弹性盒子是 CSS3 的一种新的布局模式。CSS3 弹性盒( Flexible Box 或 flexbox),是一种当页面需要适应不同的屏幕大小以及设备类型时确保元素拥有恰当的行为的布局方式。引入弹性盒布局模型的目的是提供一种更加有效的方式来对一个容器中的子元素进行排列、对齐和分配空白空间。
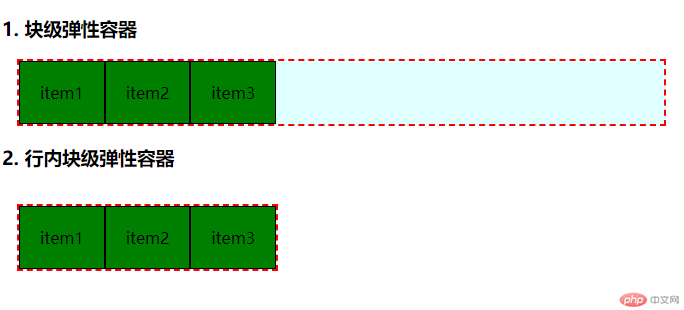
1. 弹性容器
任何元素,都可以通过添加flex属性转为弹性盒子,这个弹性盒子, 就是弹性容器(Flex Container)。
弹性容器为分二种:display: flex: 块级弹性容器;display: inline-flex: 行内块级弹性容器
弹性元素:弹性容器的子元素, 会自动成为弹性元素;弹性元素(Flex item)必须是弹性容器的直接子元素;任何类型的元素,只要转为弹性元素, 都转为块级元素
实例
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>弹性容器的两种类型</title>
<style>
/*弹性容器的通用样式*/
.container {
border: 2px dashed red;
margin: 15px;
background-color: lightcyan;
}
/*弹性元素的通用样式*/
.item {
box-sizing: border-box;
border: 1px solid;
padding: 20px;
background-color: green;
}
/*块级弹性容器*/
.flex {
display: flex;
}
/*行内/内联弹性盒子*/
.inline-flex {
display: inline-flex;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h3>1. 块级弹性容器</h3>
<div class="container flex">
<span class="item">item1</span>
<span class="item">item2</span>
<span class="item">item3</span>
</div>
<h3>2. 行内块级弹性容器</h3>
<div class="container inline-flex">
<span class="item">item1</span>
<span class="item">item2</span>
<span class="item">item3</span>
</div>
</body>
</html>运行实例 »
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例

2. 弹性容器做导航
实例
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>弹性盒子做导航</title>
<style>
/*链接样式重置*/
a {
padding: 5px 10px;
margin: 0 5px;
/*去掉下划线*/
text-decoration-line: none;
background-color: lightseagreen;
color: black;
/*添加圆角边框*/
border-radius: 5px 5px 0 0;
/*添加阴影*/
box-shadow: 2px 0 1px lightslategrey;
}
/*:hover 选择器用于选择鼠标指针浮动在上面的元素*/
/*:focus 选择器用于选取获得焦点的元素*/
/*:active 选择器用于选择活动链接*/
a:hover, a:focus, a:active {
background-color: orangered;
color: white;
}
nav {
display: flex;
border-bottom: 1px solid gray;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<nav>
<a href="">首页</a>
<a href="">教学视频</a>
<a href="">社区问答</a>
<a href="">软件下载</a>
<a href="">联系我们</a>
</nav>
</body>
</html>运行实例 »
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例


3. 定义弹性容器的主轴方向:弹性元素在主轴上的排列方向
实例
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>定义弹性容器的主轴方向:弹性元素的主轴上的排列方向</title>
<style>
/*弹性容器的通用样式*/
.container {
border: 2px dashed red;
margin: 15px;
background-color: #cdc;
