Whether it's a simple formatting mistake or a more complex syntax issue, knowing how to fix #VALUE errors in Excel is essential for anyone who wants to create error-free spreadsheets and ensure the accuracy of their data.
When working with Excel, it is common to encounter errors. One of the most frustrating errors is #VALUE, which is raised when a formula or function is unable to process data. This error can be caused by several factors including incorrect syntax, mismatched cell references, or hidden characters. In this article, we will explore the various causes of the #VALUE error and provide tips on how to fix it.
When is #VALUE error raised in Excel?
The #VALUE! error in Excel is commonly caused by the following reasons:
- Unexpected data type. If an Excel function requires a specific data type, such as a number or text, and a cell contains a different data type.
- Incorrect formula syntax. When the function's arguments are incorrect, missing or in wrong order.
- Spaces. If a formula refers to a cell that contains a space character. Visually, such cells look absolutely empty.
- Invisible characters. Sometimes, cells may contain hidden or non-printing characters that prevent a formula from calculating correctly.
- Dates formatted as text. When dates are input in the format that Excel does not understand, they are treated as text strings rather than valid dates.
- Ranges have incompatible dimensions. When formula references a few ranges that are not of the same size or shape, Excel cannot calculate the formula and throws an error.
As you see, the #VALUE error in Excel can be caused by a variety of factors. By understanding the root cause, you can more easily find the right remedy to fix it.

How to troubleshoot and fix #VALUE error in Excel
Once you identify the cause of the error, use the appropriate troubleshooting steps to resolve the issue.
Check if data type is valid
To avoid the #VALUE error in Excel, verify that the data type in the referred cell is correct. If a formula or function requires numeric data, make sure the cell contains a number and not text.
A typical example is math operations such as addition and multiplication. When one of the values that you add up or multiply is non-numeric, a #VALUE error occurs:

To fix the error, you can use one of these options:
- Enter the missing numeric values.
- Use Excel functions that automatically ignore text values.
- Write an IF statement that corresponds to your business logic.
In this example, you can use the PRODUCT function:
=PRODUCT(B3, C3)
If one of the referenced cells contains text, logical value, or is empty, that cell is ignored. The result is as if you multiply the other value by 1.
Alternatively, you can build an IF statement like this:
=IF(AND(ISNUMBER(B3), ISNUMBER(C3)), B3*C3, 0)
This formula multiplies two cells only if both values are numeric and returns zero if either cell contains a non-numeric value. For this particular case, it makes perfect sense.

Remove spaces and hidden characters
In some formulas, a cell with errant spaces or invisible characters may also cause a #VALUE! error, as shown in the screenshot below:

Visually, cells such as D3, B7 and C14 may appear to be completely empty. However, they do contain one or more spaces or non-printing characters. In Excel, a space character is considered text, and it can potentially trigger the #VALUE! error. In fact, it is just another case of the previous example, so it can be fixed in a similar manner:
- Ensure that the problematic cells are really empty. To do this, select the cell and press the Delete key to remove any hidden character in it.
- Use an Excel function that ignores text values, such as the SUM function instead of the arithmetic operation of addition.

Verify that referred ranges are compatible
Many Excel functions that accept multiple ranges in their arguments require those ranges to be of the same size and shape. If not, a formula raises the #VALUE error.
For example, the dynamic array FILTER function results in a #VALUE error when the include and array arguments have incompatible dimensions. For example:
=FILTER(A3:B20, A3:A22="Apple")
Once the range references are changed accordingly, the error is gone:
=FILTER(A3:B20, A3:A20="Apple")

Make sure dates are not stored as text
In Excel, dates are typically stored as numeric values. However, some dates in your worksheet may be stored as text strings instead. When this happens, Excel will return the #VALUE! error if you try to perform calculations or operations on these dates, as text values cannot be added, subtracted or somehow else calculated.
To resolve this issue, you need to convert text-formatted dates to valid Excel dates.

