在web前端开发中,清除浮动是一个小难题,总结了一下解决浮动的几个方式,简单粗暴,直接有效
清除子元素浮动
实例
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<style>
.box1 {
width: 300px;
border: 5px dashed red;
}
.box2 {
width: inherit;
height: 300px;
background-color: lightblue;
}
.box2 {
float: left;
}
</style>
<title>清除浮动的影响</title>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box1">
<div class="box2">子元素</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>运行实例 »
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
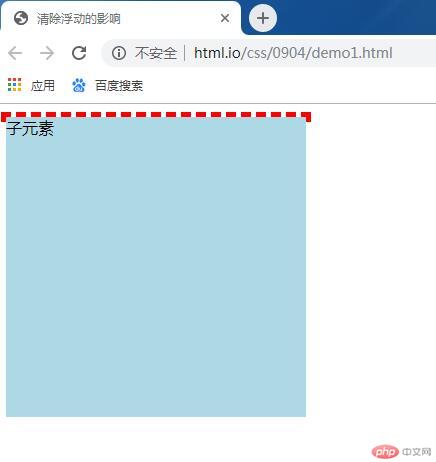
问题描述:当子元素使用了float属性时,父容器无法根据子元素高度而自适应高度,为了解决该问题,通常有以下三种做法:
1.让父元素也浮动起来
实例
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<style>
.box1 {
width: 300px;
border: 5px dashed red;
}
.box2 {
width: inherit;
height: 300px;
background-color: lightblue;
}
.box2 {
float: left;
}
.box1 {
float: left;
}
</style>
<title>清除浮动的影响</title>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box1">
<div class="box2">子元素</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>运行实例 »
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
这种方式是会让父元素也变得浮动,影响后面的布局,其实有副作用,而且如果有多个父元素的话,都要设置浮动,太繁琐。
2.比较常见的处理,在浮动元素后面加一个清楚浮动的空标签
实例
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<style>
.box1 {
width: 300px;
border: 5px dashed red;
}
.box2 {
width: inherit;
height: 300px;
background-color: lightblue;
}
.box2 {
float: left;
}
.clear {
clear: both;
}
</style>
<title>清除浮动的影响</title>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box1">
<div class="box2">子元素</div>
