模型文件:tp51/application/index/model/User.php
<?php
namespace app\index\model;
use think\Model;
class User extends Model
{
protected $table = 'users'; //设置数据库表名
protected $pk = 'id'; //设置主键
}控制器文件:tp51/application/index/controller/staff.php
<?php
namespace app\index\controller;
use think\Controller;
use app\index\model\Users; //导入模型
use think\facade\Request;
class Staff extends Controller
{
//循环标签
public function users()
{
}
//分页显示
public function page()
{
}
//文件上传界面
public function upload()
{
}
//处理文件上传
public function file()
{
}
}循环标签
控制器文件:tp51/application/index/controller/staff.php
//循环标签
public function users()
{
//用模型all方法来获取表中数据,传入闭包查询
$users = User::all(function($query){
$query->field(['id','user','pass','name','money','email','phone','upline']);//限定字段
});
//halt($users); === dump($users);exit; //测试能否获取到数据
//模版赋值
$this->view->assign('users',$users);
//渲染模板
return $this->view->fetch();
}//测试能否获取到数据
halt($users); ==== dump($users); exit;
视图文件知识点:
资源文件加载:
系统提供了专门的标签来简化上面的导入:
{load href="/static/js/common.js" /}
{load href="/static/css/style.css" /}并且支持同时加载多个资源文件合并:
{load href="/static/js/common.js,/static/css/style.css" /}系统还提供了两个标签别名 js 和 css 用法和 load 一致:
{js href="/static/js/common.js" /}
{css href="/static/css/style.css" /}tp51\public\static 目录专门用来存入外部访问目录 例如:images js css uptemp等等
模板中的二种注释的区别: {//这种双斜杠注释:源码中看不到} <!--这种html格式注释:源码中可以看到-->
视图文件:tp51/application/index/view/staff/users.html
一、foreach循环标签:类似于原生的foreach语句
{css href="/static/bootstrap/css/bootstrap.css" /}
<div class="container">
<div class="row">
<h3 class="text-center" style="color:red;">会员信息表</h3>
<div class="col-md-12">
<table class="table table-bordered table-hover text-center">
<tr class="warning">
<td>ID</td>
<td>帐号</td>
<td>密码</td>
<td>姓名</td>
<td>余额</td>
<td>邮箱</td>
<td>手机</td>
<td>代理</td>
</tr>
{//基本用法: $staff是控制器或模板中的变量,$key与$value可自定义}
{foreach $users as $user}
<tr>
<td>{$user.id}</td>
<td>{$user.user}</td>
<td>{$user.pass}</td>
<td>{$user.name}</td>
<td>{$user.money}</td>
<td>{$user.email}</td>
<td>{$user.phone}</td>
<td>{$user.upline}</td>
</tr>
{/foreach}
</table>
</div>
</div>
</div>其实模板可以绕过控制器,直接获取数据:assign标签可以在模板中直接定义变量
{//assign name="users" value=":\app\index\model\User::all()" /}
{//name值的获取过程可以用助手函数model进行简化,这也是推荐的方式}
{//assign name="users" value=":model('user')::all()" /}二、volist循环标签:使用最广泛,参数众多,功能强大
{//基本用法:name="变量名,与控制器对应不可更改" id="循环变量,可自定义"}
