1. 将课堂中的全部案例照写一遍, 并达到默写级别
实例
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>弹性元素增长因子</title>
<!-- <link rel="stylesheet" href="css/style1.css">-->
<style>
/*@import "public.css";*/
/*设置容器宽度*/
.con {
width: 400px;
}
/*设置元素宽度*/
.item {
width: 80px;
}
/*设置增长因子demo1的默认值 0 不增长*/
.demo1 > .item {
flex-grow: 0;
}
/*将剩余空间指定增长给第二个元素*/
.demo2 > .item:nth-of-type(2) {
flex-grow: 1;
}
/*
计算:400-(80*3)=160
160+80=240px 则第二个元素宽度为240px
*/
/*将剩余空间不同因子值分配给弹性元素*/
.demo3 > .item:first-of-type {
flex-grow: 1;
}
.demo3 > .item:nth-of-type(2) {
flex-grow: 2;
}
.demo3 > .item:last-of-type{
flex-grow: 5;
}
/*
计算:
400-(80*3) =160
因子和:1+2+5=8
比例:1/8=0.125
2/8=0.25
5/8=0.625
增长量:160*0.125=20
160*0.25=40
160*0.625=100
最终宽度:80+20=100
80+40=120
80+100=180
*/
/*增长因子使用小数分配*/
.demo4 > .item:first-of-type {
flex-grow: 0.5;
}
.demo4 > .item:nth-of-type(2) {
flex-grow: 0.2;
}
.demo4 > .item:last-of-type{
flex-grow: 0.3;
}
/*
计算:
宽度和:400-(80*3) =160
因子和:0.5+0.2+0.3=1
比例:0.5/1=0.5
0.2/1=0.2
0.3/1=0.3
增长量:160*0.5=80
160*0.2=32
160*0.3=48
最终宽度:80+80=160
80+32=112
80+48=128
*/
/*每个弹性元素的宽度不等时 同样适用以上分配方式*/
.demo5 > .item:first-of-type {
width: 100px;
flex-grow: 3;
}
.demo5 > .item:nth-of-type(2) {
width: 60px;
flex-grow: 5;
}
.demo5 > .item:last-of-type{
width: 120px;
flex-grow: 2;
}
/*
计算:
宽度和:100+60+120=280
剩余空间:400-280=120
因子和:3+5+2=10
因子比例:0.3 0.5 0.2
增长量:120*0.3=36
120*0.5=60
120*0.2=24
总宽度:100+36=136
60+60=120
120+24=144
*/
</style>
<style>
/*弹性容器通用样式*/
.con {
border: 2px dashed orangered;
background: #f9906f;
margin: 10px;
}
/*弹性元素通用样式*/
.item {
box-sizing: border-box;
border: 1px solid red;
background: #CCFFFF;
padding: 18px;
}
/*块级弹性容器*/
.flex {
display: flex;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>flex-grow: 弹性元素增长因子</h1>
<hr>
<h3>默认显示 所有元素不增长 增长因子设置为0</h3>
<div class="con flex demo1">
<span class="item">item1</span>
<span class="item">item2</span>
<span class="item">item3</span>
</div>
<hr>
<h3>将剩余空间指定增长给第二个元素</h3>
<div class="con flex demo2">
<span class="item">item1</span>
<span class="item">item2</span>
<span class="item">item3</span>
</div>
<hr>
<h3>将剩余空间不同因子值分配给弹性元素</h3>
<div class="con flex demo3">
<span class="item">item1</span>
<span class="item">item2</span>
<span class="item">item3</span>
</div>
<hr>
<h3>增长因子使用小数分配</h3>
<div class="con flex demo4">
<span class="item">item1</span>
<span class="item">item2</span>
<span class="item">item3</span>
</div>
<hr>
<h3>每个弹性元素的宽度不等时 同样适用以上分配方式</h3>
<div class="con flex demo5">
<span class="item">item1</span>
<span class="item">item2</span>
<span class="item">item3</span>
</div>
</body>
</html>运行实例 »
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例



实例
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>弹性元素缩减因子</title>
<!-- <link rel="stylesheet" href="css/style2.css">-->
<style>
/*@import "public.css";*/
.con {
width: 400px;
}
.item {
width: 150px;
}
/*所有弹性元素不缩减 默认显示 缩减因子值为0*/
.demo1 > .item {
flex-shrink: 0;
}
/*所有弹性元素自适应容器宽度不换行 缩减因子值为1*/
.demo2 > .item {
flex-shrink: 1;
}
/*
计算:
需要缩放的空间:150*3-400=50
缩减因子和: 1+1+1=3
缩减因子比例:1/3=0.3333
1/3=0.3333
1/3=0.3333
元素缩减宽度:50*0.3333=16.665
50*0.3333=16.665
50*0.3333=16.665
缩减后宽度: 150-16.665=133.335
150-16.665=133.335
150-16.665=133.335
*/
/*弹性元素的缩减因子不同*/
.demo3 > .item:first-of-type {
flex-shrink: 2;
}
.demo3 > .item:nth-of-type(2) {
flex-shrink: 5;
}
.demo3 > .item:last-of-type {
flex-shrink: 3;
}
/*
计算:
需要缩放的空间:150*3-400=50
缩减因子和: 2+5+3=10
缩减因子比例:2/10=0.2
5/10=0.5
3/10=0.3
元素缩减宽度:50*0.2=10
50*0.5=25
50*0.3=15
缩减后宽度: 150-10=140
150-25=125
150-15=135
*/
/*缩减因子可以是小数*/
.demo4 > .item:first-of-type {
flex-shrink: 0.2;
}
.demo4 > .item:nth-of-type(2) {
flex-shrink: 0.5;
}
.demo4 > .item:last-of-type {
flex-shrink: 0.3;
}
/*
计算:
需要缩放的空间:150*3-400=50
缩减因子和: 0.2+0.5+0.3=1
缩减因子比例:0.2/1=0.2
0.5/1=0.5
0.3/1=0.3
元素缩减宽度:50*0.2=10
50*0.5=25
50*0.3=15
缩减后宽度: 150-10=140
150-25=125
150-15=135
*/
/*当每个弹性元素不一样时*/
.demo5 > .item:first-of-type {
width: 100px;
flex-shrink: 3;
}
.demo5 > .item:nth-of-type(2) {
width: 150px;
flex-shrink: 5;
}
.demo5 > .item:last-of-type {
width: 200px;
flex-shrink: 2;
}
/*
计算:
总宽度:100+150+200=450
需要缩减的空间:450-400=50
比例:50 / (100 *3) + (150 *5) +(200 *2)=50 / 1450 =0.0344827
缩减量:100 * (3 * 0.0344827)= 10.34481
150 * (5 * 0.0344827)= 25.86202
200 * (2 * 0.0344827)= 13.79308
总和:100-10.34481=89.65519
150-25.86202=124.13798
200-13.79308=186.20692
*/
</style>
<style>
/*弹性容器通用样式*/
.con {
border: 2px dashed orangered;
background: #f9906f;
margin: 10px;
}
/*弹性元素通用样式*/
.item {
box-sizing: border-box;
border: 1px solid red;
background: #CCFFFF;
padding: 18px;
}
/*块级弹性容器*/
.flex {
display: flex;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
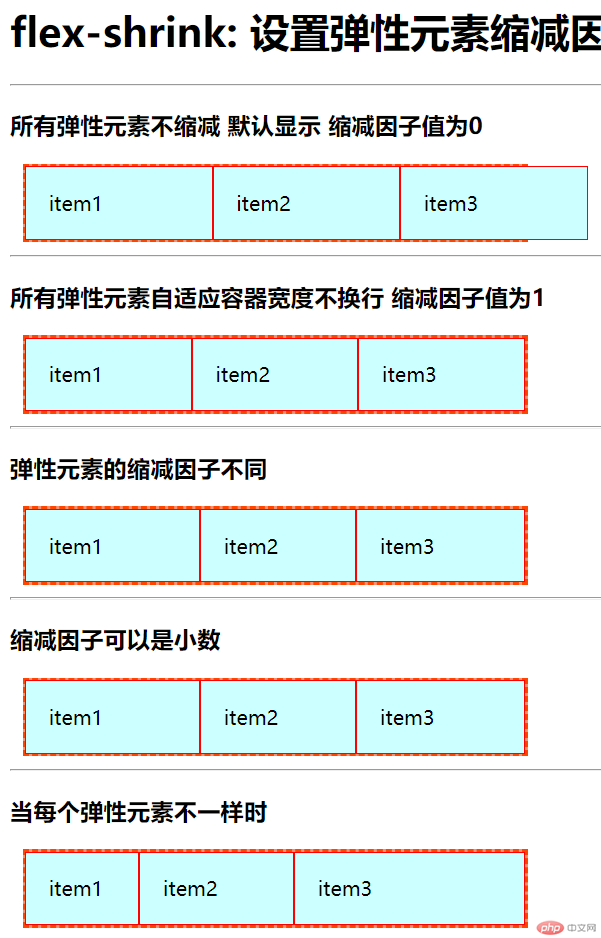
<h1>flex-shrink: 设置弹性元素缩减因子</h1>
<hr>
<h3>所有弹性元素不缩减 默认显示 缩减因子值为0</h3>
<div class="con flex demo1">
<span class="item">item1</span>
<span class="item">item2</span>
<span class="item">item3</span>
</div>
<hr>
<h3>所有弹性元素自适应容器宽度不换行 缩减因子值为1</h3>
<div class="con flex demo2">
<span class="item">item1</span>
<span class="item">item2</span>
<span class="item">item3</span>
</div>
<hr>
<h3>弹性元素的缩减因子不同</h3>
<div class="con flex demo3">
<span class="item">item1</span>
<span class="item">item2</span>
<span class="item">item3</span>
</div>
<hr>
<h3>缩减因子可以是小数</h3>
<div class="con flex demo4">
<span class="item">item1</span>
<span class="item">item2</span>
<span class="item">item3</span>
</div>
<hr>
<h3>当每个弹性元素不一样时</h3>
<div class="con flex demo5">
<span class="item">item1</span>
<span class="item">item2</span>
<span class="item">item3</span>
</div>
</body>
</html>运行实例 »
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例



实例
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>弹性元素的基准尺寸</title>
<!-- <link rel="stylesheet" href="css/style3.css">-->
<style>
/*@import "public.css";*/
