一、相邻选择器与兄弟选择器
实例
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
<style type="text/css">
ul {
width: 500px;
height: 50px;
list-style: none;
border: dashed 1px pink;
padding: 10px;
}
li {
float: left;
width: 50px;
height: 50px;
line-height: 50px;
background-color: blue;
text-align: center;
border-radius: 50%;
}
/* 相邻选择器 */
#two+* {
background-color: green;
}
/* 兄弟选择器 */
#five~* {
background-color: red;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<ul>
<li>1</li>
<li id="two">2</li>
<li>3</li>
<li>4</li>
<li id="five">5</li>
<li>6</li>
<li>7</li>
<li>8</li>
</ul>
</body>
</html>运行实例 »
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
相邻和兄弟选择器都可以选中该元素后面的元素,不过相邻选择器只可以选择与该元素相邻的后面第一个元素,而兄弟元选择器可以选择该元素后面的所有兄弟元素。
二、:nth-child() 和 :nth-of-type()选择器
实例
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
<style type="text/css">
div :nth-child(2) {
color: red;
}
div p:nth-of-type(2) {
color: green;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<p>苹果</p>
<li>香蕉</li>
<p>橘子</p>
</div>
<div>
<p>苹果2</p>
<li>香蕉2</li>
</div>
</body>
</html>运行实例 »
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
:nth-child() 和 :nth-of-type()伪类选择器都可以选择指定位置的元素,而:nth-of-type()在指定位置的同时还限制了元素类型。
三、padding 对盒子大小的影响与解决方案
![1567600884728057.png }4$SH(1HVZI]CFV$$PJ4(K7.png](https://img.php.cn/upload/image/789/255/830/1567600884728057.png)
要实现上图图片在盒子居中效果 我们可以使用给盒子加padding属性,但是加了padding盒子就会整体变大,如下图

本身图片为200px;盒子定义的为200px;当添加50px的padding时,此时盒子大小为300*300px。
为了解决这个问题我们可以使用css3的属性box-sizing;我们设置盒子本身为300px;在设置padding为50px;此时设置盒子的box-sizing:border-box;这时盒子本身还是300px;并不会变大,此时盒子设置的widht值可以理解为content宽度+padding。如下图
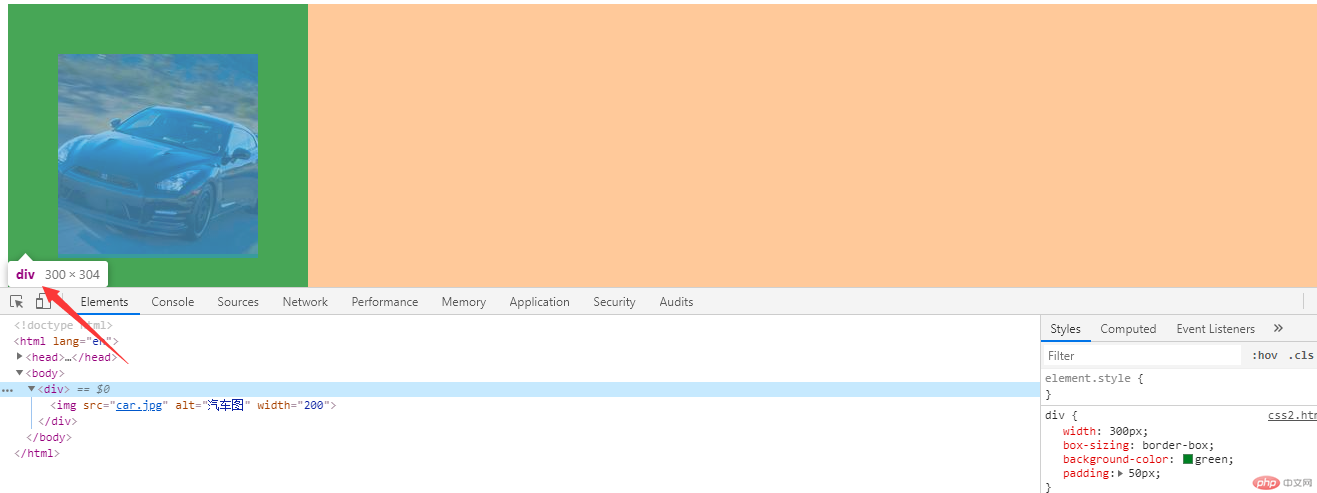
四、margin中的同级塌陷, 嵌套传递与自动挤压
margin中的同级塌陷
实例
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
<style type="text/css">
.box1 {
width: 50px;
height: 50px;
background-color: green;
margin-bottom: 50px;
}
.box2 {
width: 50px;
height: 50px;
background-color: red;
margin-top: 30px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box1">
</div>
<div class="box2">
</div>
</body>
</html>运行实例 »
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
嵌套传递
实例
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
<style type="text/css">
.box1 {
width: 150px;
height: 150px;
background-color: green;
}
.box2 {
width: 50px;
height: 50px;
background-color: red;
margin-top: 100px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box1">
<div class="box2"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>运行实例 »
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
解决嵌套传递,可以父盒子的加个对应的padding值,而子盒子的margin值去掉。
自动挤压
实例
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
<style type="text/css">
.box1 {
width: 150px;
height: 150px;
background-color: green;
margin: auto;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box1"></div>
</body>
</html>运行实例 »
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
自动挤压常用于实现将盒子水平居中的效果。
总结:
1、兄弟选择器和相邻选择器可以很方便的按需求选取一个或者多个元素。
2、:nth-child() 和 :nth-of-type()和伪类可以很方便的指定位置和指定位置同时限制元素。
3、在使用padding的时候可以加上box-sizing属性来解决盒子变大问题
4、margin中有同级塌陷(垂直方向),嵌套传递问题(父盒子上加相关属性解决),而自动挤压可以实现特殊效果(水平居中)。