}
/*弹性元素的通用样式*/
.item {
box-sizing: border-box;
border: 1px solid;
padding: 20px;
background-color: green;
}
/*块级弹性容器*/
.flex {
display: flex;
}
/*弹性元素在主轴上排列方向*/
.row {
/*默认从左向右,水平排列*/
flex-direction: row;
}
.row-reverse {
/*从右向左,水平排列*/
flex-direction: row-reverse;
}
.column {
/*从上向下,垂直排列*/
flex-direction: column;
}
.column-reverse {
/*从下向上,垂直排列*/
flex-direction: column-reverse;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h3>1. row:默认从左向右,水平排列</h3>
<div class="container flex row">
<span class="item">item1</span>
<span class="item">item2</span>
<span class="item">item3</span>
</div>
<h3>2. row-reverse:从右向左,水平排列</h3>
<div class="container flex row-reverse">
<span class="item">item1</span>
<span class="item">item2</span>
<span class="item">item3</span>
</div>
<h3>3. column:从上向下,垂直排列</h3>
<div class="container flex column">
<span class="item">item1</span>
<span class="item">item2</span>
<span class="item">item3</span>
</div>
<h3>4. column:从下向上,垂直排列</h3>
<div class="container flex column-reverse">
<span class="item">item1</span>
<span class="item">item2</span>
<span class="item">item3</span>
</div>
</body>
</html>运行实例 »
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例


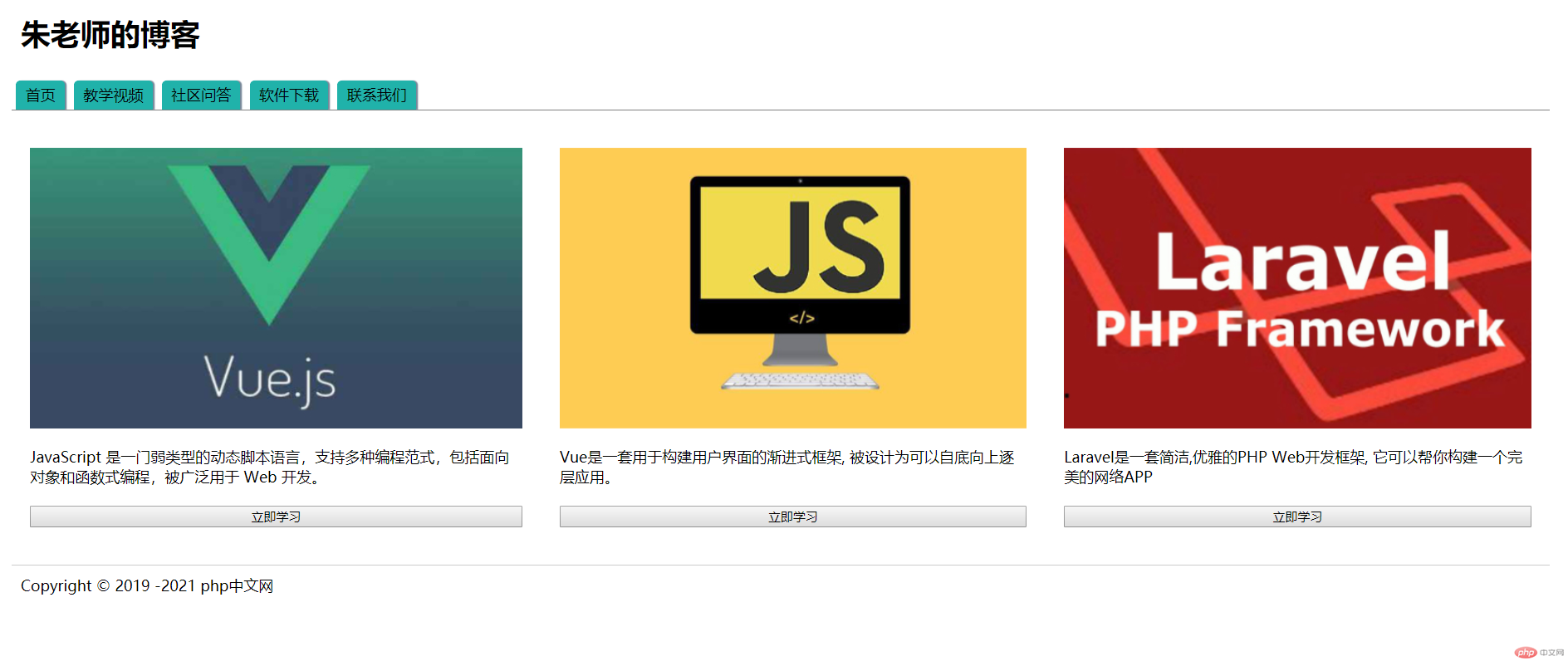
4. 制作简单网站首页
实例
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>制作简单网站首页</title>
<style>
* {
/*参考轮廓线,不占据页面空间*/
/*outline: 1px solid #ccc;*/
margin: 10px;
/*padding: 10px;*/
}
/*链接样式重置*/
a {
padding: 5px 10px;
margin: 0 5px;
/*去掉下划线*/
text-decoration-line: none;
background-color: lightseagreen;
color: black;
/*添加圆角边框*/
border-radius: 5px 5px 0 0;
/*添加阴影*/
box-shadow: 2px 0 1px lightslategrey;
}
/*:hover 选择器用于选择鼠标指针浮动在上面的元素*/
/*:focus 选择器用于选取获得焦点的元素*/
/*:active 选择器用于选择活动链接*/
a:hover, a:focus, a:active {
background-color: orangered;
color: white;
}
nav {
display: flex;
border-bottom: 1px solid gray;
}
/*将页面中主要布局元素全部转为弹性容器*/
body, nav, main, article {
display: flex;
}
/*设置全局, 内容区主轴垂直, 元素沿主轴排列*/
body, article {
flex-direction: column;
}
/*页脚添加上边框*/
footer {
border-top: 1px solid #ccc;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<!--页眉-->
<header>
<h1>朱老师的博客</h1>
</header>
<!--导航-->
<nav>
<a href="">首页</a>
<a href="">教学视频</a>