Check formula syntax
Another possible cause of a #VALUE error in Excel could be a syntax error in your formula. Excel's Formula Auditing tools can help you identify and correct such issues.
- Select the cell with the formula that is producing the #VALUE error.
- On the Formulas tab, in the Formula Auditing group, click on Evaluate Formula or Error Checking.
Excel will step through the formula one section at a time, showing the result of each step. If there is a syntax error, Excel will highlight the specific part of the formula is causing the error. Once you have detected the syntax error, correct it and re-evaluate the formula to ensure that it is now working as expected.
For example, consider the following formula in the dataset below:
=SORT(CHOOSECOLS(A3:B20, 3))
The #VALUE error occurs because the col_num argument (3) of the CHOOSECOLS function is greater than the total number of columns in the referred array (2).

Setting the last argument to 2 resolves the issue and returns the desired result – the Total column sorted from smallest to largest:

#VALUE error in Excel XLOOKUP and VLOOKUP
The VLOOKUP function and its modern successor XLOOKUP are commonly used in Excel to search and retrieve matching data. However, both functions can produce the #VALUE error under certain circumstances.
One common cause of the #VALUE error in XLOOKUP is when the dimensions of the lookup and return arrays are incomparable. For example, you cannot search in a horizontal array and return values from a vertical array. Also, the lookup array cannot be bigger or smaller than the return array. If there is any mismatch in the size of these arrays, XLOOKUP will not be able to perform the lookup and return the #VALUE error.
For example, the below XLOOKUP formula returns a #VALUE error because the lookup and return arrays contain a different number of rows:
=XLOOKUP(D3, A3:A20, B3:B22)
Adjusting the return_array reference resolves the error:
=XLOOKUP(D3, A3:A20, B3:B20)

In VLOOKUP, two common reasons for the #VALUE error are when the lookup value exceeds 255 characters and when the col_index_num argument is less than 1. For more information, please see #VALUE error in VLOOKUP.
Get rid of #VALUE error using IFERROR function
To eliminate the #VALUE error in your Excel sheets, you can use the IFERROR function in Excel 2007 - 365 or the IF ISERROR combination in earlier versions.
Suppose you are using a DATEDIF formula to find the difference between the dates in B3 and C3:
=DATEDIF(B3, C3, "d")
If one or both dates are invalid, the formula results in a #VALUE error. To fix it, wrap your core formula in the IFERROR function like this:
=IFERROR(DATEDIF(B3, C3, "d"), "Invalid date!")
If Excel doesn't recognize the referenced cell value as a date, the IFERROR function will explicitly point it out.

