 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals AI
AI Sequencer giant Illumina launches AI algorithm based on primate genes to predict disease-causing gene mutations
Sequencer giant Illumina launches AI algorithm based on primate genes to predict disease-causing gene mutationsSequencer giant Illumina launches AI algorithm based on primate genes to predict disease-causing gene mutations
As large models such as ChatGPT ignite a new wave of artificial intelligence craze, another "language" that has been accumulated for millions of years is also trying to use this technology to obtain the latest decoding. Recently, Illumina, the global leader in gene sequencers, announced the launch of a new artificial intelligence algorithm, PrimateAI-3D, in an effort to more accurately predict patient-causing gene mutations.
The total amount of genomic data generated each year is close to 40 billion gigabytes, according to data released by the National Institutes of Health. However, obtaining these data is only the first step in solving many mysteries of life. For them to be truly helpful to human health, in-depth interpretation and analysis are required.
Current scientific research shows that everyone carries millions of genetic variations. It is these variations that lead to individual differences in health and disease risk, but the way most variations work is currently unclear. The Human Genome Sequencing Center of Baylor College of Medicine and the Illumina Artificial Intelligence Laboratory hope to further solve the problem with the help of PrimateAI-3D.

According to Illumina, PrimateAI-3D uses a deep neural network architecture similar to ChatGPT and AlphaFold. The difference is that PrimateAI-3D is trained based on genome sequences rather than human language. "You can train generative language models like ChatGPT on existing text from Wikipedia and elsewhere. We use a similar deep learning architecture, but our data comes from millions of years of natural selection." Illumina Vice President of Artificial Intelligence President Kyle Farh said.
In addition, in generative language models such as ChatGPT, existing text can provide information for training, while the genetic variations that cause disease in the human genome are largely unknown. To solve this problem, PrimateAI-3D uses natural selection to train the parameters of a deep neural network. This training is based on the millions of benign genetic variants discovered by previously sequencing 233 different primate species. The largest sequencing effort of a non-human primate species to date.
Translation: We have shown that the more we know about genetic variation in non-human primates, the more accurately we can predict variants that may cause disease in humans. Rewrite: We have demonstrated that as our understanding of genetic variation in nonhuman primates increases, we are able to more accurately predict which mutations are likely to cause disease in humans. ” said Jeffrey Rogers from Baylor College of Medicine in the United States.
Subsequently, researchers from the Human Genome Sequencing Center and Department of Molecular and Human Genetics at Baylor College of Medicine in the United States, including Rogers, and the Illumina Artificial Intelligence Laboratory team led by Farh, applied the PrimateAI-3D algorithm to the British Biotech Identify potentially disease-causing human mutations among nearly 500,000 individuals in the sample library. Recently, two related studies were published in Science, a top academic journal.
They found that across 90 different clinical conditions investigated, 97% of healthy members of the general population harbored at least one highly modifiable variant lurking in their genomes. The findings also identified rare genetic variants that lead to higher risk for common diseases. Overall, PrimateAI-3D is at least 12 percent more accurate than any previous method in estimating genetic risks for health problems such as cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes, Farh said.
Farh added that one of the advantages of this new technology is that it can be used by all humans. It also means it overcomes the bias against people of white European ancestry inherent in existing genetic risk assessments, which are largely based on data from these groups.
Alex Aravanis, chief technology officer of Illumina, said, “The launch of this technology applies the latest artificial intelligence technology to genomics to reveal critical underlying information about complex genetic diseases such as diabetes, heart disease and autoimmune diseases. This brings huge opportunities to Illumina in genetic risk prediction and drug target discovery."
According to Illumina, PrimateAI-3D will be integrated into Illumina’s Internet software for use by the genomics community.
