Home >Web Front-end >JS Tutorial >This article will give you an in-depth understanding of Angular11
This article will give you an in-depth understanding of Angular11
- 青灯夜游forward
- 2021-05-24 10:28:513444browse
This article introduces Angular11 to you. It has certain reference value. Friends in need can refer to it. I hope it will be helpful to everyone.

Angular has experienced a leap in development from version 1.0 to 2.0. Combined with the powerful tool TypeScript, Angular is becoming an important option for large-scale front-ends. , this question mainly introduces the basic concepts of Anguar 10, and helps readers to get started quickly through the corresponding code. [Related recommendations: "angular Tutorial"]
1. Angular Development Milestone
AngularJS was originally developed by Misko Hevery and Adam Abrons A personal project developed in his spare time in 2009. The original project name was GetAngular. The design goal was to allow web designers (non-developers) to create simple applications using only HTML tags. Over time, AngularJS evolved into a comprehensive development framework. In 2010, in order to promote the development speed of Google Feedback and the progress of the project, Misko Hevery reconstructed Google Feedbac based on GWT, compressing the original more than 17,000 lines of code to only more than 1,500 lines. Since then, Angularjs has attracted attention, and AngularJS has transformed into Google company projects. Angular1.0 introduces the concept of two-way data binding. In 2016, Microsoft and Google cooperated and adopted TypeScript as a new development language and released Angular 2.0. Angular2.0 and Angularjs1.x are completely different architectures. Angular2.0 and later versions are collectively called Angular2. The user group of Angular1.x is also relatively large, and the corresponding version framework continues to be maintained. The latest version is 1.8.2. The latest version of Angular2 is 11.0.0.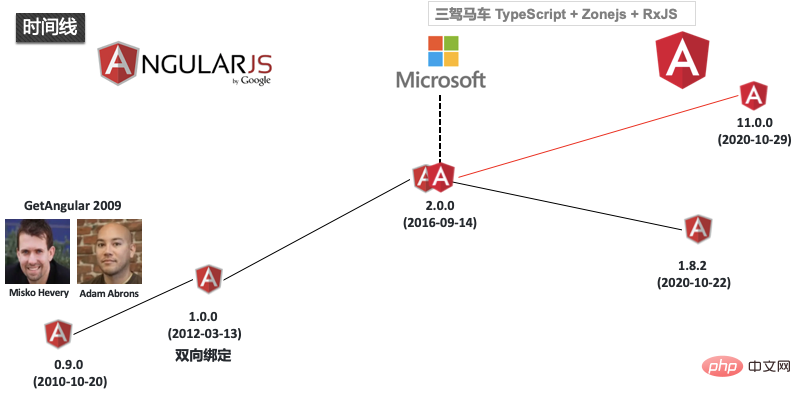
2. Development overview
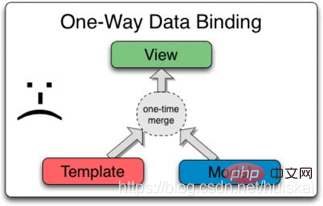
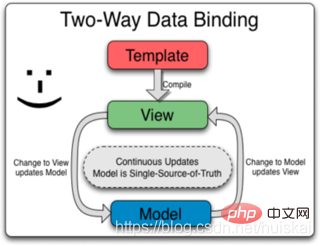
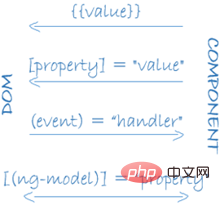
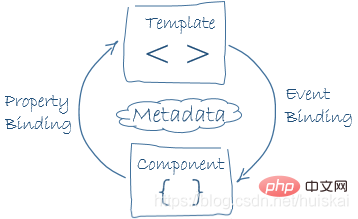
##2.1 Two-way data binding In conventional front-end development, data and views are often related through single binding. The advantage of this model is that the results are relatively simple. The model is responsible for updating data and rendering combined with the template, and the view layer is only responsible for display. The disadvantage of this structure is that data changes in the view layer cannot be fed back to the model layer, which cannot meet the needs of highly interactive pages. This is when two-way data binding comes into being.
 |
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
|---|---|---|
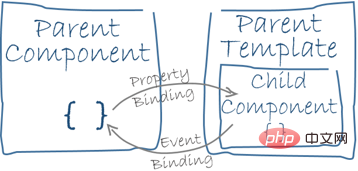
| Attribute binding and event binding | Template nesting |
| 主要点 | Angular | VUE |
|---|---|---|
| 设计目标 | 全面的解决方案(浏览器端、服务端、客户端),基本包含了开发全流程 | 渐进增强,扩展性强,用户选择余地大 |
| 组件 | 组件是ng2+应用核心,支持Web Component标准,组件生命周期明确 | 完善的组件系统,可以从template生成或者render渲染,组件有明确的生命周期,使用virtual dom渲染 |
| 异步处理 | 原生支持RxJS,通过流模型处理异步任务 | 没有官方异步处理方案,可以用Promise,也可以用RxJS染 |
| 构建部署 | 支持Just In Time(JIT)和Ahead Of Time(AOT)模式,配合tree shaking可以大幅减少代码体积 | 配合Webpack打包工具,在不引入组件的情况下,体积更小 |
| 状态管理 | ngrx | vuex |
| 安全 | 对不信值进行编码,避免XSS攻击,使用离线模版编译器,防止模版注入。官方http库防止XSRF | 没有强制性阻止XSS攻击机制,输出HTML要注意配合v-html指令 |
| 优点 | 框架对几乎任何场景,都提供了标准化,更工程化,更适合大型项目多人协作面向新特性,发展空间大 | 框架可被不同程度的使用,可单独使用核心,也可加入状态管理,提供了更多选项。适合初期快速迭代,性能上没有很大缺陷 |
| 缺点 | 使用大量第三方库和组件,增加了潜在风险,应用性能可控性降低 | 由于提供了开发选项,多人协作下,对与使用程度和场景的处理可能不一样,随着项目增大,以快为特点的技术,在工程化和代码管理上可能存在困难。需要程序员手动实现类似依赖注入的功能、代码组织 |
| 选型 | 业务要求稳定、能够增量开发的项目 | 快速迭代、可以被替换的项目 |
5.2 开源组件库资源对比
| Angular | Vue |
|---|---|
| Angular Material2 | Element UI |
| DEVUI | Mint UI |
| PrimeNg | iView UI |
| Kendo UI | Bootstrap-Vue UI |
| Ng-lightning | Ant Design Vue UI |
| Ng-bootstrap | AT-UI UI |
| NG-ZORRO | cube-ui UI |
| NGX Bootstrap | Muse-UI UI |
更多编程相关知识,请访问:编程视频!!
The above is the detailed content of This article will give you an in-depth understanding of Angular11. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
Related articles
See more- A brief discussion on the differences of @, =, & instructions in angular
- A brief discussion on the relationship between controllers, services and instructions in Angular
- Detailed explanation of several ways to add css classes to HTML elements in angular
- A brief discussion on the 4 design patterns in angular instructions
- Let's talk about the preLink and postLink functions in the angular directive

