PHP form validation
HTML Form Validation
When the form is used to collect customer input information, do not take it for granted that the customer will input the required content as expected. Customer input must be strictly checked at all times.
Client-side verification
Client-side form verification is generally a verification method based on Javascript scripts. This verification method can effectively reduce the burden on the server and can also instantly remind customers of input errors.
Server-side verification
In some cases, in addition to client-side verification, server-side verification may also be required (such as accessing the database). At this time, logical verification needs to be done in the PHP program.
We need to consider security when processing PHP forms.
In this chapter we will demonstrate the secure processing of PHP form data. In order to prevent hackers and spam, we need to perform data security verification on the form.
The HTML form introduced in this chapter contains the following input fields: required and optional text fields, radio buttons, and submit buttons:
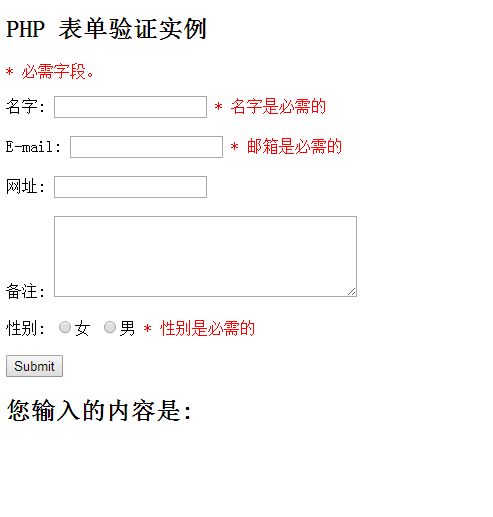 View Code »
View Code »
The above form validation rules are as follows:
Fields Validation rules
#Name + Can only contain letters and spaces
Text field
The "Name", "E-mail", and "Website" fields are text input elements, and the "Remarks" field is a textarea. The HTML code is as follows:
"Name": <input type="text" name="name">
E-mail: <input type="text" name="email ">
URL: <input type="text" name="website">
Remarks: <textarea name="comment" rows="5" cols="40">< /textarea>
Radio button
The "Gender" field is a radio button, the HTML code is as follows:
HTML form code is as follows:
<form method="post" action="<?php echo htmlspecialchars($_SERVER["PHP_SELF"]);?>">
This form uses the method="post" method to submit data.
The htmlspecialchars() function converts some predefined characters into HTML entities. The predefined characters for
are:
& (ampersand) becomes &
" (double quotation mark) becomes "
' (single quotation mark ) become'
< (less than) become<
> (greater than) become>
Things that need attention in PHP forms Where?
##$_SERVER["PHP_SELF"] variables may be used by hackers!
When hackers use cross-site scripting HTTP links to attack, the $_SERVER["PHP_SELF"] server variable will also be embedded in the script. The reason is that cross-site scripting is appended to the path of the executable file, so the string of $_SERVER["PHP_SELF"] will contain the JavaScript program code behind the HTTP link.
XSS is also called CSS (Cross-Site Script), a cross-site scripting attack. Malicious attackers insert malicious HTML code into a Web page. When a user browses the page, the HTML code embedded in the Web page will be executed, thereby achieving the special purpose of the malicious user.
Specify the following form file name as "test_form.php":
<?php echo $_SERVER["PHP_SELF"];?>">
Now, we use the URL to specify the submission address "test_form.php", the above code is modified as follows ;
However, considering that the user will enter the following address in the browser address bar:
How to avoid $_SERVER["PHP_SELF"] from being exploited?
$_SERVER["PHP_SELF"] can be avoided by using the htmlspecialchars() function.
The form code is as follows:
;
htmlspecialchars() Convert some predefined characters into HTML entities. Now if the user wants to take advantage of the PHP_SELF variable, the result will be output as follows: ,,,,, The vulnerability failed!
This code will not be executed because it will be saved as HTML escaped code, as shown below: 'http://www.php.cn')</script>
Use the PHP stripslashes() function to remove backslashes (\) in user input data
Next let us write these filtering functions in a function we define, so It can greatly improve the reusability of code.
Name the function test_input().
Now, we can use the test_input() function to detect all variables in $_POST. The script code is as follows:
Example
<?php
// 定义变量并默认设置为空值
$name = $email = $gender = $comment = $website = "";
if($_SERVER["REQUEST_METHOD"] == "POST")
{
$name = test_input($_POST["name"]);
$email = test_input($_POST["email"]);
$website = test_input($_POST["website"]);
$comment = test_input($_POST["comment"]);
$gender = test_input($_POST["gender"]);
}
function test_input($data)
{
$data = trim($data);
$data = stripslashes($data);
$data = htmlspecialchars($data);
return $data;
}
?>Note that we are When the above script is executed, $_SERVER["REQUEST_METHOD"] will be used to detect whether the form has been submitted. If REQUEST_METHOD is POST, the form will be submitted - and the data will be validated. If the form is not submitted validation will be skipped and displayed blank. The use of input items in the above examples is optional, and it can be displayed normally even if the user does not enter any data. In the next chapter we will introduce how to verify the data entered by the user. 