本文实例讲述了python开发之tkinter实现图形随鼠标移动的方法。分享给大家供大家参考,具体如下:
做这个东西的时候,灵感源自于一个js效果:
两个眼睛随鼠标移动而移动
运行效果:
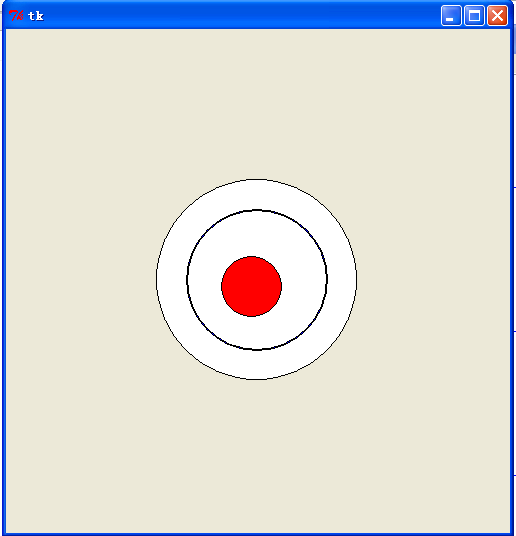
代码部分:
from tkinter import *
#1.获取到小圆当前的圆心坐标(x1, y1)
#2.获取到小圆移动的圆心坐标(x2, y2)
#3.把小圆从坐标(x1, y1)移动到坐标(x2, y2)
__author__ = {'name' : 'Hongten',
'mail' : 'hongtenzone@foxmail.com',
'blog' : 'http://blog.csdn.net/',
'QQ': '648719819',
'created' : '2013-09-20'}
class Eay(Frame):
def createWidgets(self):
## The playing field
self.draw = Canvas(self, width=500, height=500)
#鼠标位置
self.mouse_x = 450
self.mouse_y = 250
#圆心坐标(x,y)
self.oval_zero_x = 250
self.oval_zero_y = 250
#外面大圆半径
self.oval_r = 100
#里面小圆半径
self.oval_R = 30
self.oval_r1 = self.oval_r - self.oval_R + 0.5
self.oval_r2 = self.oval_r - self.oval_R - 0.5
#小圆
self.letter_ball_x1 = 250
self.letter_ball_y1 = 250
# The ball 外面大圆
self.ball = self.draw.create_oval((self.oval_zero_x - self.oval_r),
(self.oval_zero_y - self.oval_r),
(self.oval_zero_x + self.oval_r),
(self.oval_zero_y + self.oval_r),
fill="white")
self.ball = self.draw.create_oval((self.oval_zero_x - self.oval_r1),
(self.oval_zero_y - self.oval_r1),
(self.oval_zero_x + self.oval_r1),
(self.oval_zero_y + self.oval_r1),
fill="blue")
self.ball = self.draw.create_oval((self.oval_zero_x - self.oval_r2),
(self.oval_zero_y - self.oval_r2),
(self.oval_zero_x + self.oval_r2),
(self.oval_zero_y + self.oval_r2),
fill="white")
#里面小圆
self.ball_over = self.draw.create_oval((self.oval_zero_x - self.oval_R),
(self.oval_zero_y - self.oval_R),
(self.oval_zero_x + self.oval_R),
(self.oval_zero_y + self.oval_R),
fill="red")
self.draw.pack(side=LEFT)
def mouseMove(self, event):
self.mouse_x = event.x
self.mouse_y = event.y
if SHOW_LOG:
print('#' * 50)
print('鼠标的坐标为:({}, {})'.format(self.mouse_x, self.mouse_y))
print('小圆当前坐标为:({}, {})'.format(self.letter_ball_x1, self.letter_ball_y1))
'''获取到小圆移动的圆心坐标(x2, y2)'''
ax_x = abs(self.mouse_x - self.oval_zero_x)
ax_y = abs(self.mouse_y - self.oval_zero_y)
if SHOW_LOG:
print('坐标A(oval_zero_x, oval_zero_y)到坐标X(mouse_x, mouse_y)的距离为AX')
print('AX中ax_x = {}, ax_y = {}'.format(ax_x, ax_y))
ax_len = ((ax_x ** 2) + (ax_y ** 2))**0.5
if SHOW_LOG:
print('AX的长度为:{}'.format(ax_len))
#如果鼠标坐标在(ax_len > |r-R|)
if ax_len > abs(self.oval_r - self.oval_R):
ac_len = abs(self.oval_r - self.oval_R)
if SHOW_LOG:
print('AC的产度为:{}'.format(ac_len))
if int(self.mouse_x - self.oval_zero_x) != 0:
if int(self.mouse_y - self.oval_zero_y) != 0:
#求直线斜率 y = kx + b
k = (self.mouse_y - self.oval_zero_y)/(self.mouse_x - self.oval_zero_x)
if SHOW_LOG:
print('鼠标到大圆圆心的直线的斜率为:{}'.format(k))
b = self.mouse_y - (k * self.mouse_x)
###################################################
#小圆移动后的坐标
#这里有三个条件:
# 1.小圆的圆心坐标(x1, y1)在直线AC上(y = kx + b)
# 2.(r-R)^2 = x1^2 + y1^2 由1,2可以得到 => (r-R)^2 = x1^2 + 2*x1*k*b + b^2 => x1有两个值,通过3判断x1的符号,从而求出y1
# 3.if self.mousex_x > 0:
# x1 > 0
#这是一个二元二次方程,方程的解有两组,不过通过鼠标的位置self.mouse_x(self.mouse_y)可以判断圆心坐标x1(y1)
letter_ball_x2 = ((ac_len * (abs(self.mouse_x - self.oval_zero_x)))/ax_len) + self.letter_ball_x1
letter_ball_y2 = (letter_ball_x2 * k) + b
if SHOW_LOG:
print('小圆当前坐标为:({}, {})'.format(self.letter_ball_x1, self.letter_ball_y1))
print('小圆移动后坐标为:({}, {})'.format(letter_ball_x2, letter_ball_y2))
#把小圆从坐标(x1, y1)移动到坐标(x2, y2)