<a href="">社区问答</a>
<a href="">软件下载</a>
<a href="">联系我们</a>
</nav>
<!--主体-->
<main>
<article>
<img src="static/images/1.jpg" alt="">
<p>JavaScript 是一门弱类型的动态脚本语言,支持多种编程范式,包括面向对象和函数式编程,被广泛用于 Web 开发。</p>
<button>立即学习</button>
</article>
<article>
<img src="static/images/2.jpg" alt="">
<p>Vue是一套用于构建用户界面的渐进式框架, 被设计为可以自底向上逐层应用。</p>
<button>立即学习</button>
</article>
<article>
<img src="static/images/3.jpg" alt="">
<p>Laravel是一套简洁,优雅的PHP Web开发框架, 它可以帮你构建一个完美的网络APP</p>
<button>立即学习</button>
</article>
</main>
<!--页脚-->
<footer>
<p>Copyright © 2019 -2021 php中文网</p>
</footer>
</body>
</html>运行实例 »
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例

5. 弹性元素溢出与创建多行容器
a. 主轴为水平方向时
实例
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>弹性元素溢出与创建多行容器</title>
<style>
/*弹性容器的通用样式*/
.container {
border: 2px dashed red;
margin: 15px;
background-color: #cdc;
}
/*弹性元素的通用样式*/
.item {
box-sizing: border-box;
border: 1px solid;
padding: 20px;
background-color: green;
}
/*块级弹性容器*/
.flex {
display: flex;
}
.container {
width: 500px;
}
/*不换行*/
.nowrap {
flex-direction: row;
flex-wrap: nowrap;
}
/*换行*/
.wrap {
flex-direction: row;
flex-wrap: wrap;
}
/*换行后,弹性元素在垂直方向反向排列*/
.wrap-reverse {
flex-direction: row;
flex-wrap: wrap-reverse;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>以主轴水平方向为例演示:</h1>
<!--默认: 弹性元素不会在主轴上换行,不会自动调整大小, 当主轴空间不足时, 会从边界溢出-->
<h3>1. nowrap:默认不换行,元素自动缩小适应容器</h3>
<div class="container flex row nowrap">
<span class="item">item1</span>
<span class="item">item2</span>
<span class="item">item3</span>
<span class="item">item4</span>
<span class="item">item5</span>
<span class="item">item6</span>
<span class="item">item7</span>
<span class="item">item8</span>
<span class="item">item9</span>
<span class="item">item10</span>
<span class="item">item11</span>
</div>
<h3>2. wrap: 换行,元素超出容器边界后换到下一行继续显示</h3>
<div class="container flex row wrap">
<span class="item">item1</span>
<span class="item">item2</span>
<span class="item">item3</span>
<span class="item">item4</span>
<span class="item">item5</span>
<span class="item">item6</span>
<span class="item">item7</span>
<span class="item">item8</span>
<span class="item">item9</span>
<span class="item">item10</span>
