 Web Front-end
Web Front-end CSS Tutorial
CSS Tutorial Let's talk about the new CSS feature content-visibility to help you improve page rendering performance
Let's talk about the new CSS feature content-visibility to help you improve page rendering performanceLet's talk about the new CSS feature content-visibility to help you improve page rendering performance

For front-end personnel, the most troublesome thing should be page performance. When users visit a page, they always hope that it can be quickly presented in front of them and interactive. state. If your page loads too slowly, your users are likely to leave you. Therefore, page performance is a top priority for front-end developers. In fact, if you understand the entire process from loading to rendering, you will know where to start.
Well, don’t go off track, today we will mainly study the rendering performance of long list pages
Today’s pages are becoming more and more complex, and a page often carries a large number of elements. The most common How do you ensure that the rendering of tens of thousands of product lists on some e-commerce pages does not freeze? When faced with such a long list rendering scenario, we generally use paging or virtual lists to slow down the one-time rendering of the page. Pressure, but these methods need to be implemented with JS, so is there any solution that can be implemented using only CSS?
The answer is yes, it is our protagonist today - content visibility (content-visibility). [Recommended learning: css video tutorial]
content-visibility
Attribute value
content-visibilityis a new attribute of CSS, mainly used to improve page rendering performance. It can control whether an element renders its content, and allows the browser to skip the layout and rendering of these elements.
- visible: Default value, no effect. The element's content is laid out and rendered normally.
- hidden: The element skips its content. Skipped content cannot be accessed by user agent functions, such as finding within the page, tab order navigation, etc., nor can it be selected or focused. This is similar to setting
display: noneto content. - auto: This element turns on layout inclusion, style inclusion, and drawing inclusion. It will also skip its content if the element is not relevant to the user. Unlike hidden , skipped content must still be properly usable for user-agent functionality, such as finding in the page, tab order navigation, etc., and must be properly focusable and selectable.
content-visibility: hiddenManually manage visibility
As mentioned above, the effect of content-visibility: hidden is the same as display: none is similar, but in fact there is a big difference between the two:
- content-visibility: hidden only hides the child elements and will not hide itself