self.moved_x2 = letter_ball_x2 - self.letter_ball_x1
self.moved_y2 = letter_ball_y2 - self.letter_ball_y1
if SHOW_LOG:
print('需要移动的距离是:({}, {})'.format(int(self.moved_x2), int(self.moved_y2)))
self.draw.move(self.ball_over, int(self.moved_x2), int(self.moved_y2))
self.letter_ball_x1 = letter_ball_x2
self.letter_ball_y1 = letter_ball_y2
else:
print('鼠标在X轴上')
else:
print('鼠标在Y轴上')
else:
if SHOW_LOG:
print('小圆的移动后的坐标就是鼠标坐标')
#小圆移动后的坐标
letter_ball_x2 = self.mouse_x
letter_ball_y2 = self.mouse_y
if SHOW_LOG:
print('小圆移动后坐标为:({}, {})'.format(letter_ball_x2, letter_ball_y2))
#把小圆从坐标(x1, y1)移动到坐标(x2, y2)
self.moved_x2 = letter_ball_x2 - self.letter_ball_x1
self.moved_y2 = letter_ball_y2 - self.letter_ball_y1
if SHOW_LOG:
print('需要移动的距离是:({}, {})'.format(int(self.moved_x2), int(self.moved_y2)))
self.draw.move(self.ball_over, int(self.moved_x2), int(self.moved_y2))
self.letter_ball_x1 = letter_ball_x2
self.letter_ball_y1 = letter_ball_y2
def move_ball(self, *args):
#当鼠标在窗口中按下左键拖动的时候执行
#Widget.bind(self.draw, "<B1-Motion>", self.mouseMove)
#当鼠标在大圆内移动的时候执行
self.draw.tag_bind(self.ball, "<Any-Enter>", self.mouseMove)
def __init__(self, master=None):
global letter_ball_x2
letter_ball_x2 = 0
global letter_ball_y2
letter_ball_y2 = 0
global SHOW_LOG
SHOW_LOG = True
Frame.__init__(self, master)
Pack.config(self)
self.createWidgets()
self.after(10, self.move_ball)
game = Eay()
game.mainloop()
希望本文所述对大家Python程序设计有所帮助。
 What are some common operations that can be performed on Python arrays?Apr 26, 2025 am 12:22 AM
What are some common operations that can be performed on Python arrays?Apr 26, 2025 am 12:22 AMPythonarrayssupportvariousoperations:1)Slicingextractssubsets,2)Appending/Extendingaddselements,3)Insertingplaceselementsatspecificpositions,4)Removingdeleteselements,5)Sorting/Reversingchangesorder,and6)Listcomprehensionscreatenewlistsbasedonexistin
 In what types of applications are NumPy arrays commonly used?Apr 26, 2025 am 12:13 AM
In what types of applications are NumPy arrays commonly used?Apr 26, 2025 am 12:13 AMNumPyarraysareessentialforapplicationsrequiringefficientnumericalcomputationsanddatamanipulation.Theyarecrucialindatascience,machinelearning,physics,engineering,andfinanceduetotheirabilitytohandlelarge-scaledataefficiently.Forexample,infinancialanaly
 When would you choose to use an array over a list in Python?Apr 26, 2025 am 12:12 AM
When would you choose to use an array over a list in Python?Apr 26, 2025 am 12:12 AMUseanarray.arrayoveralistinPythonwhendealingwithhomogeneousdata,performance-criticalcode,orinterfacingwithCcode.1)HomogeneousData:Arrayssavememorywithtypedelements.2)Performance-CriticalCode:Arraysofferbetterperformancefornumericaloperations.3)Interf
 Are all list operations supported by arrays, and vice versa? Why or why not?Apr 26, 2025 am 12:05 AM
Are all list operations supported by arrays, and vice versa? Why or why not?Apr 26, 2025 am 12:05 AMNo,notalllistoperationsaresupportedbyarrays,andviceversa.1)Arraysdonotsupportdynamicoperationslikeappendorinsertwithoutresizing,whichimpactsperformance.2)Listsdonotguaranteeconstanttimecomplexityfordirectaccesslikearraysdo.
 How do you access elements in a Python list?Apr 26, 2025 am 12:03 AM