.con {
width: 400px;
}
/*在未设置弹性元素宽度时 以内容宽度显示*/
.demo1 > .item {
flex-basis: content;
}
/*设置自定义元素宽度 以该宽度显示*/
.demo2 > .item {
width: 120px;
}
/*自动状态下 浏览器工具预设值自行判断*/
.demo3 > .item {
flex-basis: auto;
}
/*元素同时存在自定义宽度与基准宽度时 以基准宽度为准*/
.demo4 > .item {
width: 200px;
flex-basis: 120px;
}
/*元素基准宽度用百分比设置*/
.demo5 > .item:first-of-type {
flex-basis: 30%;
}
.demo5 > .item:nth-of-type(2) {
flex-basis: 50%;
}
.demo5 > .item:last-of-type {
flex-basis: 20%;
}
</style>
<style>
/*弹性容器通用样式*/
.con {
border: 2px dashed orangered;
background: #f9906f;
margin: 10px;
}
/*弹性元素通用样式*/
.item {
box-sizing: border-box;
border: 1px solid red;
background: #CCFFFF;
padding: 18px;
}
/*块级弹性容器*/
.flex {
display: flex;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>flex-basis: 设置弹性元素基准尺寸</h1>
<hr>
<h3>在未设置弹性元素宽度时 以内容宽度显示</h3>
<div class="con flex demo1">
<span class="item">item1</span>
<span class="item">item2</span>
<span class="item">item3</span>
</div>
<hr>
<h3>设置自定义元素宽度 以该宽度显示</h3>
<div class="con flex demo2">
<span class="item">item1</span>
<span class="item">item2</span>
<span class="item">item3</span>
</div>
<hr>
<h3>自动状态下 浏览器工具预设值自行判断</h3>
<div class="con flex demo3">
<span class="item">item1</span>
<span class="item">item2</span>
<span class="item">item3</span>
</div>
<hr>
<h3>元素同时存在自定义宽度与基准宽度时 以基准宽度为准</h3>
<div class="con flex demo4">
<span class="item">item1</span>
<span class="item">item2</span>
<span class="item">item3</span>
</div>
<hr>
<h3>元素基准宽度用百分百设置</h3>
<div class="con flex demo5">
<span class="item">item1</span>
<span class="item">item2</span>
<span class="item">item3</span>
</div>
</body>
</html>运行实例 »
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例



实例
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>简化弹性元素</title>
<!-- <link rel="stylesheet" href="css/style4.css">-->
<style>
/*@import "public.css";*/
.con {
width: 400px;
}
/*flex:增长因子0 缩减因子1 宽度基数*/
/*根据宽度计算 允许缩减适应容器*/
.demo1 > .item {
width: 120px;
height: 50px;
/*flex:0 1 auto;*/
/*默认状态*/
flex:initial;
}
/*根据宽度计算 元素自适应容器*/
.demo2 > .item {
width: 120px;
height: 50px;
/*flex:1 1 auto;*/
flex: auto;
}
/*原始大小呈现*/
.demo3 > .item {
width: 120px;
height: 50px;
/*flex:0 0 auto;*/
flex:none;
}
/*只表示增长因子 其他默认*/
.demo4 > .item {
width: 120px;
height: 50px;
/*flex: 1 1 auto;*/
flex:1;
}
</style>
<style>
/*弹性容器通用样式*/
.con {
border: 2px dashed orangered;
background: #f9906f;
margin: 10px;
}
/*弹性元素通用样式*/
.item {
box-sizing: border-box;
border: 1px solid red;
background: #CCFFFF;
padding: 18px;
}
/*块级弹性容器*/
.flex {
display: flex;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>简化弹性元素的基本设置</h1>
<hr>
<h3>根据宽度计算 允许缩减适应容器</h3>
<div class="con flex demo1">
<span class="item">item1</span>
<span class="item">item2</span>
<span class="item">item3</span>
</div>
<hr>
<h3>根据宽度计算 元素自适应容器</h3>
<div class="con flex demo2">
<span class="item">item1</span>
<span class="item">item2</span>