<span class="item">item11</span>
</div>
<h3>3. wrap-reverse: 换行后,弹性元素在垂直方向反向排列</h3>
<div class="container flex row wrap-reverse">
<span class="item">item1</span>
<span class="item">item2</span>
<span class="item">item3</span>
<span class="item">item4</span>
<span class="item">item5</span>
<span class="item">item6</span>
<span class="item">item7</span>
<span class="item">item8</span>
<span class="item">item9</span>
<span class="item">item10</span>
<span class="item">item11</span>
</div>
</body>
</html>运行实例 »
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例

b. 主轴为垂直方向时
弹性元素不换行时
.nowrap {
flex-direction: column;
flex-wrap: nowrap;
}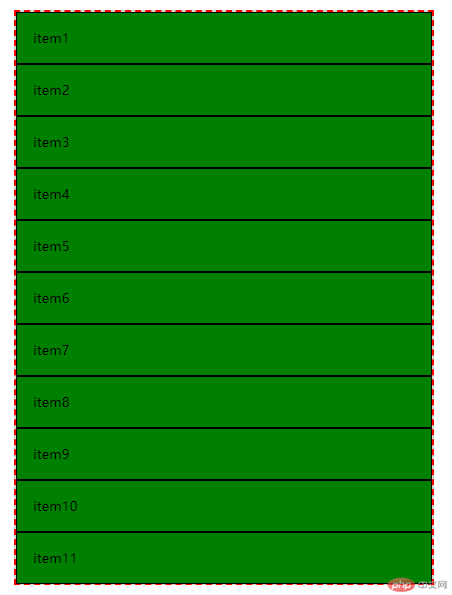
通过测试结果我们可以发现,弹性元素沿着主轴的方向从上到下依次排列,而且水平方向充满容器,不会出现溢出。
弹性元素换行时
.wrap {
flex-direction: column;
flex-wrap: wrap;
}
通过测试结果我们可以发现,弹性元素沿着主轴的方向从上到下依次排列,而且水平方向充满容器,不会出现溢出,更不会出现换行。
弹性元素换行后,弹性元素在垂直方向反向排列,
.wrap-reverse {
flex-direction: column-reverse;
flex-wrap: wrap-reverse;
}
通过测试结果我们可以发现,弹性元素从下到上依次排列,而且水平方向充满容器,不会出现溢出,更不会出现换行。

6. 弹性元素流体布局的简化
格式:flex-flow: 属性值1 属性值2;
属性值1代表flex-direction,属性值2代表flex-wrap;
A. 主轴为水平方向时
a. 不换行
.nowrap {
/*也是默认值*/
flex-flow: row nowrap;
} b. 换行
.wrap {
flex-flow: row wrap;
} c. 换行后,弹性元素在垂直方向反转排列
.wrap-reverse {
flex-flow: row wrap-reverse;
} B. 主轴为垂直方向时
a. 不换行
.nowrap {
/*也是默认值*/
flex-flow: column nowrap;
} b. 换行
.wrap {
flex-flow: column wrap;
}c. 换行后,弹性元素在垂直方向反转排列
.wrap-reverse {
flex-flow: column wrap-reverse;
}
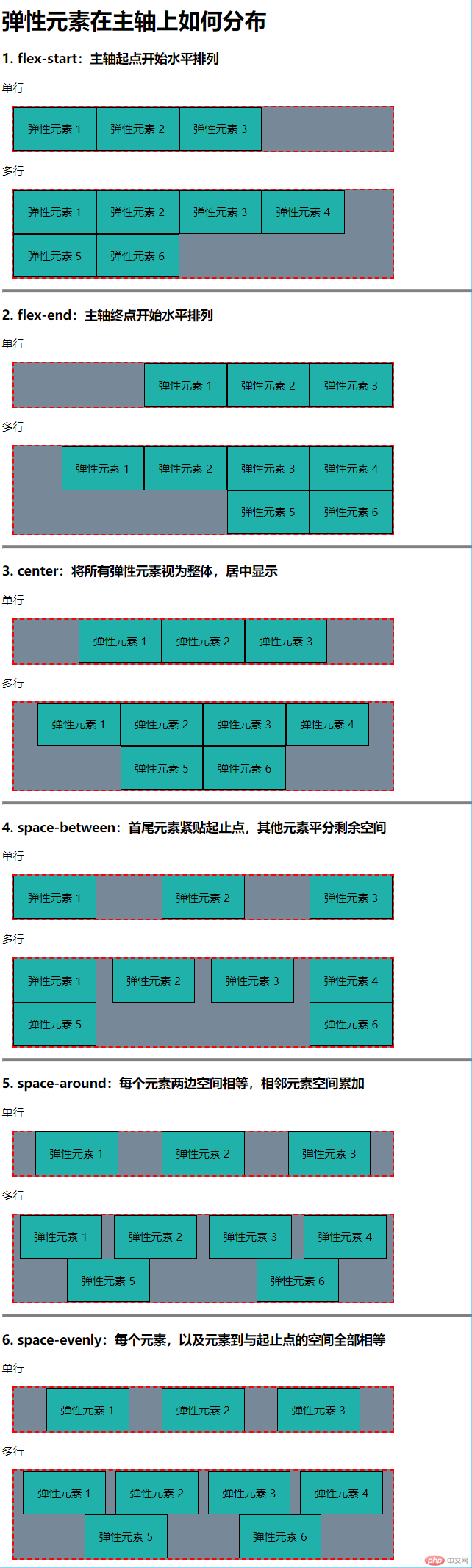
7. 弹性元素在主轴上如何分布
实例
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>弹性元素在主轴上如何分布</title>
<style>
/*弹性容器的通用样式*/
.container {
border: 2px dashed red;
margin: 15px;
background-color: lightslategrey;
}
/*弹性元素的通用样式*/
.item {
box-sizing: border-box;
border: 1px solid;
padding: 20px;
background-color: lightseagreen;
}
/*块级弹性容器*/
.flex {
display: flex;
}
.container {
width: 550px;
}
/*允许换行*/
.wrap {
flex-wrap: wrap;
}
/*默认值:弹性元素紧贴主轴起点开始排列*/
.flex-start {
justify-content: flex-start;
}
/*弹性元素紧贴主轴终点开始排列*/
.flex-end {
justify-content: flex-end;
}
/*将所有弹性元素视为整体,居中显示*/
.center {
justify-content: center;
}
/*首尾元素紧贴起止点,其他元素平分剩余空间*/
.space-between {
justify-content: space-between;
}
/*每个元素两边空间相等,相邻元素空间累加*/
/*首尾元素与容器边界的空间,只有其它元素之间空间的一半*/
.space-around {
justify-content: space-around;
}
/*每个元素,以及元素到与起止点的空间全部相等*/
.space-evenly {
justify-content: space-evenly;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>弹性元素在主轴上如何分布</h1>
<h3>1. flex-start:主轴起点开始水平排列</h3>
<p>单行</p>
<div class="container flex flex-start">
<span class="item">弹性元素 1</span>
<span class="item">弹性元素 2</span>
<span class="item">弹性元素 3</span>
</div>
<p>多行</p>
<div class="container wrap flex flex-start">
<span class="item">弹性元素 1</span>
<span class="item">弹性元素 2</span>
<span class="item">弹性元素 3</span>
<span class="item">弹性元素 4</span>
<span class="item">弹性元素 5</span>
<span class="item">弹性元素 6</span>
</div>
<hr style="height: 3px;background-color: grey;">
<h3>2. flex-end:主轴终点开始水平排列</h3>
<p>单行</p>
<div class="container flex flex-end">
<span class="item">弹性元素 1</span>
<span class="item">弹性元素 2</span>
<span class="item">弹性元素 3</span>
</div>
<p>多行</p>
<div class="container wrap flex flex-end">
<span class="item">弹性元素 1</span>
<span class="item">弹性元素 2</span>
<span class="item">弹性元素 3</span>
<span class="item">弹性元素 4</span>
<span class="item">弹性元素 5</span>
<span class="item">弹性元素 6</span>
</div>
<hr style="height: 3px;background-color: grey;">
<h3>3. center:将所有弹性元素视为整体,居中显示</h3>
<p>单行</p>
<div class="container flex center">
<span class="item">弹性元素 1</span>
<span class="item">弹性元素 2</span>
<span class="item">弹性元素 3</span>
</div>
<p>多行</p>
<div class="container wrap flex center">
<span class="item">弹性元素 1</span>
<span class="item">弹性元素 2</span>
<span class="item">弹性元素 3</span>
<span class="item">弹性元素 4</span>
<span class="item">弹性元素 5</span>
<span class="item">弹性元素 6</span>
</div>
<hr style="height: 3px;background-color: grey;">
<h3>4. space-between:首尾元素紧贴起止点,其他元素平分剩余空间</h3>
<p>单行</p>
<div class="container flex space-between">
<span class="item">弹性元素 1</span>
<span class="item">弹性元素 2</span>
<span class="item">弹性元素 3</span>
</div>
<p>多行</p>
<div class="container wrap flex space-between">
<span class="item">弹性元素 1</span>
<span class="item">弹性元素 2</span>
<span class="item">弹性元素 3</span>
<span class="item">弹性元素 4</span>
<span class="item">弹性元素 5</span>
<span class="item">弹性元素 6</span>
</div>
