 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals AI
AI When will AI technology help the pharmaceutical industry break 'Inverted Moore's Law'?
When will AI technology help the pharmaceutical industry break 'Inverted Moore's Law'?When will AI technology help the pharmaceutical industry break 'Inverted Moore's Law'?

In 2020, the first year of the COVID-19 outbreak, the US Food and Drug Administration approved only 53 new drugs. In the same year, the global pharmaceutical industry’s overall drug R&D investment reached nearly US$200 billion. This means that the average cost of each drug approved in 2020 is close to $3.8 billion. A study published that year gave a relatively conservative estimate of the cost of new drugs, arguing that although the cost of new drugs has increased dramatically over the past decade, the specific range is still between US$314 million and US$2.8 billion. The study also found that the median total research and development expenditure invested in bringing a new drug to the market is close to US$1 billion, while the average is estimated to be around US$1.3 billion. In addition, the average launch cycle of new drugs is 10 to 15 years, of which about half of the time and investment is spent on the clinical trial stage, and the remaining half of the cost is used to support preclinical compound discovery, testing and supervision. As for why each new drug costs so much and has a long cycle, the reasons include lack of clinical efficacy, lack of commercial benefits and improper strategic planning. In short, all these complex factors have turned the effectiveness of the pharmaceutical industry into a metaphysics. Many people have even become skeptics due to the high cost of launching new drugs, questioning why the pharmaceutical industry has made significant progress since its technical level and management capabilities have improved significantly. You will still be stuck in the current predicament and unable to extricate yourself.
These are the proponents of what’s known as “Inverted Moore’s Law,” in which the cost of developing new drugs has grown exponentially over the past few decades despite improvements in technology. Inverse Moore's Law states that the cost of developing a new drug doubles approximately every nine years, discounting the effects of inflation. This observation proposes a law similar to diminishing returns. According to the concept of economics, if a certain input in the production of a certain commodity is increased while all other inputs remain unchanged, the overall situation will eventually Reaching a critical point - if you continue to increase input, the corresponding output will begin to gradually decrease. The term "Inverse Moore's Law" was proposed by Dr. Jack Scannell and colleagues in "Nature·Reviews·Drug Discovery" in 2012.
Inverted Moore’s Law naturally points to the famous Moore’s Law. This conceptual observation from the 1960s found that the number of transistors on large-scale integrated circuits doubled every two years or so. Moore's Law is named after Gordon Moore, co-founder of Intel Corporation, and is his observation and summary of historical trends.
Dr. Scannell emphasized that there are four main reasons for the current predicament. First of all, regulatory agencies have increasingly higher standards for therapies; regulatory agencies are less and less able to bear risks, which increases the cost and difficulty of research and development; a money-throwing mentality, which relies on flooding resources to promote projects , it is easy to cause project overruns; and then there is brute force cracking of basic research, that is, overestimating the possibility of using crude trial and error to break through basic research problems.
Despite all the difficult factors we face, we will one day defeat the challenge of Moore's Law, and a powerful weapon that will determine the outcome of the battle is AI. The good news is that someone has already taken the first steps toward exploring this path.
Dr. Scannell and his co-scientists are calling on pharmaceutical companies to appoint a chief drug officer who will be responsible for summarizing the causes of failures at each stage of the development process and publishing the results in scientific journals. Currently, pharmaceutical companies rarely even publish failed experiments or clinical results, and most have not yet thought of appointing dedicated executives to handle the valuable information in failed cases. However, Dr. Scannell emphasized that in order to break the inverse Moore's Law, companies must first change their R&D processes. Collaboration and information sharing are of course a good starting point, but in the pharmaceutical industry, there is only one way to truly break Moore's Law - AI.
