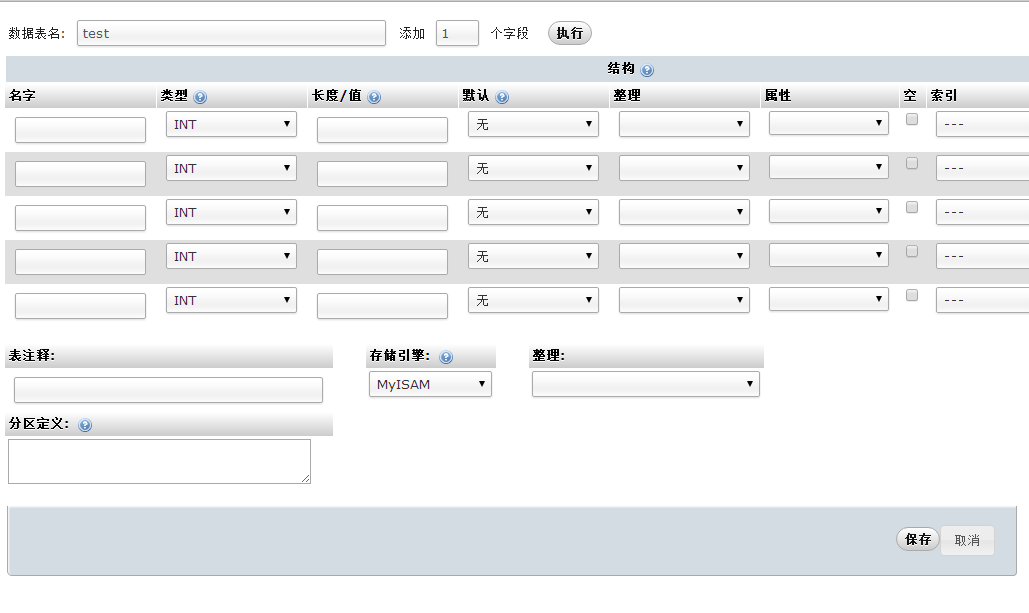 Deleting or modifying fields is also done in phpAdmin. You can try it yourselfNext Section<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>php.cn</title>
</head>
<body>
<?php
echo "Hello World!!!";
?>
</body>
</html>
|
|
|
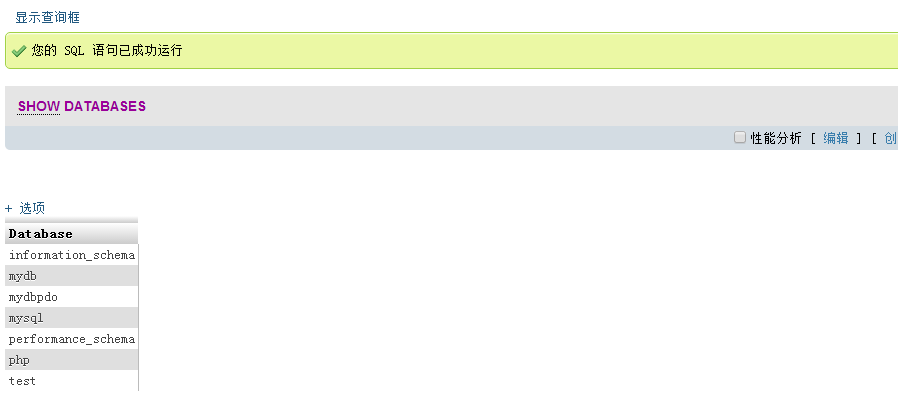
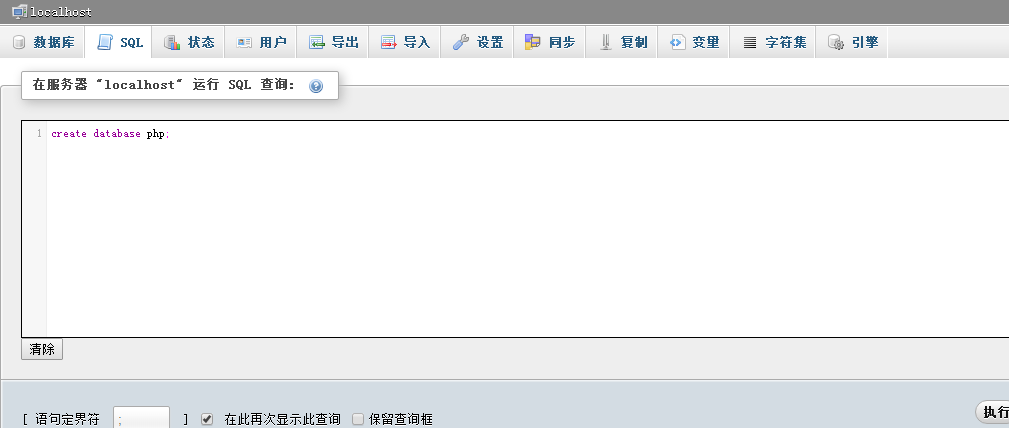
 # Note: We can use the USE statement to switch the database to be operated at any time
# Note: We can use the USE statement to switch the database to be operated at any time 