- content-visibility: hidden The rendering state of hidden content will be cached, so when it is removed or made visible, the browser will not re-render, but will apply the cache, so if you need to frequently switch to display hidden elements, This property can greatly improve rendering performance.
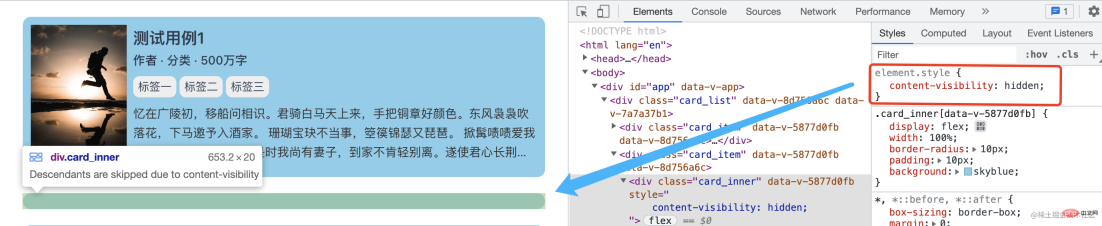
We can see from the above that the child elements of the content-visibility: hidden element are indeed not rendered, but it It can render itself!
content-visibility: auto skips rendering work
Let’s think about it carefully. Although there will be many elements on the page, will they be presented to the user at the same time? Obviously not. Every time the user can actually see only the content in the visible area of the device, the user will never see the content in the non-visible area as long as the page does not scroll. Although the user cannot see it, the browser will actually render it, which wastes a lot of performance. So we have to find a way to improve page rendering performance by preventing the browser from rendering content in non-visible areas.
The principle of the virtual list we mentioned above is actually similar to this. When the first screen is loaded, only the content of the visual area is loaded. When the page scrolls, the dynamics are obtained through calculation. Visible area content, and non-visual area content is deleted, which can greatly improve the rendering performance of long lists.
But this needs to be implemented with JS. Now we can use content-visibility: auto in CSS, which can be used to skip the rendering of off-screen content. For this kind of separation, there are a lot of A long list of screen content can greatly reduce page rendering time.
We slightly change the above example:
<template>
<div>
<div>
<img src="/static/imghwm/default1.png" data-src="book.bookCover" class="lazy" : / alt="Let's talk about the new CSS feature content-visibility to help you improve page rendering performance" >
<div>
<div>{{ `${book.bookName}${index + 1}` }}</div>
<div>{{ book.catlog }}</div>
<div>
<div v-for="(item, index) in book.tags" :key="index">
{{ item }}
</div>
</div>
<div>
{{ book.desc }}
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { toRefs } from "vue";
const props = defineProps<{
book: any;
index: any;
}>();
const { book, index } = toRefs(props);
</script>
<style scoped>
.card_item {
margin: 20px auto;
content-visibility: auto;
}
/ *
...
*/
</style>First of all, there is no effect of adding content-visibility: auto, regardless of whether these elements are in the visible area, they will Rendered
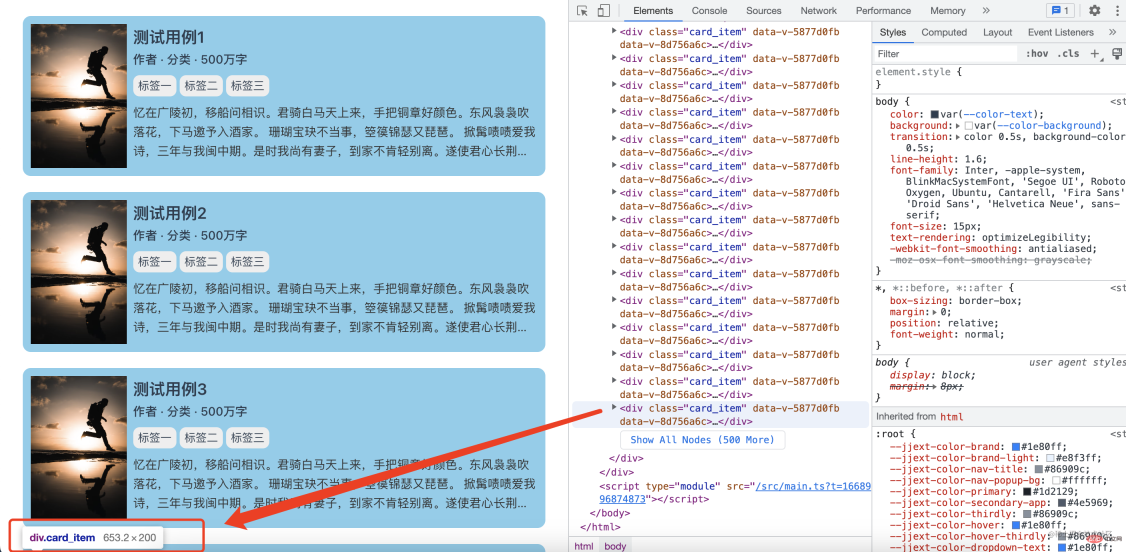
If we write like this in normal business, the user may spit out the fragrance directly when entering this page. For performance considerations, we add Above:
.card_item {
content-visibility: auto;
}Let’s take a look at the effect at this time:

从第10个开始,这些没在可视区的元素就没有被渲染,这可比上面那种全部元素都渲染好太多了,但是如果浏览器不渲染页面内的一些元素,滚动将是一场噩梦,因为无法正确计算页面高度。这是因为,content-visibility会将分配给它的元素的高度(height)视为0,浏览器在渲染之前会将这个元素的高度变为0,从而使我们的页面高度和滚动变得混乱。

这里我们可以看到页面上的滚动条会出现抖动现象,这是因为可视区外的元素只有出现在了可视区才会被渲染,这就回导致前后页面高度会发生变化,从而出现滚动条的诡异抖动现象,这是虚拟列表基本都会存在的问题。
⚠️注意:当元素接近视口时,浏览器不再添加size容器并开始绘制和命中测试元素的内容。这使得渲染工作能够及时完成以供用户查看。
这也是为什么上面我们看到的是从第十个才开始不渲染子元素,因为它需要一个缓冲区以便浏览器能够在页面发生滚动时及时渲染呈现在用户眼前。
上面提到的size其实是一种 CSS 属性的潜在值contain,它指的是元素上的大小限制确保元素的框可以在不需要检查其后代的情况下进行布局。这意味着如果我们只需要元素的大小,我们可以跳过后代的布局。
contain-intrinsic-size 救场
页面在滚动过程中滚动条一直抖动,这是一个不能接受的体验问题,为了更好地实现content-visibility,浏览器需要应用 size containment 以确保内容的渲染结果不会以任何方式影响元素的大小。这意味着该元素将像空的一样布局。如果元素没有在常规块布局中指定的高度,那么它将是 0 高度。
这个时候我们可以使用contain-intrinsic-size来指定的元素自然大小,确保我们未渲染子元素的 div 仍然占据空间,同时也保留延迟渲染的好处。
语法
此属性是以下 CSS 属性的简写:
contain-intrinsic-widthcontain-intrinsic-height
/* Keyword values */ contain-intrinsic-width: none; /* <length> values */ contain-intrinsic-size: 1000px; contain-intrinsic-size: 10rem; /* width | height */ contain-intrinsic-size: 1000px 1.5em; /* auto <length> */ contain-intrinsic-size: auto 300px; /* auto width | auto height */ contain-intrinsic-size: auto 300px auto 4rem;
contain-intrinsic-size 可以为元素指定以下一个或两个值。如果指定了两个值,则第一个值适用于宽度,第二个值适用于高度。如果指定单个值,则它适用于宽度和高度。
实现
我们只需要给添加了content-visibility: auto的元素添加上contain-intrinsic-size就能够解决滚动条抖动的问题,当然,这个高度约接近真实渲染的高度,效果会越好,如果实在无法知道准确的高度,我们也可以给一个大概的值,也会使滚动条的问题相对减少。
.card_item {
content-visibility: auto;
contain-intrinsic-size: 200px;
}
之前没添加contain-intrinsic-size属性时,可视区外的元素高度都是0,现在这些元素高度都是我们设置的contain-intrinsic-size的值,这样的话整个页面的高度就是不会发生变化(或者说变化很小),从而页面滚动条也不会出现抖动问题(或者说抖动减少)

性能对比
上面说了这么多,content-visibility是否真的能够提高页面的渲染性能呢,我们来实际对比看看:
- 首先是没有
content-visibility的页面渲染

- 然后是有
content-visibility的页面渲染

上面是用1000个列表元素进行测试的,有content-visibility的页面渲染花费时间大概是37ms,而没有content-visibility的页面渲染花费时间大概是269ms,提升了足足有7倍之多!!!
对于列表元素更多的页面,content-visibility带来的渲染性能提升会更加明显。
思考?
能否减小页面的内存占用?
之前有同学问到了content-visibility: auto是否会减少页面内存的占用,这个我们可以查看下使用前后页面所占用内存的大小是否有变化。
我们可以通过chrome浏览器 设置 --> 更多工具 --> 任务管理器 查看页面占用内存大小。

- 首先是没有
content-visibility: auto,页面占用内存大概为96.2MB

- 然后是添加了
content-visibility: auto,页面占用内存仍然是96.2MB

也就是说,它并不会减少页面占用内存大小,这些元素是真实存在于DOM树中的,并且我们也可以通过JS访问到

是否会影响脚本的加载行为?
如果我们在添加了content-visibility: auto的元素内去加载脚本,并且此时的元素处于一个不可见的状态,那么此时元素内的脚本能够正常加载呢?
<!-- ... 第十二个 -->
<div class="visibility_item">
<div class="inner">
测试脚本
<img src="/static/imghwm/default1.png" data-src="./2.js" class="lazy" alt="">
<script ></script>
</div>
</div>
很明显它并不会影响脚本与图片的加载行为,并且脚本再加载后能够正常执行。结合上面第一点,我们可以得出结论,使用了content-visibility: auto的元素影响的只是子元素的渲染,对于内部静态资源的加载还是正常进行。
但我们需要注意的是脚本的执行时机,如果要获取DOM元素的话,此时的脚本只能获取到它加载位置之前的DOM元素,而与它自身DOM有没有渲染无关!
// 2.js console.log('测试脚本') console.log('第十一个', document.querySelectorAll('.visibility_item')[10]) console.log('第十三个', document.querySelectorAll('.visibility_item')[12])

可访问性
使用了content-visibility: auto并且在非可视区的元素是否存在于可访问树中?

这里我们可以看出content-visibility: auto是屏幕外的内容在文档对象模型中仍然可用,因此在可访问性树中(与visibility: hidden不同)。这意味着我们可以在页面上搜索并导航到该内容,而无需等待它加载或牺牲渲染性能。
这个功能特性是在chrome 90 中更新的,在 chrome 85-89 中,屏幕外的子元素content-visibility: auto被标记为不可见。
兼容性
content-visibility是chrome85新增的特性,所以兼容性还不是很高,但它是一个非常实用的CSS属性,由于跳过了渲染,如果我们大部分内容都在屏幕外,利用该content-visibility属性可以使初始用户加载速度更快。相信兼容性的问题在不久的将来会得到解决~
原文地址:https://juejin.cn/post/7168629736838463525
(学习视频分享:web前端)
The above is the detailed content of Let's talk about the new CSS feature content-visibility to help you improve page rendering performance. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Next Level CSS Styling for CursorsApr 23, 2025 am 11:04 AM
Next Level CSS Styling for CursorsApr 23, 2025 am 11:04 AMCustom cursors with CSS are great, but we can take things to the next level with JavaScript. Using JavaScript, we can transition between cursor states, place dynamic text within the cursor, apply complex animations, and apply filters.
 Worlds Collide: Keyframe Collision Detection Using Style QueriesApr 23, 2025 am 10:42 AM
Worlds Collide: Keyframe Collision Detection Using Style QueriesApr 23, 2025 am 10:42 AMInteractive CSS animations with elements ricocheting off each other seem more plausible in 2025. While it’s unnecessary to implement Pong in CSS, the increasing flexibility and power of CSS reinforce Lee's suspicion that one day it will be a
 Using CSS backdrop-filter for UI EffectsApr 23, 2025 am 10:20 AM
Using CSS backdrop-filter for UI EffectsApr 23, 2025 am 10:20 AMTips and tricks on utilizing the CSS backdrop-filter property to style user interfaces. You’ll learn how to layer backdrop filters among multiple elements, and integrate them with other CSS graphical effects to create elaborate designs.
 SMIL on?Apr 23, 2025 am 09:57 AM
SMIL on?Apr 23, 2025 am 09:57 AMWell, it turns out that SVG's built-in animation features were never deprecated as planned. Sure, CSS and JavaScript are more than capable of carrying the load, but it's good to know that SMIL is not dead in the water as previously
 'Pretty' is in the eye of the beholderApr 23, 2025 am 09:40 AM
'Pretty' is in the eye of the beholderApr 23, 2025 am 09:40 AMYay, let's jump for text-wrap: pretty landing in Safari Technology Preview! But beware that it's different from how it works in Chromium browsers.
 CSS-Tricks Chronicles XLIIIApr 23, 2025 am 09:35 AM
CSS-Tricks Chronicles XLIIIApr 23, 2025 am 09:35 AMThis CSS-Tricks update highlights significant progress in the Almanac, recent podcast appearances, a new CSS counters guide, and the addition of several new authors contributing valuable content.
 Tailwind's @apply Feature is Better Than it SoundsApr 23, 2025 am 09:23 AM
Tailwind's @apply Feature is Better Than it SoundsApr 23, 2025 am 09:23 AMMost of the time, people showcase Tailwind's @apply feature with one of Tailwind's single-property utilities (which changes a single CSS declaration). When showcased this way, @apply doesn't sound promising at all. So obvio
 Feeling Like I Have No Release: A Journey Towards Sane DeploymentsApr 23, 2025 am 09:19 AM
Feeling Like I Have No Release: A Journey Towards Sane DeploymentsApr 23, 2025 am 09:19 AMDeploying like an idiot comes down to a mismatch between the tools you use to deploy and the reward in complexity reduced versus complexity added.


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

SAP NetWeaver Server Adapter for Eclipse
Integrate Eclipse with SAP NetWeaver application server.

DVWA
Damn Vulnerable Web App (DVWA) is a PHP/MySQL web application that is very vulnerable. Its main goals are to be an aid for security professionals to test their skills and tools in a legal environment, to help web developers better understand the process of securing web applications, and to help teachers/students teach/learn in a classroom environment Web application security. The goal of DVWA is to practice some of the most common web vulnerabilities through a simple and straightforward interface, with varying degrees of difficulty. Please note that this software

EditPlus Chinese cracked version
Small size, syntax highlighting, does not support code prompt function

PhpStorm Mac version
The latest (2018.2.1) professional PHP integrated development tool

SublimeText3 Linux new version
SublimeText3 Linux latest version