In the past few years, people have made many attempts to use AI to break the inverse Moore's Law. Now, many institutions such as Exscientia and Insilico Medicine are sprinting towards this end.
Headquartered in Oxford, Exscientia is a global pharmaceutical technology company that puts patients at the center and accelerates drug discovery through AI technology. Last year, the company announced that the first immuno-oncology molecule designed by AI had entered human clinical trials. In the project, Exsientia is collaborating with Evotec to develop A2a receptor antagonists for adult patients with advanced TB, using the former's Centaur Chemist drug discovery platform. This is not the first attempt made by Exscientia. In 2020, the company announced an obsessive-compulsive disorder treatment drug designed by AI-driven software and has entered Phase I clinical trials.
In addition, there is Schrodinger, who have developed the most advanced chemical simulation software in the pharmaceutical industry. Schrodinger recently received FDA approval to study its computer-designed treatment for non-Hodgkin's lymphoma in early-stage trials. The company's platform, based on machine learning technology, classified 8.2 billion potential compounds within 10 months and ultimately identified 78 compounds that could successfully pass preclinical experimental synthesis and screening. Now, the company has plans to launch a Phase I clinical study and begin recruiting patients with relapsed or refractory non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
Meanwhile, Utah-based Recursion Pharmaceuticals is also using AI technology to find new uses for existing drugs. Last year, Roche and Genetech established a project collaboration with Recursion to jointly explore new areas of cell biology and try to develop new treatments in the fields of neuroscience and oncology indications. Through the collaboration, the two companies will use Recursion's AI drug discovery platform to conduct comprehensive screening of new drug targets, thereby accelerating the development of small molecule drugs.
In Insilico, a leading anti-fibrosis drug candidate has also successfully completed Phase 0 clinical research and officially entered the Phase I clinical stage. The new target of this drug candidate was discovered by the Pharma.AI platform. The total time from target discovery to the launch of the first phase of the project was even less than 30 months, which has set a new record for the speed of new drug development in the pharmaceutical industry.
Don’t forget that AI technology will also play a role in brain-computer interface, deep learning, human-computer interface, machine learning and other intelligent simulation scenarios. These concepts have existed for decades. Early medical AI systems once relied heavily on clinical knowledge and logical rules provided by medical experts, but now trained supercomputers can complete these tasks on their own.
In order to break the inverse Moore's Law, data scientists and medical scientists must jointly plan achievable use cases, apply AI technology to various clinical trials, and combine AI technology with existing technologies that will replace/complement it. Contrast. In this way, AI is expected to smoothly enter the clinical trial ecosystem, effectively reducing R&D failure rates and costs while rapidly improving the industry's drug discovery and development processes. Today, almost all large pharmaceutical companies are using internal original research algorithms, cooperating with AI vendors, or directly acquiring AI vendors/technology to enrich their product portfolios and drug discovery pipelines. The partnership statements from Massive Financing and multiple pharmaceutical companies also tell us that the industry has high expectations for the application of AI tools in the drug research and development process. There have been many changes in this field. It is hoped that in the next few years, companies will be able to combine better investment strategies with advanced AI technology to break the "curse" of inverted Moore's Law in one fell swoop.
The above is the detailed content of When will AI technology help the pharmaceutical industry break 'Inverted Moore's Law'?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 7 Powerful AI Prompts Every Project Manager Needs To Master NowMay 08, 2025 am 11:39 AM
7 Powerful AI Prompts Every Project Manager Needs To Master NowMay 08, 2025 am 11:39 AMGenerative AI, exemplified by chatbots like ChatGPT, offers project managers powerful tools to streamline workflows and ensure projects stay on schedule and within budget. However, effective use hinges on crafting the right prompts. Precise, detail