How do you access elements in a Python list?Apr 26, 2025 am 12:03 AMToaccesselementsinaPythonlist,useindexing,negativeindexing,slicing,oriteration.1)Indexingstartsat0.2)Negativeindexingaccessesfromtheend.3)Slicingextractsportions.4)Iterationusesforloopsorenumerate.AlwayschecklistlengthtoavoidIndexError.
 How are arrays used in scientific computing with Python?Apr 25, 2025 am 12:28 AM
How are arrays used in scientific computing with Python?Apr 25, 2025 am 12:28 AMArraysinPython,especiallyviaNumPy,arecrucialinscientificcomputingfortheirefficiencyandversatility.1)Theyareusedfornumericaloperations,dataanalysis,andmachinelearning.2)NumPy'simplementationinCensuresfasteroperationsthanPythonlists.3)Arraysenablequick
 How do you handle different Python versions on the same system?Apr 25, 2025 am 12:24 AM
How do you handle different Python versions on the same system?Apr 25, 2025 am 12:24 AMYou can manage different Python versions by using pyenv, venv and Anaconda. 1) Use pyenv to manage multiple Python versions: install pyenv, set global and local versions. 2) Use venv to create a virtual environment to isolate project dependencies. 3) Use Anaconda to manage Python versions in your data science project. 4) Keep the system Python for system-level tasks. Through these tools and strategies, you can effectively manage different versions of Python to ensure the smooth running of the project.
 What are some advantages of using NumPy arrays over standard Python arrays?Apr 25, 2025 am 12:21 AM
What are some advantages of using NumPy arrays over standard Python arrays?Apr 25, 2025 am 12:21 AMNumPyarrayshaveseveraladvantagesoverstandardPythonarrays:1)TheyaremuchfasterduetoC-basedimplementation,2)Theyaremorememory-efficient,especiallywithlargedatasets,and3)Theyofferoptimized,vectorizedfunctionsformathematicalandstatisticaloperations,making


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

MinGW - Minimalist GNU for Windows
This project is in the process of being migrated to osdn.net/projects/mingw, you can continue to follow us there. MinGW: A native Windows port of the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC), freely distributable import libraries and header files for building native Windows applications; includes extensions to the MSVC runtime to support C99 functionality. All MinGW software can run on 64-bit Windows platforms.

SAP NetWeaver Server Adapter for Eclipse
Integrate Eclipse with SAP NetWeaver application server.

Safe Exam Browser
Safe Exam Browser is a secure browser environment for taking online exams securely. This software turns any computer into a secure workstation. It controls access to any utility and prevents students from using unauthorized resources.

mPDF
mPDF is a PHP library that can generate PDF files from UTF-8 encoded HTML. The original author, Ian Back, wrote mPDF to output PDF files "on the fly" from his website and handle different languages. It is slower than original scripts like HTML2FPDF and produces larger files when using Unicode fonts, but supports CSS styles etc. and has a lot of enhancements. Supports almost all languages, including RTL (Arabic and Hebrew) and CJK (Chinese, Japanese and Korean). Supports nested block-level elements (such as P, DIV),

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools






