CSS元素的单位与选择器的学习与运用
1、css的元素单位包括px、rm、rem,px是像素单位,相对于显示器,em是元素单位,相对于当前元素或父元素大小,默认1em=16px,rem是根元素单位,相对于根元素html字体大小,默认1rem=16px。
实例
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>CSS中常用的三种单位案例</title>
</head>
<body>
<div class="px">px</div>
<div class="em">em</div>
<div class="rem">rem</div>
<style type="text/css">
html{
/*浏览器默认字体大小*/
font-size:21px;
}
/*1、px 屏幕像素,相对于显示器*/
.px{
font-size:20px;
width:100px;
height:100px;
background-color: lightgreen;
text-align: center;
line-height: 100px;
}
/*2、em 元素单位,相对当前元素字体大小,1em=16px*/
.em{
font-size: 20px;/*1em=20px*/
width:5em;
height:5em;
background-color: lightblue;
text-align:center;
line-height:100px;
}
/*3、rem 根元素单位 r=root,1rem=1em=16px*/
.rem{
font-size: 1.25rem;
width:6.25rem;
height:6.25rem;
background-color:lightcoral;
text-align: center;
line-height: 6.25rem;
}
</style>
</body>
</html>运行实例 »
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
执行结果:
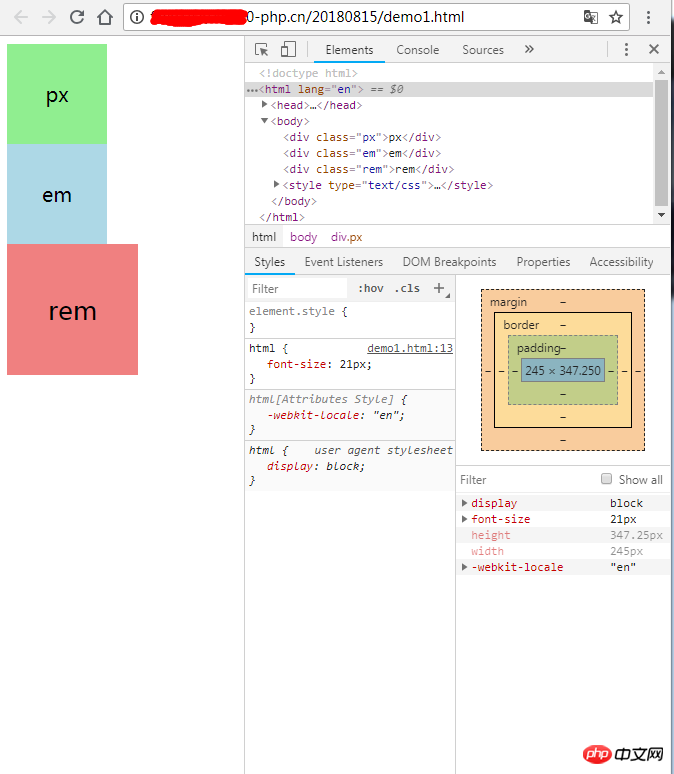
执行结果说明,px相对于显示器,em相对于当前元素或父元素大小,rem相对于根元素html字体大小。
2、css选择器可以分成四种,根据元素特征的选择器,根据元素位置的选择器,根据元素分组的选择器,伪类选择器。
实例
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>CSS中常用的选择器</title>
</head>
<style type="text/css">
/*一、根据元素特征选择:标签、id、class、属性*/
span{
background-color:red;
}
div{
width:100px;
height:100px;
color:#fff;
}
#trait2{
background-color:pink;