<hr style="height: 3px;background-color: grey;">
<h3>5. space-around:每个元素两边空间相等,相邻元素空间累加</h3>
<p>单行</p>
<div class="container flex space-around">
<span class="item">弹性元素 1</span>
<span class="item">弹性元素 2</span>
<span class="item">弹性元素 3</span>
</div>
<p>多行</p>
<div class="container wrap flex space-around">
<span class="item">弹性元素 1</span>
<span class="item">弹性元素 2</span>
<span class="item">弹性元素 3</span>
<span class="item">弹性元素 4</span>
<span class="item">弹性元素 5</span>
<span class="item">弹性元素 6</span>
</div>
<hr style="height: 3px;background-color: grey;">
<h3>6. space-evenly:每个元素,以及元素到与起止点的空间全部相等</h3>
<p>单行</p>
<div class="container flex space-evenly">
<span class="item">弹性元素 1</span>
<span class="item">弹性元素 2</span>
<span class="item">弹性元素 3</span>
</div>
<p>多行</p>
<div class="container wrap flex space-evenly">
<span class="item">弹性元素 1</span>
<span class="item">弹性元素 2</span>
<span class="item">弹性元素 3</span>
<span class="item">弹性元素 4</span>
<span class="item">弹性元素 5</span>
<span class="item">弹性元素 6</span>
</div>
</body>
</html>运行实例 »
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例

8. 使用弹性元素主轴对齐来改写导航
从主轴起点开始
nav {
justify-content: flex-start;
}
从主轴终点开始
nav {
justify-content: flex-end;
}
居中显示
nav {
justify-content: center;
}

9. 弹性元素在垂直方向上的对齐方式
实例
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>弹性元素在垂直方向(交叉轴)上的对齐方式</title>
<style>
/*弹性容器的通用样式*/
.container {
border: 2px dashed red;
margin: 15px;
background-color: lightslategrey;
}
/*弹性元素的通用样式*/
.item {
box-sizing: border-box;
border: 1px solid;
padding: 20px;
background-color: lightseagreen;
}
/*块级弹性容器*/
.flex {
display: flex;
}
.container {
width: 500px;
height: 300px;
}
/*允许换行*/
.wrap {
flex-wrap: wrap;
}
/************ 单行容器 ************/
/*1. 默认值:单行自动拉伸*/
.stretch {
align-items: stretch;
}
/*2. 单行起点对齐*/
.flex-start {
align-items: flex-start;
}
/*3. 单行终点对齐*/
.flex-end {
align-items: flex-end;
}
/*4. 单行居中对齐*/
.center {
align-items: center;
}
/************ 多行容器 ************/
/*1. 默认值:多行自动拉伸*/
.wrap-stretch {
/*每一行的对齐方式*/
align-content: stretch;
}
/*2. 多行起点对齐*/
.wrap-flex-start {
align-content: flex-start;
}
/*3. 多行终点对齐*/
.wrap-flex-end {
align-content: flex-end;
}
/* 4. 多行居中对齐 */
.wrap-center {