<div class="clear"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>运行实例 »
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
本例中clear类是为了清除浮动而设置的,理论上没有问题,但是多加了一个空标签,一定程度上破坏了语义化。
3.直接在父容器中清除浮动
实例
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<style>
.box1 {
width: 300px;
border: 5px dashed red;
}
.box2 {
width: inherit;
height: 300px;
background-color: lightblue;
}
.box2 {
float: left;
}
.box1 {
overflow: hidden;
}
</style>
<title>清除浮动的影响</title>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box1">
<div class="box2">子元素</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>运行实例 »
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
给父元素添加 overflow:hidden,这是最直接有效的方法,而且不会带来其他影响,建议采用.
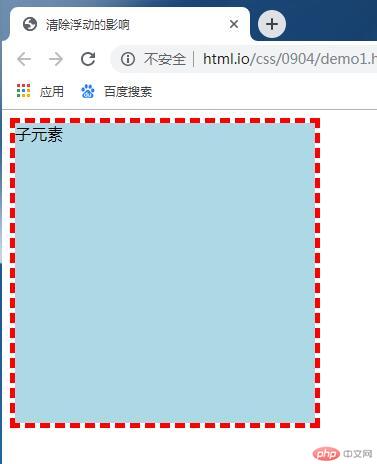
三列布局--绝对定位
实例
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<!-- <link rel="stylesheet" href="css/style7.css"> -->
<style>
.container {
width: 1000px;
margin: 0 auto;
}
.header,
.footer {
height: 60px;
background-color: lightgray;
}
.main {
background-color: lightblue;
margin: 5px auto;
}
.left {
width: 200px;
min-height: 600px;
background-color: lightcoral;
}
.cent {
min-height: 600px;
background-color: lightgreen;
}
.right {
width: 200px;
min-height: 600px;
background-color: lightpink;
}
.main {
position: relative;
}
.left {
position: absolute;
left: 0;
top: 0;
}
.right {
position: absolute;
right: 0;
top: 0;
}
.cent {
margin-left: 200px;
margin-right: 200px;
}
</style>
<title>三列布局:绝对定位</title>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<div class="header">头部</div>