}
.trait3{
background-color:blue;
}
div[class="trait4"]{
background-color:green;
}
div[class^="aaa"]{
background-color:#993366;
}
div[class$="ccc"]{
background-color: #336699;
}
div[class*="ddd"]{
background-color: #669933;
}
</style>
<body>
<p>第一类:根据元素特征</p>
<div class="trait1"><span>标签选择器</span></div>
<div id="trait2" class="trait2">id选择器</div>
<div class="trait3">class/类选择器</div>
<div class="trait4">普通属性选择器</div>
<div class="aaa bbb">匹配属性以某字母开头属性选择器</div>
<div class="bbb ccc">匹配属性以某字母结尾属性选择器</div>
<div class="bbb ccc ddd">匹配属性包含某字母属性选择器</div>
<style type="text/css">
/*二、根据元素位置(也叫上下文)*/
div.location1 p{
background-color:red;
}
div>p.test{
background-color:pink;
}
div[class="location3"]{
color: blue;
}
div[class="location3"]~*{
background-color: blue;
}
div.location4{
background-color: #fff;
color:green;
}
.location4+.location5{
background-color: green;
}
</style>
<p>第二类:根据元素位置(也叫上下文)</p>
<div class="location1"><p>根据祖先元素定位选择的元素</p></div>
<div class="location2"><p class="test">根据父元素定位选择的元素</p></div>
<div class="location3">根据相邻元素定位选择的元素</div>
<div>根据相邻元素定位选择的元素测试数据</div>
<div>根据相邻元素定位选择的元素测试数据</div>
<div class="location4">根据相邻兄弟元素定位选择的元素</div>
</body>
<div class="location5">根据相邻兄弟元素定位选择的元素测试数据</div>
<style type="text/css">
/*三、根据元素分组*/
div.div,h2.h2,p.p{
width:50px;
height:50px;