 Defining The Ill-Defined Meaning Of Elusive AGI Via The Helpful Assistance Of AI ItselfMay 08, 2025 am 11:37 AM
Defining The Ill-Defined Meaning Of Elusive AGI Via The Helpful Assistance Of AI ItselfMay 08, 2025 am 11:37 AMThe challenge of defining Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) is significant. Claims of AGI progress often lack a clear benchmark, with definitions tailored to fit pre-determined research directions. This article explores a novel approach to defin
 IBM Think 2025 Showcases Watsonx.data's Role In Generative AIMay 08, 2025 am 11:32 AM
IBM Think 2025 Showcases Watsonx.data's Role In Generative AIMay 08, 2025 am 11:32 AMIBM Watsonx.data: Streamlining the Enterprise AI Data Stack IBM positions watsonx.data as a pivotal platform for enterprises aiming to accelerate the delivery of precise and scalable generative AI solutions. This is achieved by simplifying the compl
 The Rise of the Humanoid Robotic Machines Is Nearing.May 08, 2025 am 11:29 AM
The Rise of the Humanoid Robotic Machines Is Nearing.May 08, 2025 am 11:29 AMThe rapid advancements in robotics, fueled by breakthroughs in AI and materials science, are poised to usher in a new era of humanoid robots. For years, industrial automation has been the primary focus, but the capabilities of robots are rapidly exp
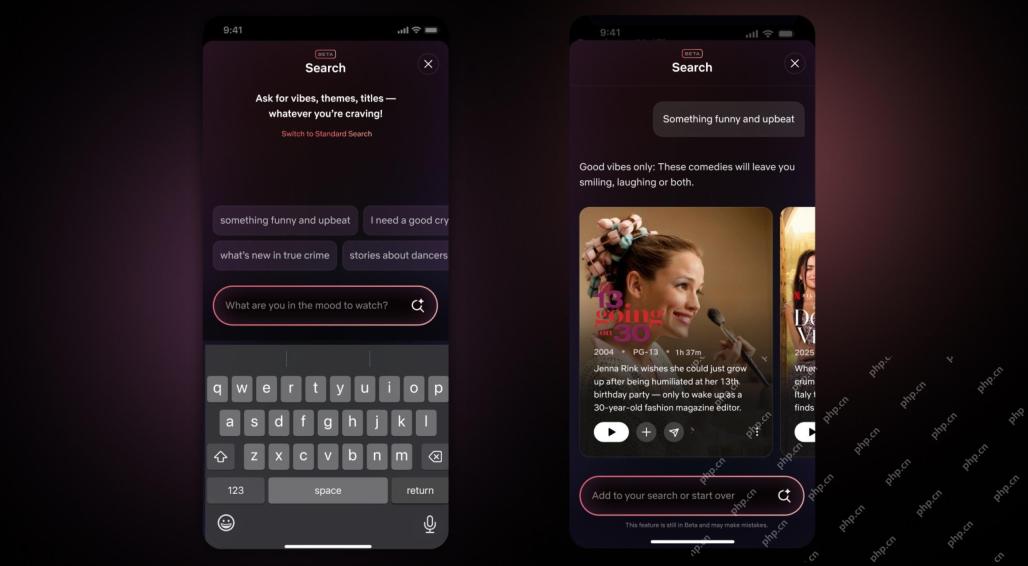 Netflix Revamps Interface — Debuting AI Search Tools And TikTok-Like DesignMay 08, 2025 am 11:25 AM
Netflix Revamps Interface — Debuting AI Search Tools And TikTok-Like DesignMay 08, 2025 am 11:25 AMThe biggest update of Netflix interface in a decade: smarter, more personalized, embracing diverse content Netflix announced its largest revamp of its user interface in a decade, not only a new look, but also adds more information about each show, and introduces smarter AI search tools that can understand vague concepts such as "ambient" and more flexible structures to better demonstrate the company's interest in emerging video games, live events, sports events and other new types of content. To keep up with the trend, the new vertical video component on mobile will make it easier for fans to scroll through trailers and clips, watch the full show or share content with others. This reminds you of the infinite scrolling and very successful short video website Ti
 Long Before AGI: Three AI Milestones That Will Challenge YouMay 08, 2025 am 11:24 AM
Long Before AGI: Three AI Milestones That Will Challenge YouMay 08, 2025 am 11:24 AMThe growing discussion of general intelligence (AGI) in artificial intelligence has prompted many to think about what happens when artificial intelligence surpasses human intelligence. Whether this moment is close or far away depends on who you ask, but I don’t think it’s the most important milestone we should focus on. Which earlier AI milestones will affect everyone? What milestones have been achieved? Here are three things I think have happened. Artificial intelligence surpasses human weaknesses In the 2022 movie "Social Dilemma", Tristan Harris of the Center for Humane Technology pointed out that artificial intelligence has surpassed human weaknesses. What does this mean? This means that artificial intelligence has been able to use humans
 Venkat Achanta On TransUnion's Platform Transformation And AI AmbitionMay 08, 2025 am 11:23 AM
Venkat Achanta On TransUnion's Platform Transformation And AI AmbitionMay 08, 2025 am 11:23 AMTransUnion's CTO, Ranganath Achanta, spearheaded a significant technological transformation since joining the company following its Neustar acquisition in late 2021. His leadership of over 7,000 associates across various departments has focused on u
 When Trust In AI Leaps Up, Productivity FollowsMay 08, 2025 am 11:11 AM
When Trust In AI Leaps Up, Productivity FollowsMay 08, 2025 am 11:11 AMBuilding trust is paramount for successful AI adoption in business. This is especially true given the human element within business processes. Employees, like anyone else, harbor concerns about AI and its implementation. Deloitte researchers are sc


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Dreamweaver Mac version
Visual web development tools

WebStorm Mac version
Useful JavaScript development tools

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 English version
Recommended: Win version, supports code prompts!

MinGW - Minimalist GNU for Windows
This project is in the process of being migrated to osdn.net/projects/mingw, you can continue to follow us there. MinGW: A native Windows port of the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC), freely distributable import libraries and header files for building native Windows applications; includes extensions to the MSVC runtime to support C99 functionality. All MinGW software can run on 64-bit Windows platforms.





