Category
| Detailed Explanation
|
Basic syntax
| insert into table (field 1, field 2, field n) values (value 1, Value 2, value n);
|
Example
| ## insert into user(id, username,sex) values(213,'小方',1);
|
Example description
| Insert the id as 213 into the user table, the username as Xiaofang, and the gender as 1 |
#Explanation
The difference between basic syntax 1 and basic syntax 2 is:
How many insert statements are there in the table for basic syntax 1? How many values must be inserted into each field. No one can be more, and no one can be less. If there is a default value and you don’t want to pass it, you can write null.
In basic syntax 2, unless there are required fields, values must be written. If you don't want to write a default value, you can ignore it. mysql will automatically supplement the default value.
In basic syntax 2, the order of user(id,username,sex) fields is the order of values.
Assume that there is a table called the user table. We describe the fields, field descriptions, types, optional fields and required states. The table structure is as follows:
Field
| id
| username
| email
| password
| sex
|
Chinese Description
|
| Username
| Email
| Password
| Gender
|
Type Description
| ##int
| varchar(50)
| ##varchar(60)
| varchar(32)
| tinyint
|
Default value description | Auto-increment
| Required
| Optional field, the default value is 123@php.com
| Optional fields
| Required fields |
Write the insert statement in the above table according to the basic syntax:
insert into user values(null,'小明','xiaoming@php.com',null ,1);
Note
You can not specify the field name, but after values The order should be consistent with the sorting of table fields.
Fields with default values do not need to be written, then they will be default values.
If there is a default value or a nullable field and you do not want to pass in a specific value, you can write null.
The data format must be consistent with the data format specified in the table.
Write the insert statement in the above table according to basic syntax 2:
insert into user(username,sex) values('小明',1);Note that
ID is an auto-incremented one There is no need to pass in a value for the segment. The value of this field will be automatically increased by 1 each time it is inserted.
Fields with default values and nullable values do not need to be passed
Subject to the insertion order of table user(username,sex)
Basic syntax 2 is the more common usage
Basic syntax variant: insert multiple records at one time