background-color: lightblue;
}
</style>
<p style="background-color:#fff;color:#000;">第三类:根据元素分组</p>
<div class="div">div</div>
<h2 class="h2">h2</h2>
<p class="p">p</p>
<style type="text/css">
p[class="weilei"]~*{
background-color: #fff;
}
a:hover{
color:red;
}
li:first-child{
background-color: pink;
}
li:last-child{
background-color: gray;
}
li:nth-child(2){
background-color: green;
}
li:nth-last-child(2){
background-color: red;
}
:empty{
width:100px;
height:100px;
background-color:pink!important;
}
</style>
<p class="weilei" style="background-color:#fff;color:#000;">第四类:伪类选择器</p>
<a href="#">php中文网</a>
<ul>
<li class="wl1">
<p>wl1</p>
</li>
<li class="wl2">
<p>wl2</p>
</li>
<li class="wl3">
<p>wl3</p>
</li>
<li class="wl4">
<p>wl4</p>
</li>
<li class="wl5">
<p>wl5</p>
</li>
<li class="wl6">
<p>wl6</p>
</li>
<li class="wl7">
<p>wl7</p>
</li>
</ul>
<div></div>
</body>
</html>运行实例 »
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
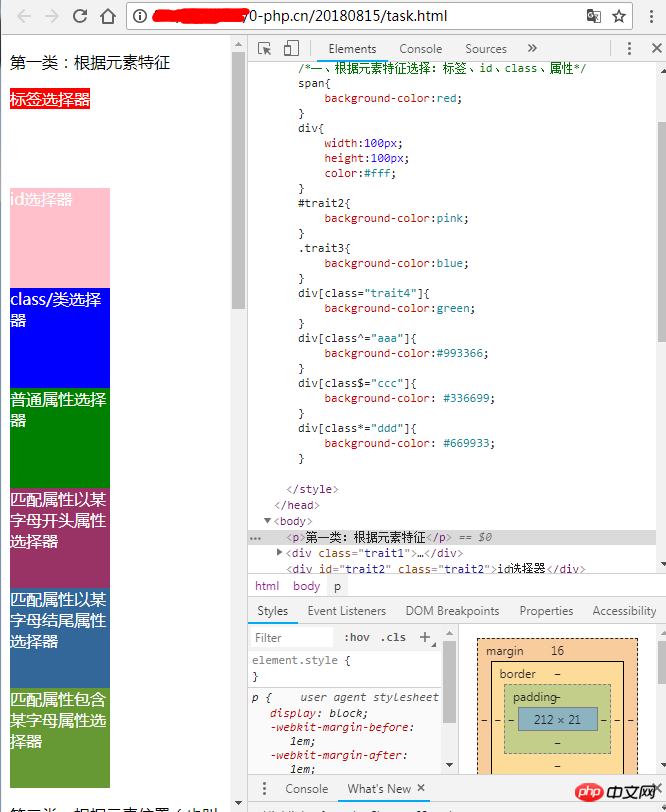
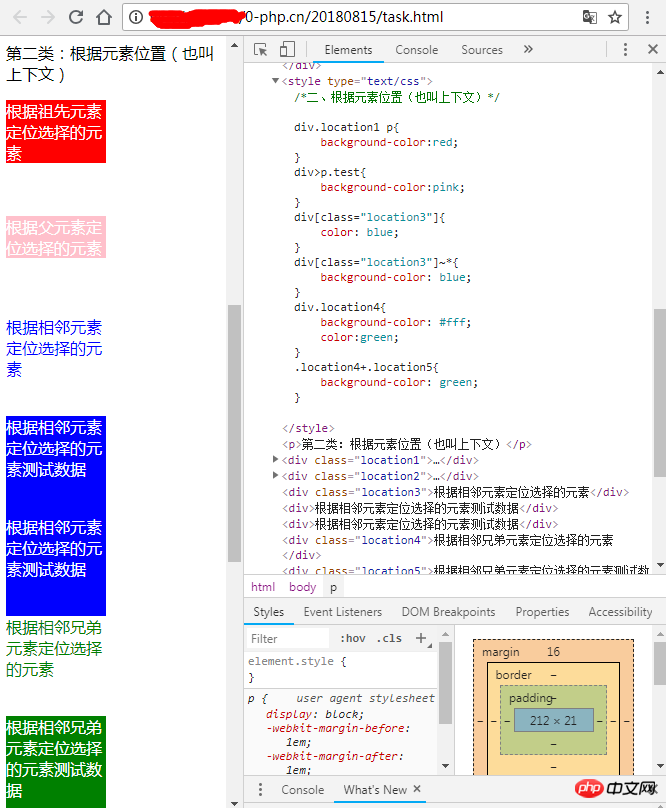
执行结果:(由于没做整块元素控制,分成四张图片展示)
第一类:根据元素特征:
第二类:根据元素位置
第三类:根据元素分组情况,第四类:伪类选择器
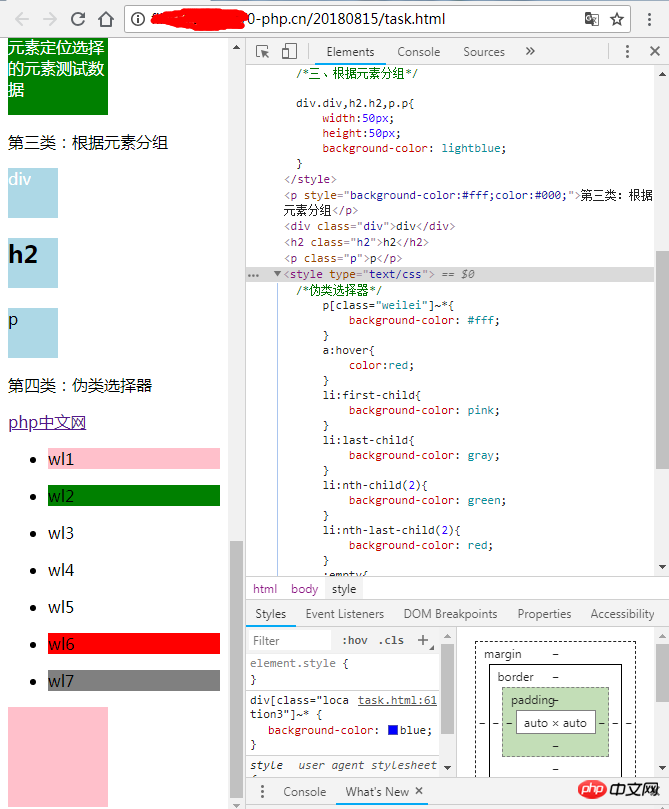
执行结果:四种类型的选择器,都可以控制元素样式,并且各有所长。
3、手抄代码

4、总结,css有三种常用元素单位,px相对于显示器,em相对于当前元素或父元素大小,rem相对于根元素html字体大小。css有四种类型的选择器,根据元素特征的选择器,根据元素位置的选择器,根据元素分组的选择器,伪类选择器。都可以控制相应元素样式,并且各有所长。