The above is the detailed content of Sequencer giant Illumina launches AI algorithm based on primate genes to predict disease-causing gene mutations. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 7 Powerful AI Prompts Every Project Manager Needs To Master NowMay 08, 2025 am 11:39 AM
7 Powerful AI Prompts Every Project Manager Needs To Master NowMay 08, 2025 am 11:39 AMGenerative AI, exemplified by chatbots like ChatGPT, offers project managers powerful tools to streamline workflows and ensure projects stay on schedule and within budget. However, effective use hinges on crafting the right prompts. Precise, detail
 Defining The Ill-Defined Meaning Of Elusive AGI Via The Helpful Assistance Of AI ItselfMay 08, 2025 am 11:37 AM
Defining The Ill-Defined Meaning Of Elusive AGI Via The Helpful Assistance Of AI ItselfMay 08, 2025 am 11:37 AMThe challenge of defining Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) is significant. Claims of AGI progress often lack a clear benchmark, with definitions tailored to fit pre-determined research directions. This article explores a novel approach to defin
 IBM Think 2025 Showcases Watsonx.data's Role In Generative AIMay 08, 2025 am 11:32 AM
IBM Think 2025 Showcases Watsonx.data's Role In Generative AIMay 08, 2025 am 11:32 AMIBM Watsonx.data: Streamlining the Enterprise AI Data Stack IBM positions watsonx.data as a pivotal platform for enterprises aiming to accelerate the delivery of precise and scalable generative AI solutions. This is achieved by simplifying the compl
 The Rise of the Humanoid Robotic Machines Is Nearing.May 08, 2025 am 11:29 AM
The Rise of the Humanoid Robotic Machines Is Nearing.May 08, 2025 am 11:29 AMThe rapid advancements in robotics, fueled by breakthroughs in AI and materials science, are poised to usher in a new era of humanoid robots. For years, industrial automation has been the primary focus, but the capabilities of robots are rapidly exp
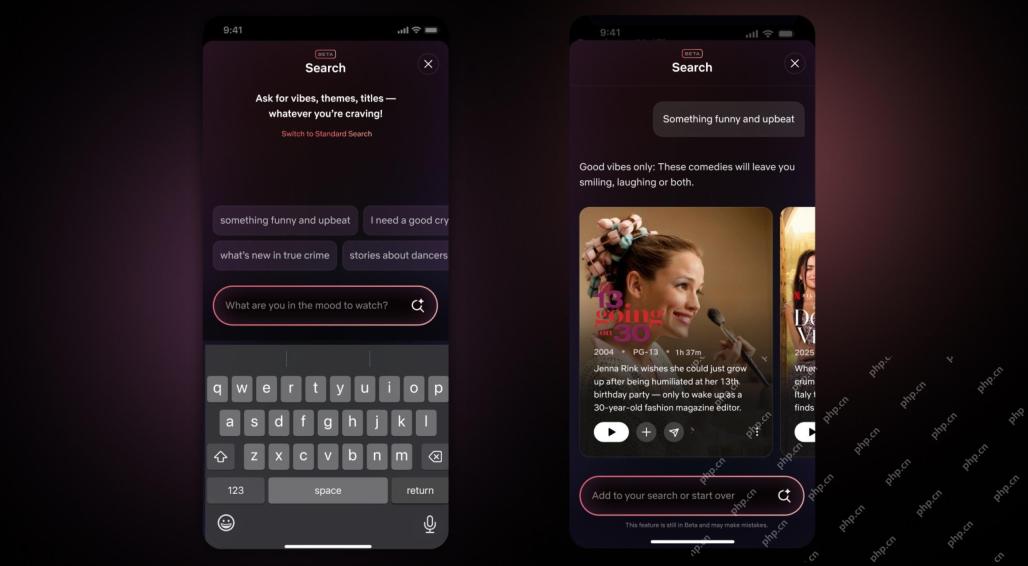 Netflix Revamps Interface — Debuting AI Search Tools And TikTok-Like DesignMay 08, 2025 am 11:25 AM
Netflix Revamps Interface — Debuting AI Search Tools And TikTok-Like DesignMay 08, 2025 am 11:25 AMThe biggest update of Netflix interface in a decade: smarter, more personalized, embracing diverse content Netflix announced its largest revamp of its user interface in a decade, not only a new look, but also adds more information about each show, and introduces smarter AI search tools that can understand vague concepts such as "ambient" and more flexible structures to better demonstrate the company's interest in emerging video games, live events, sports events and other new types of content. To keep up with the trend, the new vertical video component on mobile will make it easier for fans to scroll through trailers and clips, watch the full show or share content with others. This reminds you of the infinite scrolling and very successful short video website Ti
 Long Before AGI: Three AI Milestones That Will Challenge YouMay 08, 2025 am 11:24 AM
Long Before AGI: Three AI Milestones That Will Challenge YouMay 08, 2025 am 11:24 AMThe growing discussion of general intelligence (AGI) in artificial intelligence has prompted many to think about what happens when artificial intelligence surpasses human intelligence. Whether this moment is close or far away depends on who you ask, but I don’t think it’s the most important milestone we should focus on. Which earlier AI milestones will affect everyone? What milestones have been achieved? Here are three things I think have happened. Artificial intelligence surpasses human weaknesses In the 2022 movie "Social Dilemma", Tristan Harris of the Center for Humane Technology pointed out that artificial intelligence has surpassed human weaknesses. What does this mean? This means that artificial intelligence has been able to use humans
 Venkat Achanta On TransUnion's Platform Transformation And AI AmbitionMay 08, 2025 am 11:23 AM
Venkat Achanta On TransUnion's Platform Transformation And AI AmbitionMay 08, 2025 am 11:23 AMTransUnion's CTO, Ranganath Achanta, spearheaded a significant technological transformation since joining the company following its Neustar acquisition in late 2021. His leadership of over 7,000 associates across various departments has focused on u
 When Trust In AI Leaps Up, Productivity FollowsMay 08, 2025 am 11:11 AM
When Trust In AI Leaps Up, Productivity FollowsMay 08, 2025 am 11:11 AMBuilding trust is paramount for successful AI adoption in business. This is especially true given the human element within business processes. Employees, like anyone else, harbor concerns about AI and its implementation. Deloitte researchers are sc


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

PhpStorm Mac version
The latest (2018.2.1) professional PHP integrated development tool

EditPlus Chinese cracked version
Small size, syntax highlighting, does not support code prompt function

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor





