一、默写盒模型的全部属性,并准确说出他们的应用场景
content: 盒模型的内容
margin: 控制盒子的外边距,与其他盒子同级元素的距离
padding: 控制盒子的内边距,可以控制content距离盒子边框的距离
border: 用于设置盒子的边框样式
二、box-sizing解决了什么问题, 不用它应该如何处理
box-sizing 属性允许您以特定的方式定义匹配某个区域的特定元素。
语法:box-sizing : content-box || border-box || inherit
content-box 是默认值。如果你设置一个元素的宽为100px,那么这个元素的内容区会有100px宽,并且任何边框和内边距的宽度都会被增加到最后绘制出来的元素宽度中。
border-box 告诉浏览器去理解你设置的边框和内边距的值是包含在width内的。也就是说,如果你将一个元素的width设为100px,那么这100px会包含其它的border和padding,内容区的实际宽度会是width减去border + padding的计算值。大多数情况下这使得我们更容易的去设定一个元素的宽高。
border-box width 和 height 属性包括内容,内边距和边框,但不包括外边距。
inherit:规定应从父元素继承 box-sizing 属性的值。即父元素是什么属性的值,他自己就是什么属的性值。
如果不使用box-sizing:border-box,可以把padding和border的值从宽高中相减。
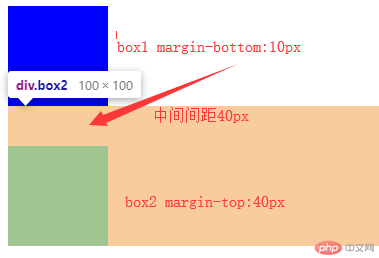
三、盒子外边距之的合并是怎么回事,并实例演示
当上下相邻的两个块元素相遇时,如果上面的元素有下外边距margin-bottom,下面的元素有上外边距margin-top,则他们之间的垂直间距不是margin-bottom与margin-top之和,而是两者中的较大者。这种现象被称为相邻块元素垂直外边距的合并(也称外边距塌陷)。
实例
<!doctype html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport"
content="width=device-width, user-scalable=no, initial-scale=1.0, maximum-scale=1.0, minimum-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>盒子外边距之的合并</title>
<style>
.box1{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background: blue;
margin-bottom: 10px;
}
.box2{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background: yellow;
margin-top: 40px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box1"></div>
<div class="box2"></div>
</body>
</html>运行实例 »
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
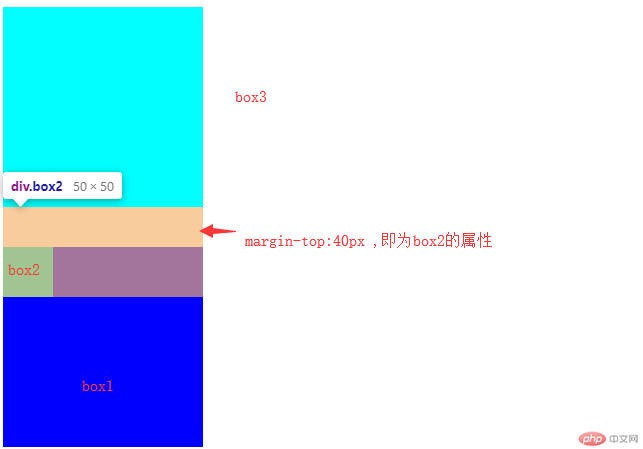
四、嵌套盒子之间内边距与外边距的表现有何不同, 如何处理
当嵌套的两个块元素,给子盒子加向上的外边距时,父盒子会跟着掉下来,此时就是外边距塌陷
解决方案:
给父盒子加padding
2 .给父盒子加上边框
3 .给父元素加overflow:hidden 属性
当同一个效果能用padding解决就最好不用margin解决
实例
<!doctype html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport"
content="width=device-width, user-scalable=no, initial-scale=1.0, maximum-scale=1.0, minimum-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title></title>
<style>
.box1{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background: blue;
margin-bottom: 10px;
}
.box2{
width: 50px;
height: 50px;
background: yellow;
margin-top: 40px;
}
.box3{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background: aqua;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box3"></div>
<div class="box1">
<div class="box2"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>运行实例 »
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
五、实例演示: 背景颜色的线性渐变
实例
<!doctype html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport"
content="width=device-width, user-scalable=no, initial-scale=1.0, maximum-scale=1.0, minimum-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title></title>
<style>
.box1{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
/* to right 即从左向右渐变,还可以to right bottom 即从左上角向右下角渐变 */
background: linear-gradient(to right,#00FFFF,#00CED1);
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box1"></div>
</body>
</html>运行实例 »
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
六、背景图片的大小与位置的设定
实例
<!doctype html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport"
content="width=device-width, user-scalable=no, initial-scale=1.0, maximum-scale=1.0, minimum-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title></title>
<style>
.box1{
width: 300px;
height: 300px;
background: url("https://ss1.bdstatic.com/70cFvXSh_Q1YnxGkpoWK1HF6hhy/it/u=2018939532,1617516463&fm=26&gp=0.jpg") no-repeat center center;
background-size: 80% 50%;
border: 1px solid #000;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box1"></div>
</body>
</html>运行实例 »
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例


