Home >Java >Javagetting Started >Algorithm learning - Java implements the longest common subsequence
Algorithm learning - Java implements the longest common subsequence
- 王林forward
- 2020-11-03 16:06:162461browse

实验目的:
输入两个相同类型的序列,用动态规划方法计算他们的最长公共子序列的长度以及序列。
(推荐教程:java视频教程)
思路:
1、先用一个二维数组存储最长公共子序列的长度,还要记录每个值的状态
2、根据记录值的状态,递归回溯求出最长公共子序列
3、递归方程:
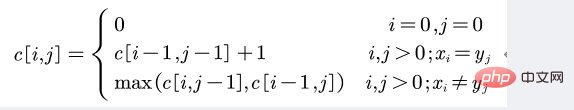
代码实现:
package c最长公共子序列;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* @author Draco
* @see 最长公共子序列(Longest common subsequence)
* @version
* @date-time 2020-04-27 - 下午4:23:36
*/
public class LCS {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 测试字符串:ABCBDAB BDCABA
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("注意:第一个串要长于第二个串");
System.out.print("请输入第一个字符串:");
String string1 = scanner.next();
System.out.print("请输入第二个字符串:");
String string2 = scanner.next();
String str1 = string1;
String str2 = string2;
// String str1 = "ABCBDAB";
// String str2 = "BDCABA";
int[][] c = getSubstringMatrix(str1, str2);
String[][] b = getTrace(str1, str2);
System.out.println("长度矩阵:");
show(c);
System.out.println();
System.out.println("方向矩阵:");
showForString(b);
System.out.println("最长公共子序列的长度:" + c[str1.length()][str2.length()]);
String sMax = str1.length() > str2.length() ? str1 : str2; // 选择最长的串,因为要取出最大子串
String sMin = str1.length() < str2.length() ? str1 : str2; // 选择最小的串
System.out.print("最长公共子串:");
print(b, sMax, sMax.length(), sMin.length());
}
/**
* @see 找出子序列的矩阵,其中最后一行,最后一列就是最长子序列的的长度
* @param x 第一个字符串
* @param y 第二个字符串
* @return 长度矩阵
*/
public static int[][] getSubstringMatrix(String x, String y) {
int xLen = x.length() + 1; // 加1是因为初始化第一个为0
int yLen = y.length() + 1;
int rLen = xLen > yLen ? xLen : yLen; // 大的串置为行
int cLen = xLen < yLen ? xLen : yLen; // 小的串置为列
int[][] c = new int[rLen][cLen]; // 矩阵c保存状态
for (int i = 1; i < rLen; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j < cLen; j++) {
if (x.charAt(i - 1) == y.charAt(j - 1)) {
// 相等,由斜对角线+1
c[i][j] = c[i - 1][j - 1] + 1;
} else if (c[i - 1][j] >= c[i][j - 1]) {
// 不相等,选取较大的
c[i][j] = c[i - 1][j];
} else {
c[i][j] = c[i][j - 1];
}
}
}
return c; // 长度矩阵
}
/**
* @see 记录每个值的状态,这样方便后面的回溯递归
* @param x 第一个字符串
* @param y 第二个字符串
* @return 方向矩阵
*/
public static String[][] getTrace(String x, String y) {
int xLen = x.length() + 1;
int yLen = y.length() + 1;
// 给矩阵c和b设置行和列
int rLen = xLen > yLen ? xLen : yLen;// 大的串置为行
int cLen = xLen < yLen ? xLen : yLen;// 小的串置为列
int[][] c = new int[rLen][cLen];
String[][] b = new String[rLen][cLen];
for (int i = 1; i < rLen; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j < cLen; j++) {
if (x.charAt(i - 1) == y.charAt(j - 1)) {// 相等
c[i][j] = c[i - 1][j - 1] + 1;
b[i][j] = "\\\\";// 指向左上角
} else if (c[i - 1][j] >= c[i][j - 1]) {// 不相等
// 当上面的数值大
c[i][j] = c[i - 1][j];
b[i][j] = "|";// 指向上边
} else {
// 当下面的数值大
c[i][j] = c[i][j - 1];
b[i][j] = "——";// 指向左边
}
}
}
return b;// 方向矩阵
}
/**
* @see 递归实现回溯,然后打印出最长公共子序列
* @param b 方向矩阵
* @param s 较长的字符串
* @param i 较长串的长度
* @param j 较短串的长度
*/
public static void print(String[][] b, String s, int i, int j) {
// 递归终止的条件
if (i == 0 || j == 0) {
return;
}
// 判断递归进行的条件
if (b[i][j].equals("\\\\")) {
// 遇到斜线,递归到左上角
print(b, s, i - 1, j - 1);
System.out.print(s.charAt(i - 1) + " ");
} else if (b[i][j].equals("|")) {
// 遇到竖线,递归到上边
print(b, s, i - 1, j);
} else if (b[i][j].equals("——")) {
// 遇到横线,递归到左边
print(b, s, i, j - 1);
}
}
/**
* @see 打印二维数组
* @param b 一个二维数组
*/
public static void show(int[][] b) {
for (int w = 0; w < b.length; w++) {
for (int p = 0; p < b[w].length; p++) {
System.out.print(b[w][p] + "\\t");
if (p == b[w].length - 1) {
System.out.println();
}
}
}
}
/**
* @see 打印字符串的二维数组
* @param b 一个字符串的二位数组
*/
public static void showForString(String[][] b) {
for (int w = 1; w < b.length; w++) {
System.out.print("\\t");
for (int p = 1; p < b[w].length; p++) {
System.out.print(b[w][p] + "\\t");
if (p == b[w].length - 1) {
System.out.println();
}
}
}
}
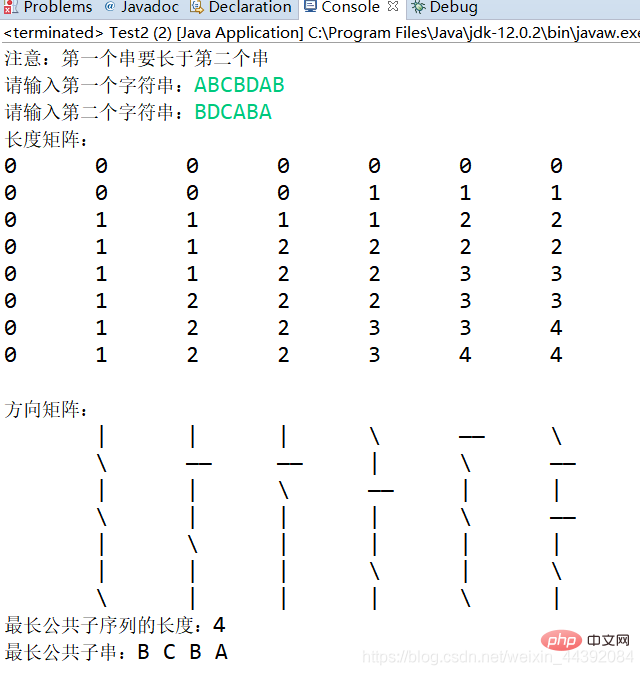
}运行结果:
相关推荐:java入门
The above is the detailed content of Algorithm learning - Java implements the longest common subsequence. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
Statement:
This article is reproduced at:csdn.net. If there is any infringement, please contact admin@php.cn delete
Previous article:How to use this keyword in java?Next article:How to use this keyword in java?

