PHP $_POST variable
In PHP, the predefined $_POST variable is used to collect values from the form with method="post".
$_POST variable
The predefined $_POST variable is used to collect values from the form with method="post".
Information sent from a form with the POST method is invisible to anyone (will not be displayed in the browser's address bar), and there is no limit on the amount of information sent.
Note: However, by default, the maximum amount of information sent by the POST method is 8 MB (can be changed by setting post_max_size in the php.ini file).
Example
form.html file code is as follows:
<html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <title>php中文网(php.cn)</title> </head> <body> <form action="welcome.php" method="post"> 名字: <input type="text" name="fname"> 年龄: <input type="text" name="age"> <input type="submit" value="提交"> </form> </body> </html>
When the user clicks the "Submit" button, the URL is similar to the following:
http: //www.php.cn/welcome.php
"welcome.php" file can now collect form data through the $_POST variable (please note that the name of the form field will automatically become $_POST key in the array):
Welcome<?php echo $_POST["fname"]; ?>!<br>
Your age is<?php echo $ _POST["age"]; ?> years old.
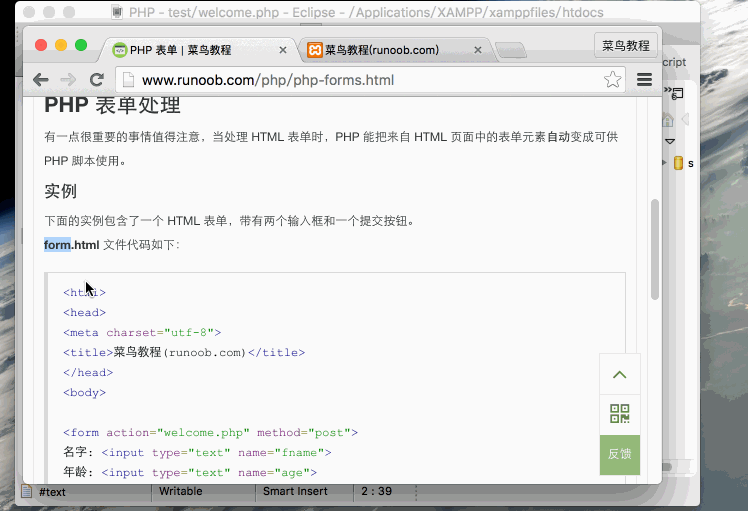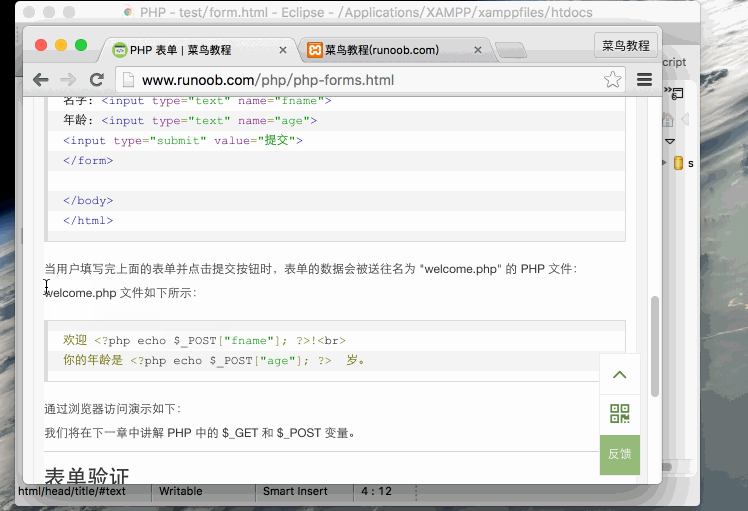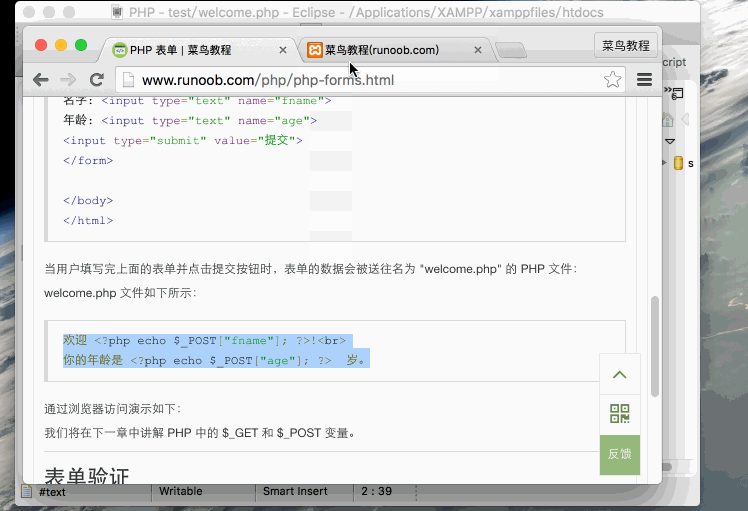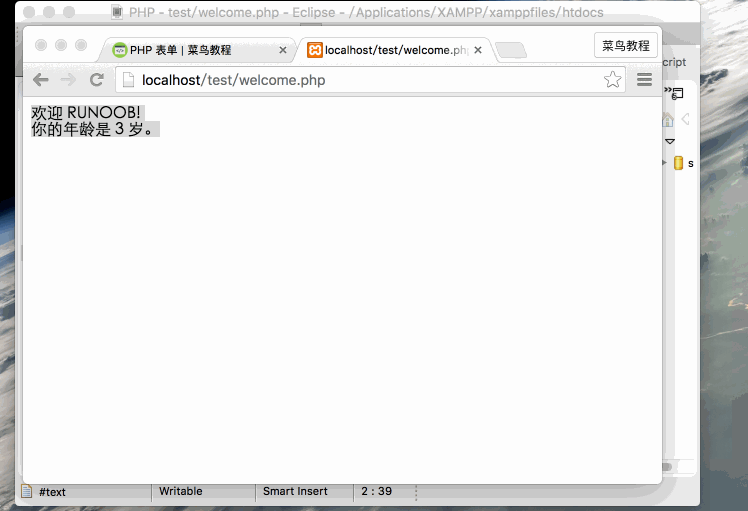
Access the demonstration through the browser as follows:
When to use method="post "?
Information sent from a form with the POST method is not visible to anyone, and there is no limit on the amount of information sent.
However, since the variable does not appear in the URL, the page cannot be bookmarked.
PHP $_REQUEST variable
The predefined $_REQUEST variable contains the contents of $_GET, $_POST and $_COOKIE.
$_REQUEST variable can be used to collect form data sent via GET and POST methods.
Example
You can modify the "welcome.php" file to the following code, which can accept $_GET, $_POST and other data.
Welcome<?php echo $_REQUEST["fname"]; ?>!<br>
Your age is<?php echo $_REQUEST["age"] ; ?> years old.