<div class="main">
<div class="left">左侧</div>
<div class="cent">内容区</div>
<div class="right">右侧</div>
</div>
<div class="footer">底部</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>运行实例 »
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
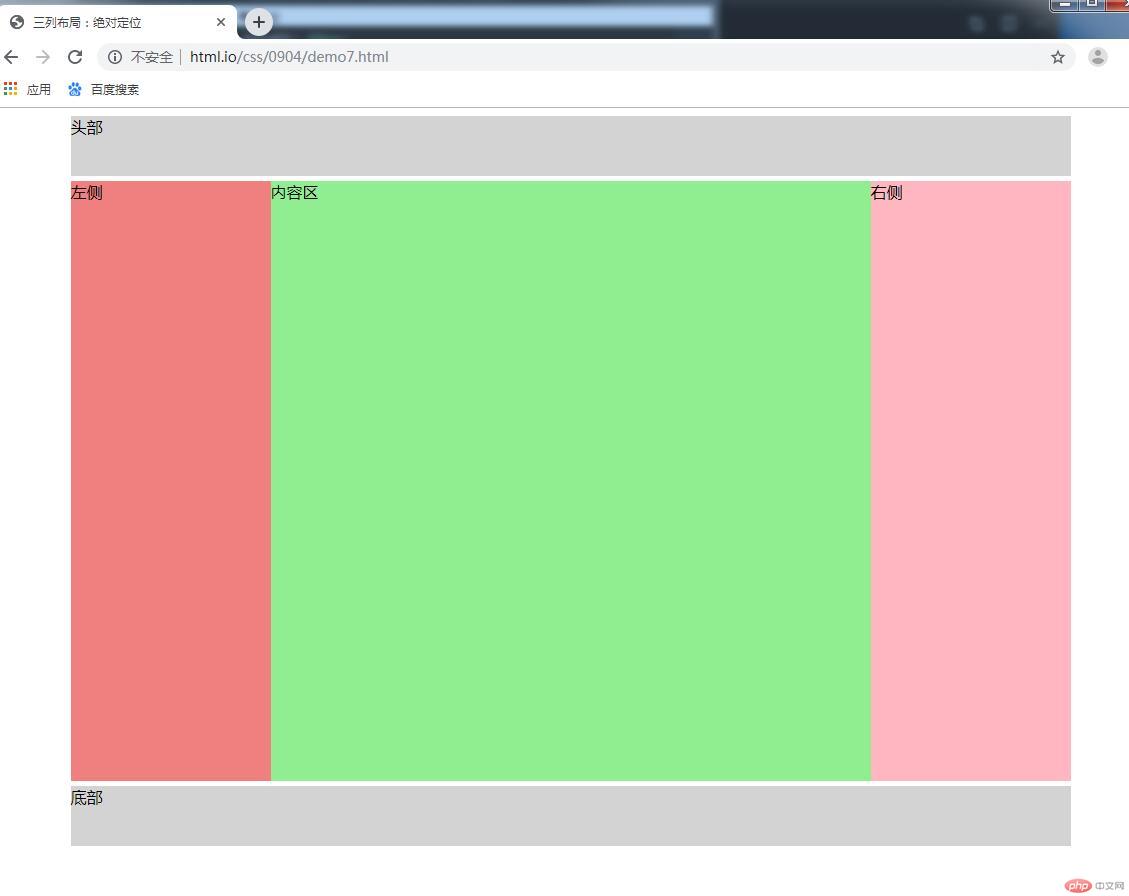
三列布局--浮动
实例
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<!-- <link rel="stylesheet" href="css/style7.css"> -->
<style>
.container {
width: 1000px;
margin: 0 auto;
}
.header,
.footer {
height: 60px;
background-color: lightgray;
}
.main {
background-color: lightblue;
margin: 5px auto;
overflow: hidden;
}
.left {
width: 200px;
min-height: 600px;
background-color: lightcoral;
}
.cent {
min-height: 600px;
background-color: lightgreen;
}
.right {
width: 200px;
min-height: 600px;
background-color: lightpink;
}
.left {
float: left;
}
.right {
float: right;
}
.cent {
float: left;
width: 600px;
}
.footer {
clear: both;
}
</style>
<title>三列布局:浮动</title>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<div class="header">头部</div>
<div class="main">
<div class="left">左侧</div>
<div class="cent">内容区</div>
<div class="right">右侧</div>
</div>
<div class="footer">底部</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>运行实例 »
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
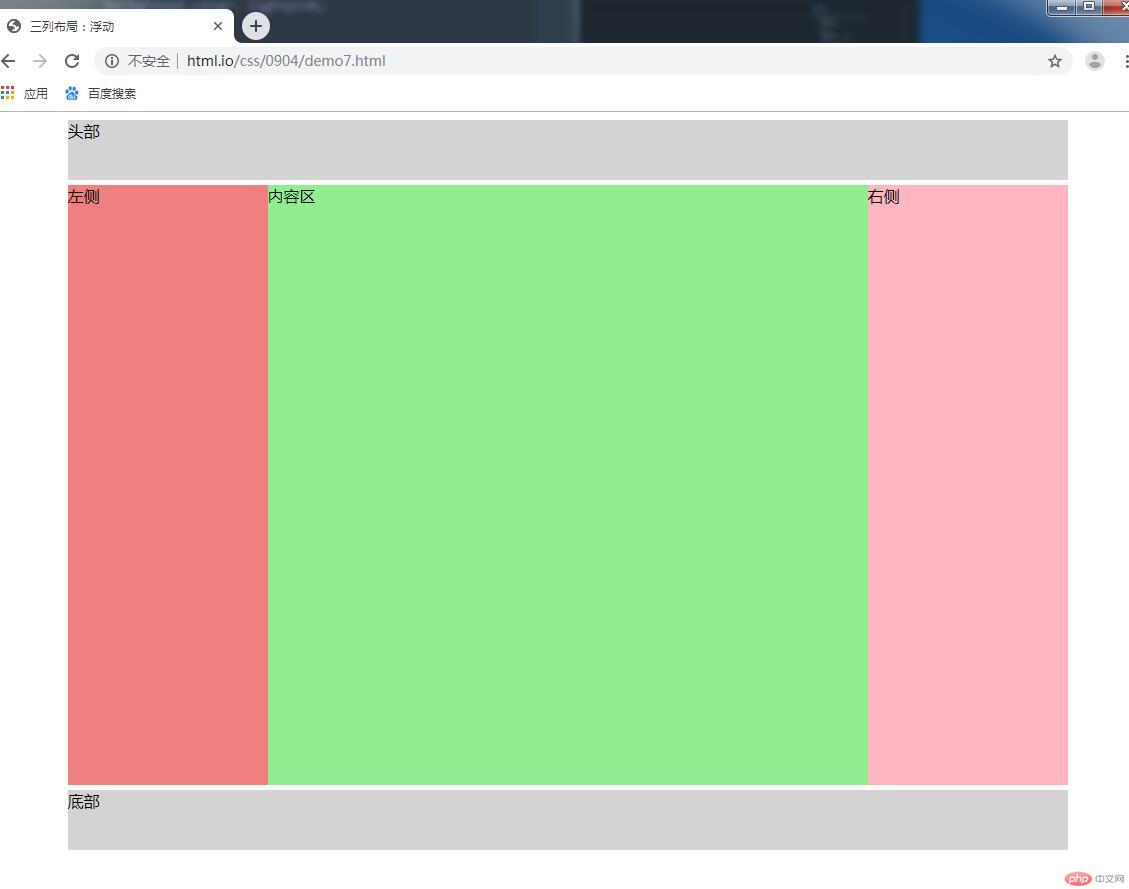
小结:浮动的大咖overflow:hidden
定位:将元素在页面重新排版
1.静态定位:static,文档流定位,流动布局
2.相对定位:relative,元素仍在文档流,只是相对它原来的位置发生偏移
3.绝对定位:absolute,元素脱离文档流,相对于离它最近的,具有定位属性的 父级元素进行定位
4.固定定位:fixed,始终相对浏览器容器进行定位,body /html

