
In the realm of Linux, where the command line is often the compass by which we navigate, the efficient management of disk space is crucial. Whether you’re sailing through personal projects or steering the ship of enterprise servers, large and forgotten files can be like hidden icebergs, threatening to sink your system's performance. This article serves as a detailed chart to help you uncover these lurking data giants. By mastering a few essential tools and commands, you’ll be able to not only find large files but also make informed decisions about how to handle them.
Understanding File Sizes and Disk Usage in LinuxBefore embarking on our voyage to track down large files, it's essential to have a clear understanding of file size units. Linux measures file sizes in bytes, with common conversions being 1024 bytes to a kilobyte (KB), 1024 KB to a megabyte (MB), and so on up to terabytes (TB) and beyond. The du (disk usage) command is an invaluable tool in this journey, offering insights into the space consumed by files and directories. Similarly, df (disk free) tells us about the overall disk space and its availability, giving a bird's-eye view of our storage landscape.
The find Command: Searching for Large FilesThe find command in Linux is a powerful utility for seeking out files that meet specific criteria. To hone in on large files, we can employ the find command with size options:
find / -type f -size 100M
This command line incantation will list all files larger than 100 megabytes from the root directory. It's possible to modify the search criteria for a range of sizes or to execute actions on the files that are found, such as removing them with -exec rm {} \; appended to the command.
The du Command: Assessing File and Directory SizesWhile find is excellent for pinpointing files, du dives deeper, allowing us to understand the sizes of directories as well:
du -h --max-depth=1 /var | sort -hr | head -10
This chain of commands will display the sizes of directories within /var, sort them in descending order, and show the top 10. This is incredibly useful for uncovering directories that have grown unexpectedly bulky.
Graphical Tools for Finding Large FilesFor those who prefer a visual approach, Linux doesn't disappoint. Tools like Baobab (for GNOME users) and KDiskFree (for KDE) provide a graphical interface to analyze disk usage. They are often more intuitive for beginners and offer a visual breakdown of disk space consumption. Installation is typically a breeze through the system's package manager, and usage is as simple as launching the application and selecting a drive to scan.
Advanced Methods: ncdu and ls Command TricksBeyond the basics lies ncdu, a simple yet robust utility that presents a disk usage analyzer with an ncurses interface, allowing users to navigate through the directory structure. Once installed via the package manager, you can launch it with ncdu /, and it will analyze the directory sizes interactively.
Additionally, the ls command can be coaxed into listing files by size with:
ls -lShr
Here, -l lists files in long format, -S sorts by file size, -h gives human-readable sizes, and -r reverses the order, showing the smallest files last.
Managing Large Files: Best PracticesUpon locating the titans of data, one must decide whether to compress, move, or delete them. It's a good practice to back up files before taking any action, especially if they're not well documented. Safely removing files can be done with the rm command, but one must always be cautious and ensure that the files are not required by any system processes or applications.
Automating the Hunt: Scripting for Regular MonitoringTo keep a constant watch for large files, one can write simple bash scripts that utilize the find or du commands and schedule them with cron jobs to run at regular intervals. The script can output its findings to a log file or even email a report to the system administrator.
ConclusionWith the tools and techniques outlined in this guide, you are now well-equipped to embark on a quest for large files within the Linux file system. Integrating these practices into your regular system maintenance will help ensure smooth sailing and prevent the potential chaos caused by unchecked data growth. As you become more familiar with these methods, you will no doubt discover additional tricks to keep your system efficient and responsive.
