Linux devices are hardware devices running Linux operating systems, including servers, personal computers, smartphones and embedded systems. They take advantage of the power of Linux to perform various tasks such as website hosting and big data analytics.

introduction
Linux devices, this term is not unfamiliar with the technology circle, but do you really understand it? Today, we will explore the essence of Linux devices in depth and unveil its mystery. Through this article, you will not only understand what a Linux device is, but also master how to interact with it and how to use its powerful features to improve your productivity.
A Linux device, as the name implies, is a hardware device running a Linux operating system. They can be servers, personal computers, smartphones, or even embedded systems. Linux's flexibility and open source features make it the preferred operating system for many devices. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced Linux user, this article will provide you with valuable insights and practical tips.
Review of basic knowledge
Before we dive into Linux devices, let's review some basic concepts first. Linux is an open source operating system based on Unix, originally developed by Linus Torvalds in 1991. It is known for its stability, security and customizability. Linux devices can run on a variety of hardware, from supercomputers to IoT devices, all inclusive.
The core of Linux is the kernel, which is responsible for managing hardware resources and providing basic services. In addition, Linux also includes a range of tools and applications, which are maintained and developed by the global developer community. Understanding these basics is essential for us to further explore Linux devices.
Core concept or function analysis
Definition and function of Linux devices
A Linux device refers to any hardware device running a Linux operating system. They can be physical devices such as servers, desktop computers, laptops, smartphones, etc., or virtual devices such as virtual machines or containers. The role of Linux devices is to leverage the power of the Linux operating system to perform various tasks, from simple file management to complex scientific computing, and everything can be done.
For example, a typical Linux server can be used to host websites, run databases, process big data analysis and other tasks. Here is a simple example showing how to install a web server on a Linux device:
# Update package list sudo apt update # Install Apache Web Server sudo apt install apache2 # Start the Apache service sudo systemctl start apache2 # Check whether Apache is running sudo systemctl status apache2
This example shows how to install and start an Apache web server on a Linux device, reflecting the flexibility and power of a Linux device.
How it works
The working principle of Linux devices mainly relies on the Linux kernel and applications in various user spaces. The kernel is responsible for managing hardware resources, such as CPU, memory, storage devices, etc., and provides basic services, such as process scheduling, memory management, file system management, etc.
User space applications interact with the kernel through system calls to perform various tasks. The flexibility of Linux devices lies in their modular design, where users can load or uninstall kernel modules according to their needs and customize system functions.
For example, file system management of Linux devices is a key feature. Linux uses virtual file system (VFS) to abstract different types of file systems, allowing users to seamlessly access various storage devices. Here is a simple example showing how to mount an external storage device on a Linux device:
# Create mount point sudo mkdir /mnt/external # Mount external storage device sudo mount /dev/sdb1 /mnt/external # Check the mount df -h
This example shows how Linux devices can manage external storage devices through VFS, reflecting their powerful file system management capabilities.
Example of usage
Basic usage
The basic usage of Linux devices includes common tasks such as file management, network configuration, and software installation. Here is a simple example showing how to create and manage files on Linux devices:
# Create a new file touch newfile.txt # Edit file content echo "Hello, Linux!" > newfile.txt # View file content cat newfile.txt # Delete file rm newfile.txt
This example shows basic file management operations on Linux devices, which are simple and easy to understand and suitable for beginners to learn.
Advanced Usage
Advanced usage of Linux devices includes complex tasks such as scripting, system monitoring, and performance optimization. Here is a simple example showing how to write a simple shell script on a Linux device to automate tasks:
#!/bin/bash
# Define a function to back up the file backup_file() {
local file=$1
local backup_dir="/backup"
if [ ! -d "$backup_dir" ]; then
mkdir -p "$backup_dir"
fi
cp "$file" "$backup_dir/$(date %Y%m%d)_${file##*/}"
}
# Call function to backup a file backup_file "/etc/passwd"This example shows how to write Shell scripts on Linux devices to automate backup tasks, suitable for users with some experience to learn.
Common Errors and Debugging Tips
When using Linux devices, common errors include permission issues, dependency issues, configuration errors, etc. Here are some common errors and their debugging tips:
- Permissions issue : If you encounter permission problems, you can use the
sudocommand to increase permissions. For example,sudo apt updatecan solve the permissions issue when the package is updated. - Dependency problem : If you encounter dependency problem, you can use package management tools such as
aptoryumto solve it. For example,sudo apt install -fcan automatically resolve dependency issues. - Configuration error : If you encounter configuration errors, you can check the configuration file to ensure that the syntax is correct. For example,