<span class="item">item3</span>
</div>
<hr>
<h3>原始大小呈现</h3>
<div class="con flex demo3">
<span class="item">item1</span>
<span class="item">item2</span>
<span class="item">item3</span>
</div>
<hr>
<h3>只表示增长因子 其他默认</h3>
<div class="con flex demo4">
<span class="item">item1</span>
<span class="item">item2</span>
<span class="item">item3</span>
</div>
</body>
</html运行实例 »
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例


2. 将flex属性的用法, 手抄, 建议二遍以上

3. 自学:align-self, order的用法
align-self:控制弹性元素单独在侧轴的位置 align-self:auto 默认 align-self:flex-start顶部显示 align-self:flex-end结尾显示
实例
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<!-- <link rel="stylesheet" href="css/style5.css">-->
<style>
body * {
display: flex;
}
.con {
border: 2px solid #f9906f;
width: 400px;
height: 200px;
}
.left {
background: #0099CC;
width: 100px;
height: 50px;
}
.self {
background: #b25d25;
width: 100px;
height: 50px;
align-self: flex-end;
}
.right {
background: #333333;
width: 100px;
height: 50px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="con">
<div class="left"></div>
<div class="self"></div>
<div class="right"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>运行实例 »
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
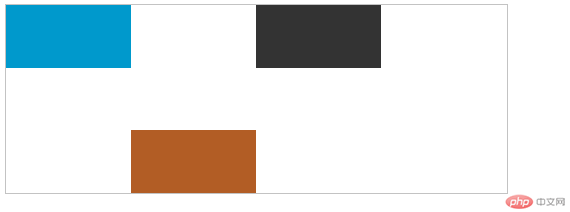
order:设置元素在弹性盒子的显示位置顺序 order:2;
实例
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<!-- <link rel="stylesheet" href="css/style5.css">-->
<style>
body * {
display: flex;
}
.con {
width: 400px;
height: 150px;
border: 1px solid #c3c3c3;
display: flex;
}
.left {
order: 2;
background: #0099CC;
width: 100px;
height: 50px;
}
.self {
order: 3;
background: #b25d25;
width: 100px;
height: 50px;
align-self: flex-end;
}
.right {
order: 1;
background: #333333;
width: 100px;
height: 50px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="con">
<div class="left"></div>
<div class="self"></div>
<div class="right"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>运行实例 »
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
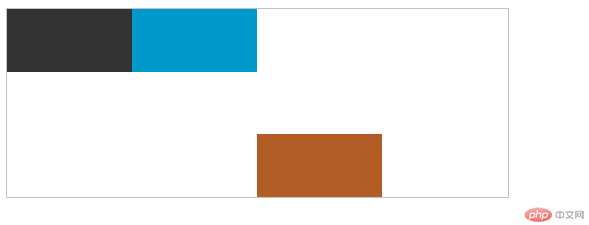
4. 试着将之前的一些案例用flex布局改定, 例如圣杯布局
实例
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>圣杯布局</title>
<!-- <link rel="stylesheet" href="css/style6.css">-->
<style>
header, footer {
height: 60px;
background-color: #d9edf7;
text-align: center;
}
main {
display: flex;
border: 2px solid red;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
main > article {
flex: 1;
background: #333333;
min-height: 600px;
order: 2;
}
main >aside:first-of-type {
float: left;
flex: 0 1 200px;
background: #b25d25;
order: 1;
}
main >aside:last-of-type {
float: left;
flex: 0 1 200px;
background: #f9906f;
order: 3;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<header>头部</header>
<main>
<article>内容</article>
<aside>左侧</aside>
<aside>右侧</aside>
</main>
<footer>底部</footer>
</body>
</html>运行实例 »
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例


