Home >System Tutorial >LINUX >How To Count Files And Directories In Linux: A Beginner's Guide
How To Count Files And Directories In Linux: A Beginner's Guide
- Christopher NolanOriginal
- 2025-03-19 10:48:241003browse
Efficiently Counting Files and Folders in Linux: A Comprehensive Guide
Knowing how to quickly count files and directories in Linux is crucial for system administrators and anyone managing large datasets. This guide demonstrates using simple command-line tools like find, wc, and ls to accurately determine the number of files and folders in Linux and Unix systems.
Table of Contents
- Counting Files in a Directory with
find - Counting Directories with
find - Advanced Counting with
find'smaxdepthandmindepthOptions- Counting Files within a Specific Depth Range
- Counting Directories at a Specific Depth
- Excluding the Top-Level Directory
- Counting Up to a Specific Depth
- Best Practices
- Counting Directories with
ls - Why
findandlsMight Produce Different Counts - Summary
Counting Files in a Directory with find
To count all files within a directory and its subdirectories, use find combined with wc -l:
find /path/to/your/directory -type f | wc -l
-
find /path/to/your/directory: Initiates the search. -
-type f: Specifies that only files should be found (not directories). -
|: Pipes thefindoutput towc -l. -
wc -l: Counts the lines (each line represents a file).
Example:
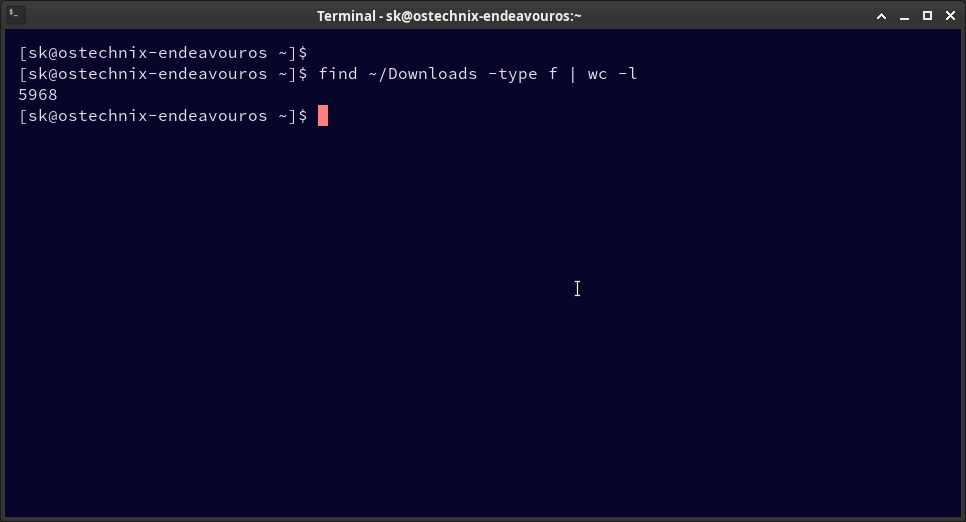
find ~/Downloads -type f | wc -l 5968
This indicates 5968 files in the Downloads directory.
Counting Directories with find
To count directories, use find with the -type d option:
find /path/to/the/directory -type d | wc -l
-
-type d: Specifies that only directories should be found.
Example:
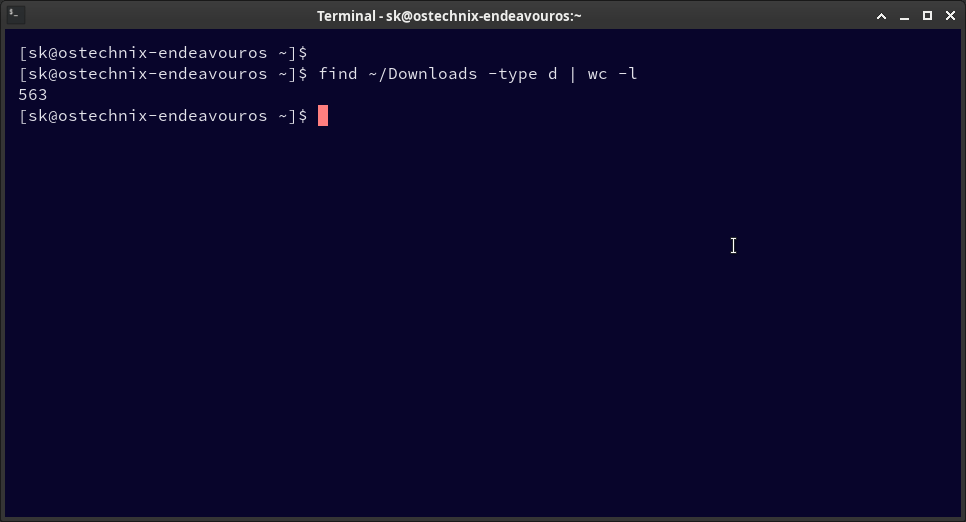
find ~/Downloads -type d | wc -l 563
This shows 563 directories (including the root directory) within ~/Downloads.
Remember to subtract 1 from the result if you need to exclude the root directory itself.
Advanced Counting with find's maxdepth and mindepth
The maxdepth and mindepth options provide fine-grained control over the search depth.
- Counting Files within a Specific Depth Range: Count files exactly two levels deep:
find /path/to/directory -mindepth 2 -maxdepth 2 -type f | wc -l
- Counting Directories at a Specific Depth: Count directories exactly three levels deep:
find /path/to/directory -mindepth 3 -maxdepth 3 -type d | wc -l
- Excluding the Top-Level Directory: Count files, excluding the top-level directory:
find /path/to/directory -mindepth 1 -type f | wc -l
- Counting Up to a Specific Depth: Count all files up to and including the second level:
find /path/to/directory -maxdepth 2 -type f | wc -l
Best Practices:
- Clearly define your target (files, directories, or both).
- Use
maxdepthandmindepthfor performance optimization in large directories. - Test your command on a small sample before running it on a large directory structure.
Counting Directories with ls
Another approach uses ls, grep, and wc:
ls -lR | grep ^d | wc -l
-
ls -lR: Lists all files and directories recursively with details. -
grep ^d: Filters for lines starting with "d" (directories). -
wc -l: Counts the lines.
This method might yield different results than find due to handling of hidden directories and the root directory.
Why find and ls Might Produce Different Counts
Discrepancies can arise because:
-
Hidden Directories:
findincludes hidden directories by default, whilelstypically doesn't (unless the-aoption is used). -
Root Directory Inclusion:
findincludes the root directory in its count, whilelsmay not, depending on interpretation.
Summary
Using find, ls, and wc, you can efficiently count files and directories in Linux. Understanding the nuances of each command and its options ensures accurate and efficient results, regardless of directory size or complexity. Remember to choose the method best suited to your specific needs and always test your command before applying it to a large directory structure.
The above is the detailed content of How To Count Files And Directories In Linux: A Beginner's Guide. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