sudo nano /etc/apache2/apache2.confcan edit Apache's configuration file.
These debugging tips can help you quickly solve common problems encountered on Linux devices and improve productivity.
Performance optimization and best practices
In practical applications, how to optimize the performance of Linux devices is a key issue. Here are some recommendations for performance optimization and best practices:
- Use a lightweight desktop environment : If your Linux device is a desktop computer, you can choose a lightweight desktop environment such as LXDE or Xfce to reduce resource consumption.
- Optimize kernel parameters : By adjusting kernel parameters, system performance can be improved. For example,
sysctl -w net.core.somaxconn=1024can increase the length of the TCP connection queue and improve network performance. - Using Cache and Read-Out : By using Cache and Read-Out technology, the performance of the file system can be improved. For example,
echo 1000 > /proc/sys/vm/vfs_cache_pressurecan adjust the pressure of file system cache and increase file access speed.
These performance optimizations and best practices can help you make the most of your Linux device's performance and improve productivity.
In short, Linux devices are a powerful and flexible tool, and through the introduction and examples of this article, you should have a deeper understanding of it. Whether you are a beginner or experienced user, you can benefit from it and improve your Linux skills.
The above is the detailed content of What is a Linux device?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Mastering Text Manipulation With the Sed CommandMar 16, 2025 am 09:48 AM
Mastering Text Manipulation With the Sed CommandMar 16, 2025 am 09:48 AMThe Linux command line interface provides a wealth of text processing tools, one of the most powerful tools is the sed command. sed is the abbreviation of Stream EDitor, a multi-functional tool that allows complex processing of text files and streams. What is Sed? sed is a non-interactive text editor that operates on pipeline inputs or text files. By providing directives, you can let it modify and process text in a file or stream. The most common use cases of sed include selecting text, replacing text, modifying original files, adding lines to text, or removing lines from text. It can be used from the command line in Bash and other command line shells. Sed command syntax sed
 How To Count Files And Directories In Linux: A Beginner's GuideMar 19, 2025 am 10:48 AM
How To Count Files And Directories In Linux: A Beginner's GuideMar 19, 2025 am 10:48 AMEfficiently Counting Files and Folders in Linux: A Comprehensive Guide Knowing how to quickly count files and directories in Linux is crucial for system administrators and anyone managing large datasets. This guide demonstrates using simple command-l
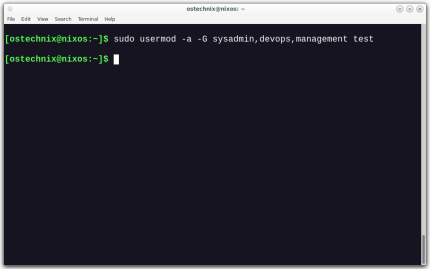 How To Add A User To Multiple Groups In LinuxMar 18, 2025 am 11:44 AM
How To Add A User To Multiple Groups In LinuxMar 18, 2025 am 11:44 AMEfficiently managing user accounts and group memberships is crucial for Linux/Unix system administration. This ensures proper resource and data access control. This tutorial details how to add a user to multiple groups in Linux and Unix systems. We
 The Secret Weapon to Supercharge Your Linux System With Liquorix KernelMar 08, 2025 pm 12:12 PM
The Secret Weapon to Supercharge Your Linux System With Liquorix KernelMar 08, 2025 pm 12:12 PMLiquorix kernel: a powerful tool to improve Linux system performance Linux is known for its flexibility, security and high performance, becoming the operating system of choice for developers, system administrators, and advanced users. However, the universal Linux kernel is not always meeting the needs of users seeking maximum performance and responsiveness. This is where the Liquorix kernel comes into play—a performance-optimized alternative that promises to enhance your Linux system. This article will explore what the Liquorix kernel is, why you might want to use it, and how to install and configure it to get the most out of your system. Liquorix kernel detailed explanation Liquorix kernel is a precompiled Linux kernel designed for
 How To Type Indian Rupee Symbol In Ubuntu LinuxMar 22, 2025 am 10:39 AM
How To Type Indian Rupee Symbol In Ubuntu LinuxMar 22, 2025 am 10:39 AMThis brief guide explains how to type Indian Rupee symbol in Linux operating systems. The other day, I wanted to type "Indian Rupee Symbol (₹)" in a word document. My keyboard has a rupee symbol on it, but I don't know how to type it. After
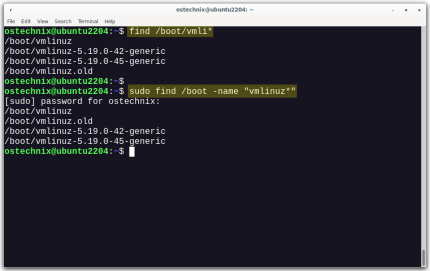 How To List Or Check All Installed Linux Kernels From CommandlineMar 23, 2025 am 10:43 AM
How To List Or Check All Installed Linux Kernels From CommandlineMar 23, 2025 am 10:43 AMLinux Kernel is the core component of a GNU/Linux operating system. Developed by Linus Torvalds in 1991, it is a free, open-source, monolithic, modular, and multitasking Unix-like kernel. In Linux, it is possible to install multiple kernels on a sing
 Locating Leviathan Files in LinuxMar 13, 2025 pm 12:11 PM
Locating Leviathan Files in LinuxMar 13, 2025 pm 12:11 PMIntroduction In the realm of Linux, where the command line is often the compass by which we navigate, the efficient management of disk space is crucial. Whether you’re sailing through personal projects or steering the ship o
![Install Fedora Linux 41 Workstation [Step-by-Step Guide]](https://img.php.cn/upload/article/001/242/473/174149047084567.png?x-oss-process=image/resize,p_40) Install Fedora Linux 41 Workstation [Step-by-Step Guide]Mar 09, 2025 am 11:21 AM
Install Fedora Linux 41 Workstation [Step-by-Step Guide]Mar 09, 2025 am 11:21 AMThis guide provides a comprehensive walkthrough for installing Fedora Linux 41 Workstation Edition. Let's get started! Table of Contents - Step 1: Prepare Your Fedora 41 Installation Media Step 2: Boot from the Fedora 41 Installation Media Step 3:


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

ZendStudio 13.5.1 Mac
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

mPDF
mPDF is a PHP library that can generate PDF files from UTF-8 encoded HTML. The original author, Ian Back, wrote mPDF to output PDF files "on the fly" from his website and handle different languages. It is slower than original scripts like HTML2FPDF and produces larger files when using Unicode fonts, but supports CSS styles etc. and has a lot of enhancements. Supports almost all languages, including RTL (Arabic and Hebrew) and CJK (Chinese, Japanese and Korean). Supports nested block-level elements (such as P, DIV),

SecLists
SecLists is the ultimate security tester's companion. It is a collection of various types of lists that are frequently used during security assessments, all in one place. SecLists helps make security testing more efficient and productive by conveniently providing all the lists a security tester might need. List types include usernames, passwords, URLs, fuzzing payloads, sensitive data patterns, web shells, and more. The tester can simply pull this repository onto a new test machine and he will have access to every type of list he needs.

WebStorm Mac version
Useful JavaScript development tools

DVWA
Damn Vulnerable Web App (DVWA) is a PHP/MySQL web application that is very vulnerable. Its main goals are to be an aid for security professionals to test their skills and tools in a legal environment, to help web developers better understand the process of securing web applications, and to help teachers/students teach/learn in a classroom environment Web application security. The goal of DVWA is to practice some of the most common web vulnerabilities through a simple and straightforward interface, with varying degrees of difficulty. Please note that this software