insert into user(username,password,sex)
values('黄晓明', 'abcdef', 1),
( 'angelababy', 'bcdeef', 0),
( '陈赫', '123456', 1),
('王宝强', '987654', 1);
Query records
Before explaining the query, I prepared a data table for everyone. This table stores the bank's balance and basic information about the user.
We have defined a table structure named php.
The statement to create the table is as follows:
CREATE TABLE money (
id INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT ,
username VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL ,
balance FLOAT NOT NULL ,
province VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL ,
age TINYINT UNSIGNED NOT NULL ,
sex TINYINT NOT NULL ,
PRIMARY KEY (id(10))
) ENGINE = InnoDB CHARACTER SET utf8;
The table structure and data are displayed as follows:
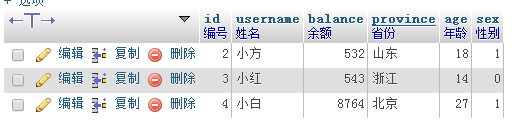
id
| username
| balance
| province
| age
| sex
|
| 1 | Xiao Ming | 1500 | Anhui | 30 | 1 |
| 2 | 小方 | 532 | 山东 | 18 | 1 |
| 3 | 小红 | 543 | Zhejiang | 14 | 0 |
| 4 | 小白 | 8764 | 北京 | 27 | 1 |
Note:
balance refers to the balance
province refers to the province
Basic query
Category
| Detailed explanation
|
Basic syntax
| select * from table;
|
##Example
| select * from php;
|
|
|
##Example description Query all results in all fields in the php table
Note: "*" is a regular expression, which means matching all , the above query statement is equivalent to the following:
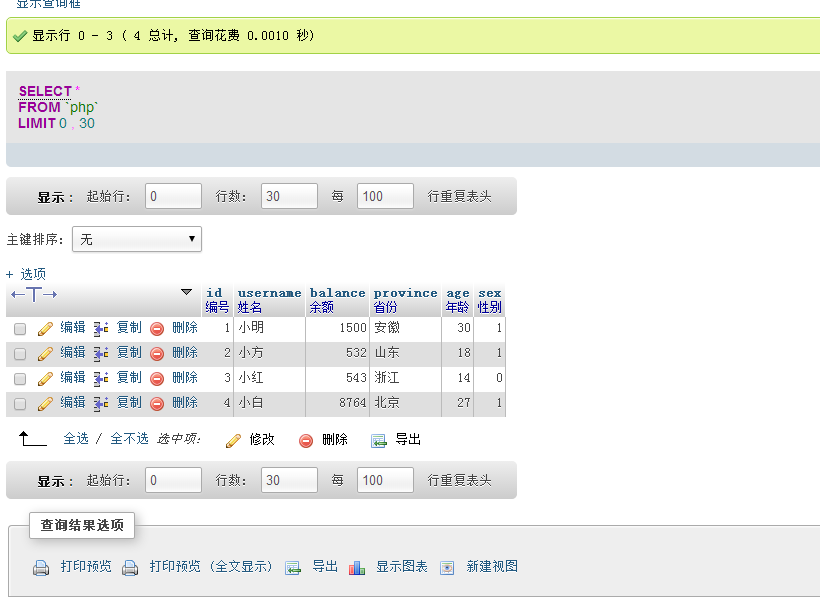
Specified field query
Category
| Detailed explanation
|
Basic syntax
| select field from table;
|
##Example
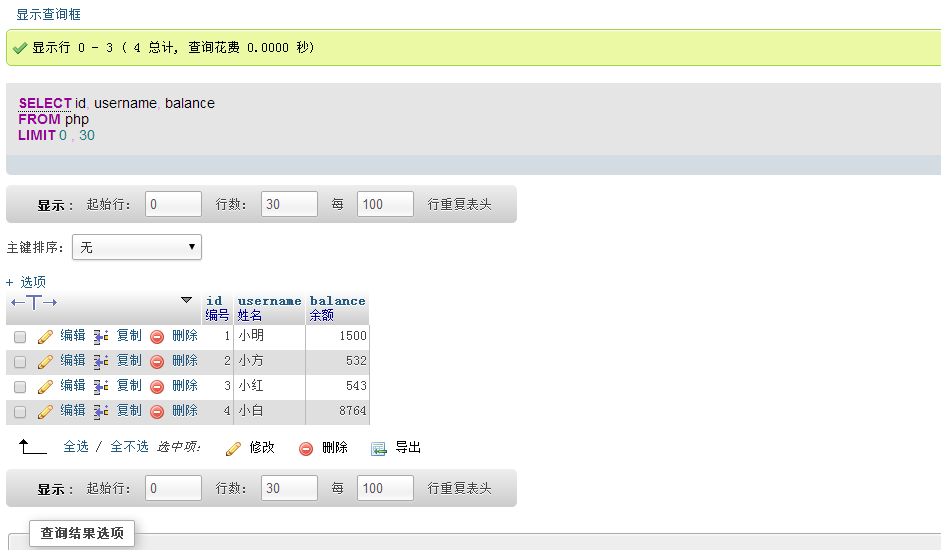
select id,username, balance from php; |
| ##Example description
Query all results in the id, username, and balance fields in the money table
| 
Conditional query where ##Category
| Detailed explanation
| Basic syntax
| select field from table where where condition;
| Example
| select * from php where age = 30;
| Example description
| ##Query all results with age 30 in the php table
|
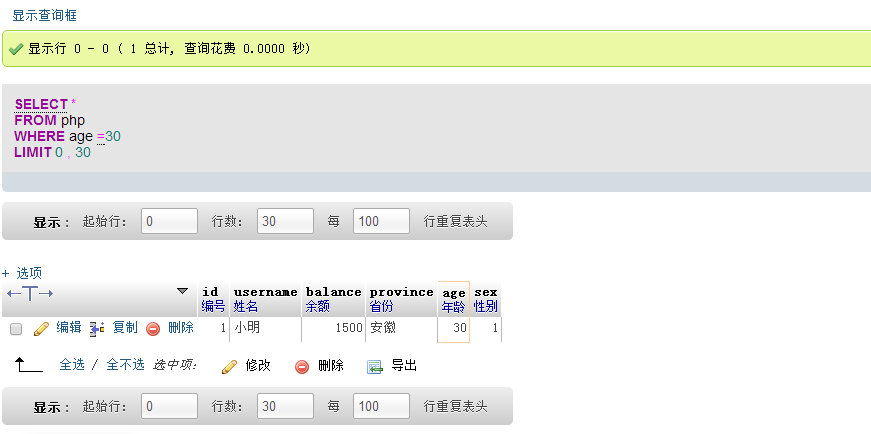
Conditions that can be followed by where Comparison operations The records that meet the conditions are listed in the result set. In the above example, the field after where is the ‘=’ of a field. In addition, you can also use comparison operators such as >, <, >=, <=, !=, etc.; ##Symbol
| Description
| ##>
| is greater than
| ##< ##is less than
|
##>= | ##greater than or equal to
| <=
| Less than or equal to
| !=
| is not equal to
| ##=
| is equal to