align-content: center;
}
/*5. 垂直方向首尾行紧贴起止点,其它行平分剩余空间*/
.wrap-space-between {
align-content: space-between;
}
/*6. 每个元素二边空间相等,相邻元素空间累加*/
.wrap-space-around {
align-content: space-around;
}
/*7. 每个元素, 以及元素到与起止点的空间全部相等*/
.wrap-space-evenly {
align-content: space-evenly;
}
/*实战: 元素的水平垂直全部平均对齐*/
.all-align {
align-content: space-around;
justify-content: space-around;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>弹性元素在垂直轴上的分布方式</h1>
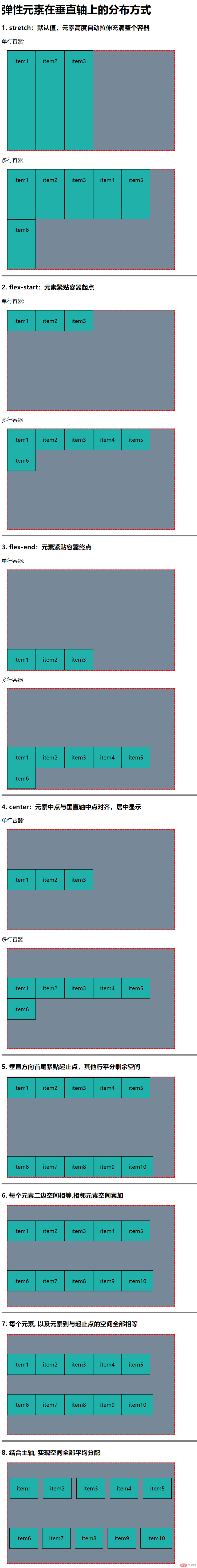
<h3>1. stretch:默认值,元素高度自动拉伸充满整个容器</h3>
<p>单行容器:</p>
<div class="container flex stretch">
<span class="item">item1</span>
<span class="item">item2</span>
<span class="item">item3</span>
</div>
<p>多行容器</p>
<div class="container flex wrap wrap-stretch">
<span class="item">item1</span>
<span class="item">item2</span>
<span class="item">item3</span>
<span class="item">item4</span>
<span class="item">item5</span>
<span class="item">item6</span>
</div>
<hr style="height: 3px; background:grey;">
<h3>2. flex-start:元素紧贴容器起点</h3>
<p>单行容器:</p>
<div class="container flex flex-start">
<span class="item">item1</span>
<span class="item">item2</span>
<span class="item">item3</span>
</div>
<p>多行容器</p>
<div class="container flex wrap wrap-flex-start">
<span class="item">item1</span>
<span class="item">item2</span>
<span class="item">item3</span>
<span class="item">item4</span>
<span class="item">item5</span>
<span class="item">item6</span>
</div>
<hr style="height: 3px; background:grey;">
<h3>3. flex-end:元素紧贴容器终点</h3>
<p>单行容器:</p>
<div class="container flex flex-end">
<span class="item">item1</span>
<span class="item">item2</span>
<span class="item">item3</span>
</div>
<p>多行容器</p>
<div class="container flex wrap wrap-flex-end">
<span class="item">item1</span>
<span class="item">item2</span>
<span class="item">item3</span>
<span class="item">item4</span>
<span class="item">item5</span>
<span class="item">item6</span>
</div>
<hr style="height: 3px; background:grey;">
<h3>4. center:元素中点与垂直轴中点对齐,居中显示</h3>
<p>单行容器:</p>
<div class="container flex center">
<span class="item">item1</span>
<span class="item">item2</span>
<span class="item">item3</span>
</div>
<p>多行容器</p>
<div class="container flex wrap wrap-center">