The above is the detailed content of Locating Leviathan Files in Linux. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
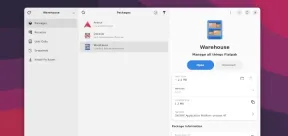 Warehouse: A GUI for Effortlessly Handling Flatpak AppsMay 09, 2025 am 11:30 AM
Warehouse: A GUI for Effortlessly Handling Flatpak AppsMay 09, 2025 am 11:30 AMA GUI for Effortless Flatpak Management: Introducing Warehouse Managing a growing collection of Flatpak applications can be cumbersome using only the command line. Enter Warehouse, a user-friendly graphical interface designed to streamline Flatpak a
 8 Powerful Linux Commands to Identify Hard Drive BottlenecksMay 09, 2025 am 11:03 AM
8 Powerful Linux Commands to Identify Hard Drive BottlenecksMay 09, 2025 am 11:03 AMThis article provides a comprehensive guide to identifying and resolving hard drive bottlenecks in Linux systems. Experienced server administrators will find this particularly useful. Slow disk operations can severely impact application performance,
 4 Best QR Code Generators for Linux UsersMay 09, 2025 am 10:27 AM
4 Best QR Code Generators for Linux UsersMay 09, 2025 am 10:27 AMEfficient QR code generation tool under Linux system In today's digital world, QR codes have become a way to quickly and conveniently share information, simplifying data access from URLs, texts, contacts, Wi-Fi credentials, and even payment information. Linux users can use a variety of tools to create QR codes efficiently. Let's take a look at some popular QR code generators that can be used directly on Linux systems. QRencode QRencode is a lightweight command line tool for generating QR codes on Linux. It is well-received for its simplicity and efficiency and is popular with Linux users who prefer direct methods. Using QRencode, you can use the URL,
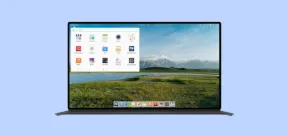 elementary OS 8: A User-Friendly Linux for macOS and WindowsMay 09, 2025 am 10:19 AM
elementary OS 8: A User-Friendly Linux for macOS and WindowsMay 09, 2025 am 10:19 AMElementary OS 8 Circe: A Smooth and Stylish Linux Experience Elementary OS, a Ubuntu-based Linux distribution, has evolved from a simple theme pack into a fully-fledged, independent operating system. Known for its user-friendly interface, elegant de
 40 Linux Commands for Every Machine Learning EngineerMay 09, 2025 am 10:06 AM
40 Linux Commands for Every Machine Learning EngineerMay 09, 2025 am 10:06 AMMastering Linux is crucial for any machine learning (ML) engineer. Its command-line interface offers unparalleled flexibility and control, streamlining workflows and boosting productivity. This article outlines essential Linux commands, explained fo
 Arch Linux Cheat Sheet: Essential Commands for BeginnersMay 09, 2025 am 09:54 AM
Arch Linux Cheat Sheet: Essential Commands for BeginnersMay 09, 2025 am 09:54 AMArch Linux: A Beginner's Command-Line Cheat Sheet Arch Linux offers unparalleled control but can feel daunting for newcomers. This cheat sheet provides essential commands to confidently manage your system. System Information & Updates These com
 How to Install Scikit-learn for Machine Learning on LinuxMay 09, 2025 am 09:53 AM
How to Install Scikit-learn for Machine Learning on LinuxMay 09, 2025 am 09:53 AMThis guide provides a comprehensive walkthrough of installing and using the Scikit-learn machine learning library on Linux systems. Scikit-learn (sklearn) is a powerful, open-source Python library offering a wide array of tools for various machine l
 How to Install Kali Linux Tools in UbuntuMay 09, 2025 am 09:46 AM
How to Install Kali Linux Tools in UbuntuMay 09, 2025 am 09:46 AMThis guide explains how to leverage Docker for accessing Kali Linux tools, a safer and more efficient alternative to outdated methods like Katoolin. Katoolin is no longer actively maintained and may cause compatibility problems on modern systems. Do


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Safe Exam Browser
Safe Exam Browser is a secure browser environment for taking online exams securely. This software turns any computer into a secure workstation. It controls access to any utility and prevents students from using unauthorized resources.

EditPlus Chinese cracked version
Small size, syntax highlighting, does not support code prompt function

ZendStudio 13.5.1 Mac
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

PhpStorm Mac version
The latest (2018.2.1) professional PHP integrated development tool

WebStorm Mac version
Useful JavaScript development tools