| Logical operators Multiple conditions can also use logical operators such as or and and to perform multi-condition joint queries Symbol
| Description
| ##or
| or
| ##and
## and | | Let’s look at an example of multiple conditions:
Type
Details |
| Example
select * from php where id < 10 and province='Anhui'; |
| ##Description Query all fields requiring id Less than 10 and province='Anhui'
|
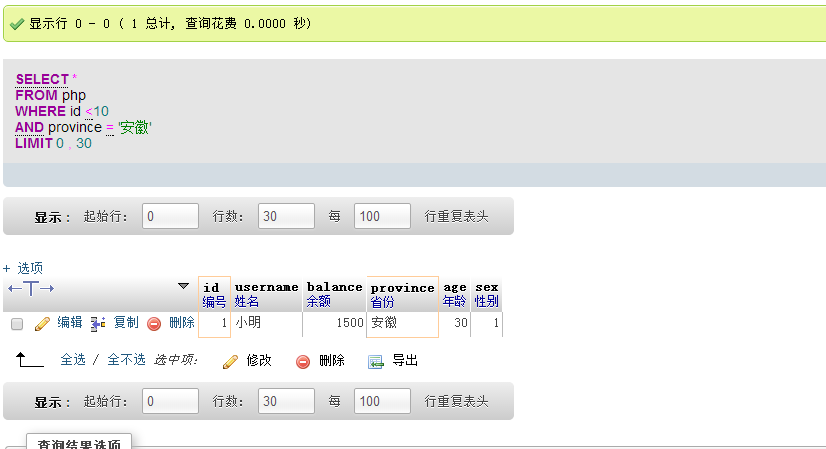
Sort the result set Category
| Detailed explanation
| Basic syntax
| select field from table order by field sort keyword
| Example
| select id,username, balance from php order by balance desc;
| ##Example description
| Query the id, username, and balance fields in the php table and sort them in descending order according to the balance |
Keywords used in sorting: Keywords
| Description
| asc
| Ascending order, from small to large (default)
| desc
| Sort in descending order, from large to small | Use order by to sort the result set after select, where desc and asc are keywords in the sort order. desc means to sort by fields in descending order, and asc means to sort in ascending order. If no keyword is written, the default is to sort in ascending order. 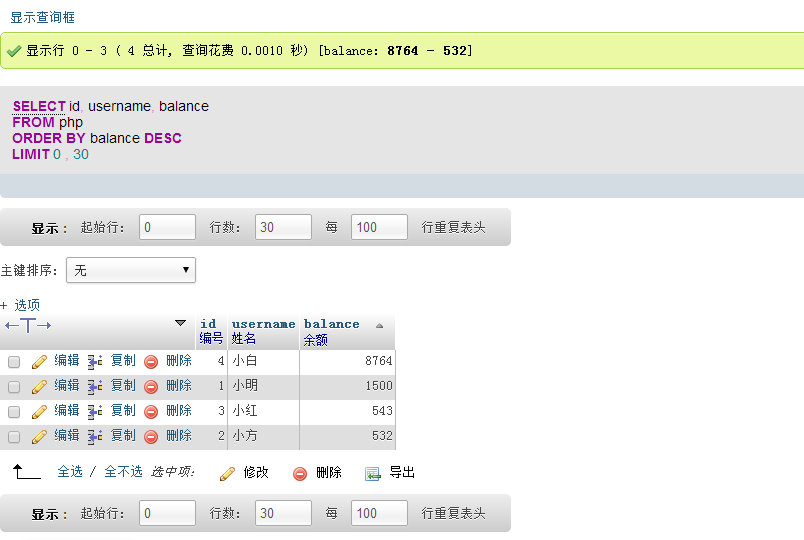
Update record Update data We have already said. When you need to modify content, modify bank card balances, or modify equipment information, you need to use update and modify statements. The basic syntax of the modification (also called update) statement is as follows: Category
| Detailed explanation
| Basic syntax
| update table name set field 1 = value 1, field 2 = value 2, field n = value n where condition
| ##Example
| update php set balance=balance-500 where id =1;
| Example description
| Modify the php table and reduce the balance balance by 500. The user id is required to be 15
|
Originally recorded as 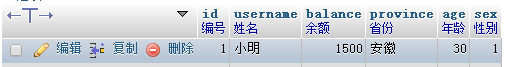
##Execute SQL statement update php set balance=balance-500 where id =1; 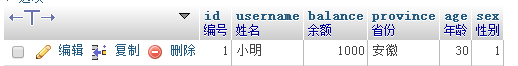
##Delete record
Category
| Detailed explanation
| Basic syntax
| delete from table [where condition];
| Example
| delete from php where id =1;
| ##Example description
Delete the data with id equal to 1 in the user table |
| Delete id=1 That row, delete the previous table content:
##Execute the SQL statement delete from php where id =1; 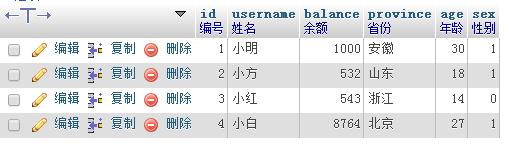
#Next Section<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>php.cn</title>
</head>
<body>
<?php
echo "Hello World!!!";
?>
</body>
</html>
|
|