<span class="item">item1</span>
<span class="item">item2</span>
<span class="item">item3</span>
<span class="item">item4</span>
<span class="item">item5</span>
<span class="item">item6</span>
</div>
<hr style="height: 3px; background:grey;">
<h3>5. 垂直方向首尾紧贴起止点,其他行平分剩余空间</h3>
<div class="container flex wrap wrap-space-between">
<span class="item">item1</span>
<span class="item">item2</span>
<span class="item">item3</span>
<span class="item">item4</span>
<span class="item">item5</span>
<span class="item">item6</span>
<span class="item">item7</span>
<span class="item">item8</span>
<span class="item">item9</span>
<span class="item">item10</span>
</div>
<hr style="height: 3px; background:grey;">
<h3>6. 每个元素二边空间相等,相邻元素空间累加</h3>
<div class="container flex wrap wrap-space-around">
<span class="item">item1</span>
<span class="item">item2</span>
<span class="item">item3</span>
<span class="item">item4</span>
<span class="item">item5</span>
<span class="item">item6</span>
<span class="item">item7</span>
<span class="item">item8</span>
<span class="item">item9</span>
<span class="item">item10</span>
</div>
<hr style="height: 3px; background:grey;">
<h3>7. 每个元素, 以及元素到与起止点的空间全部相等</h3>
<div class="container flex wrap wrap-space-evenly">
<span class="item">item1</span>
<span class="item">item2</span>
<span class="item">item3</span>
<span class="item">item4</span>
<span class="item">item5</span>
<span class="item">item6</span>
<span class="item">item7</span>
<span class="item">item8</span>
<span class="item">item9</span>
<span class="item">item10</span>
</div>
<hr style="height: 3px; background:grey;">
<h3>8. 结合主轴, 实现空间全部平均分配</h3>
<div class="container flex wrap wrap-space-evenly all-align">
<span class="item">item1</span>
<span class="item">item2</span>
<span class="item">item3</span>
<span class="item">item4</span>
<span class="item">item5</span>
<span class="item">item6</span>
<span class="item">item7</span>
<span class="item">item8</span>
<span class="item">item9</span>
<span class="item">item10</span>
</div>
</body>
</html>运行实例 »
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例

10. 总结
通过对弹性盒子的学习,掌握了弹性容器常用属性,发现弹性布局比其他的布局方式代码要精练很多,而且弹性布局更强大。