Tip. To quickly find all #VALUE errors in a worksheet, you can utilize the Go to Special feature or the Find and Replace dialog box. We discussed these options in detail when locating #NAME errors. For #VALUE errors, the steps are essentially the same.
That's how to detect and fix the #VALUE error in Excel. By understanding the causes and using the appropriate troubleshooting techniques, you can quickly get your spreadsheet back on track.
Practice workbook for download
#VALUE error in Excel - examples (.xlsx file)
以上是#excel中的價值錯誤:原因和修復的詳細內容。更多資訊請關注PHP中文網其他相關文章!
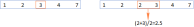
 Google電子表格Countif函數帶有公式示例Apr 11, 2025 pm 12:03 PM
Google電子表格Countif函數帶有公式示例Apr 11, 2025 pm 12:03 PMGoogle主張Countif:綜合指南 本指南探討了Google表中的多功能Countif函數,展示了其超出簡單單元格計數的應用程序。 我們將介紹從精確和部分比賽到Han的各種情況
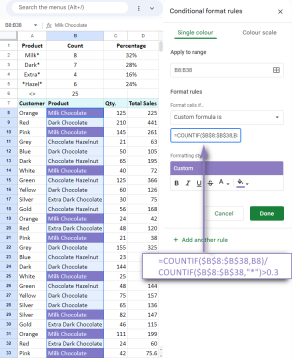
 Excel共享工作簿:如何為多個用戶共享Excel文件Apr 11, 2025 am 11:58 AM
Excel共享工作簿:如何為多個用戶共享Excel文件Apr 11, 2025 am 11:58 AM本教程提供了共享Excel工作簿,涵蓋各種方法,訪問控制和衝突解決方案的綜合指南。 現代Excel版本(2010年,2013年,2016年及以後)簡化了協作編輯,消除了M的需求
 如何將Excel轉換為JPG-保存.xls或.xlsx作為圖像文件Apr 11, 2025 am 11:31 AM
如何將Excel轉換為JPG-保存.xls或.xlsx作為圖像文件Apr 11, 2025 am 11:31 AM本教程探討了將.xls文件轉換為.jpg映像的各種方法,包括內置的Windows工具和免費的在線轉換器。 需要創建演示文稿,安全共享電子表格數據或設計文檔嗎?轉換喲
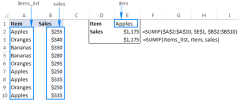 excel名稱和命名範圍:如何定義和使用公式Apr 11, 2025 am 11:13 AM
excel名稱和命名範圍:如何定義和使用公式Apr 11, 2025 am 11:13 AM本教程闡明了Excel名稱的功能,並演示瞭如何定義單元格,範圍,常數或公式的名稱。 它還涵蓋編輯,過濾和刪除定義的名稱。 Excel名稱雖然非常有用,但通常是氾濫的
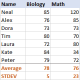 標準偏差Excel:功能和公式示例Apr 11, 2025 am 11:01 AM
標準偏差Excel:功能和公式示例Apr 11, 2025 am 11:01 AM本教程闡明了平均值的標準偏差和標準誤差之間的區別,指導您掌握標準偏差計算的最佳Excel函數。 在描述性統計中,平均值和標準偏差為interinsi
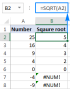 Excel中的平方根:SQRT功能和其他方式Apr 11, 2025 am 10:34 AM
Excel中的平方根:SQRT功能和其他方式Apr 11, 2025 am 10:34 AM該Excel教程演示瞭如何計算正方根和n根。 找到平方根是常見的數學操作,Excel提供了幾種方法。 計算Excel中正方根的方法: 使用SQRT函數:
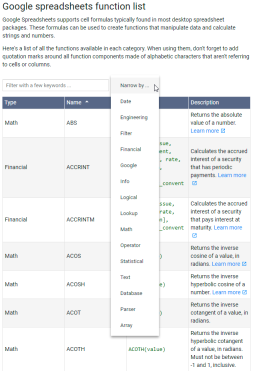 Google表基礎知識:了解如何使用Google電子表格Apr 11, 2025 am 10:23 AM
Google表基礎知識:了解如何使用Google電子表格Apr 11, 2025 am 10:23 AM解鎖Google表的力量:初學者指南 本教程介紹了Google Sheets的基礎,這是MS Excel的強大而多才多藝的替代品。 了解如何輕鬆管理電子表格,利用關鍵功能並協作


熱AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智慧驅動的應用程序,用於創建逼真的裸體照片

AI Clothes Remover
用於從照片中去除衣服的線上人工智慧工具。

Undress AI Tool
免費脫衣圖片

Clothoff.io
AI脫衣器

Video Face Swap
使用我們完全免費的人工智慧換臉工具,輕鬆在任何影片中換臉!

熱門文章

熱工具

SublimeText3漢化版
中文版,非常好用

MantisBT
Mantis是一個易於部署的基於Web的缺陷追蹤工具,用於幫助產品缺陷追蹤。它需要PHP、MySQL和一個Web伺服器。請查看我們的演示和託管服務。

MinGW - Minimalist GNU for Windows
這個專案正在遷移到osdn.net/projects/mingw的過程中,你可以繼續在那裡關注我們。 MinGW:GNU編譯器集合(GCC)的本機Windows移植版本,可自由分發的導入函式庫和用於建置本機Windows應用程式的頭檔;包括對MSVC執行時間的擴展,以支援C99功能。 MinGW的所有軟體都可以在64位元Windows平台上運作。

mPDF
mPDF是一個PHP庫,可以從UTF-8編碼的HTML產生PDF檔案。原作者Ian Back編寫mPDF以從他的網站上「即時」輸出PDF文件,並處理不同的語言。與原始腳本如HTML2FPDF相比,它的速度較慢,並且在使用Unicode字體時產生的檔案較大,但支援CSS樣式等,並進行了大量增強。支援幾乎所有語言,包括RTL(阿拉伯語和希伯來語)和CJK(中日韓)。支援嵌套的區塊級元素(如P、DIV),

Atom編輯器mac版下載
最受歡迎的的開源編輯器