{volist name="users" id="user"}
<tr>
<td>{$user.id}</td>
<td>{$user.user}</td>
<td>{$user.pass}</td>
<td>{$user.name}</td>
<td>{$user.money}</td>
<td>{$user.email}</td>
<td>{$user.phone}</td>
<td>{$user.upline}</td>
</tr>
{/volist}扩展用法_1:获取指定范围内的数据:offset="起始位置" length="记录数量"
{//从索引1开始,获取10条,索引是从0开始计算,其实是从第2条开始输出10条}
{volist name="staffs" id="staff" offset="1" length="20"}
{/volist}
{//直接输出20条数据}
{volist name="staffs" id="staff" length="20"}
{/volist}扩展用法_2:获取偶数或奇数行的数据: mod="" 将索引进行模除后的结果
{volist name="staffs" id="staff" mod="2"}
{//当前索引除以2余数为1,说明为偶数行,例如第4条记录,索引为3,余数为1}
{//eq name="mod" value="1"}
{//eq}
{//想获取所有的奇数行数据,value="0"}
{eq name="mod" value="0"}
{/eq}扩展用法_3:数据集合为空
{empty name="users"}
<h3 style="color: red;">当前没有符合条件的数据,请检查~~</h3>
{else /}
{volist name="users" id="user"}
<tr>
<td>{$user.id}</td>
<td>{$user.user}</td>
<td>{$user.pass}</td>
<td>{$user.name}</td>
<td>{$user.money}</td>
<td>{$user.email}</td>
<td>{$user.phone}</td>
<td>{$user.upline}</td>
</tr>
{/volist}
{/empty}扩展用法_4:条件判断
{//性别必须是0或1,才是合法数据}
{in name="staff.sex" value="0,1"}
{if $staff.sex == 0}
男
{else /}
女
{/if}
{/in}使用 PHP 和 between 标签
{empty name="users"}
<h3 style="color: red;">当前没有符合条件的数据,请检查~~</h3>
{else /}
{volist name="users" id="user" length="20"}
<tr>
<td>{$user.id}</td>
<td>{$user.user}</td>
<td>{//$user.pass}
{php}echo substr_replace(($user['pass']),'医院医院', 1, 4);{/php}
</td>
<td>{$user.name}</td>
<td>{//$user.money}
{//between标签:是指一定范围内}
{between name="user.money" value="0,100"}
很穷的
{/between}
{between name="user.money" value="101,500"}
有点钱
{/between}
{between name="user.money" value="501,1000"}
有钱
{/between}
{between name="user.money" value="1001,5000"}
很有钱
{/between}
</td>
<td>{$user.email}</td>
<td>{//$user.phone}
{php}echo substr_replace(($user['phone']),'医院医院', 3, 4);{/php}
</td>
<td>{$user.upline}</td>
</tr>
{/volist}
{/empty}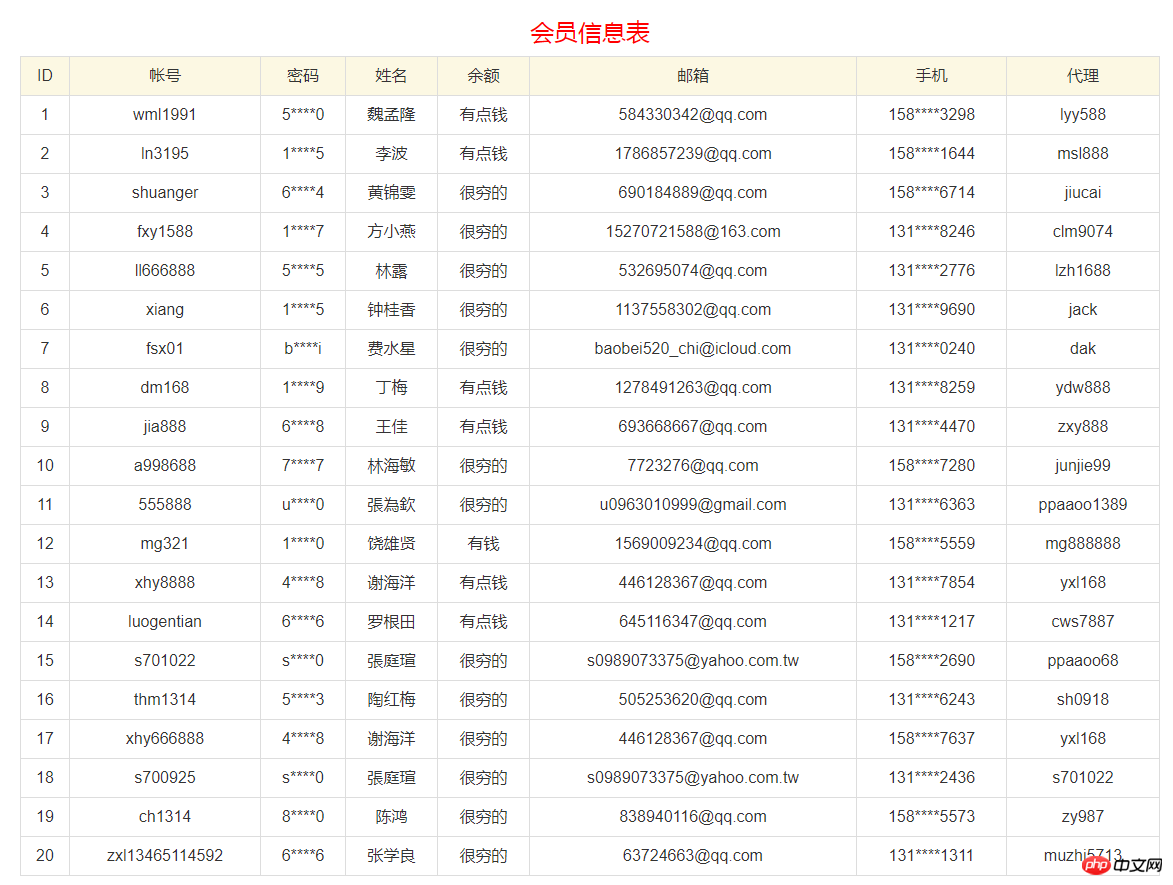
分页查询
控制器文件:tp51/application/index/controller/staff.php
//备注: tp51自带的分页功能很不灵活,更多时候,推荐使用自己写的分页类
public function page()
{
//分页配置
$config = [
'type' => 'bootstrap',
'var_page' => 'page',
];
//每页数量
$num = 15;
//是否是简单分页
$simple = false;
//获取所有分页数据:返回值是分页对象: think\Paginate
$paginate = User::paginate($num, $simple, $config);
//渲染分页的HTML,返回分页变量
$page = $paginate->render();
//将分页对象赋值给模板
$this->view->assign('users', $paginate);
//将分页变量赋值给模板
$this->view->assign('page', $page);
//渲染模板
return $this->view->fetch();
}配置分页参数
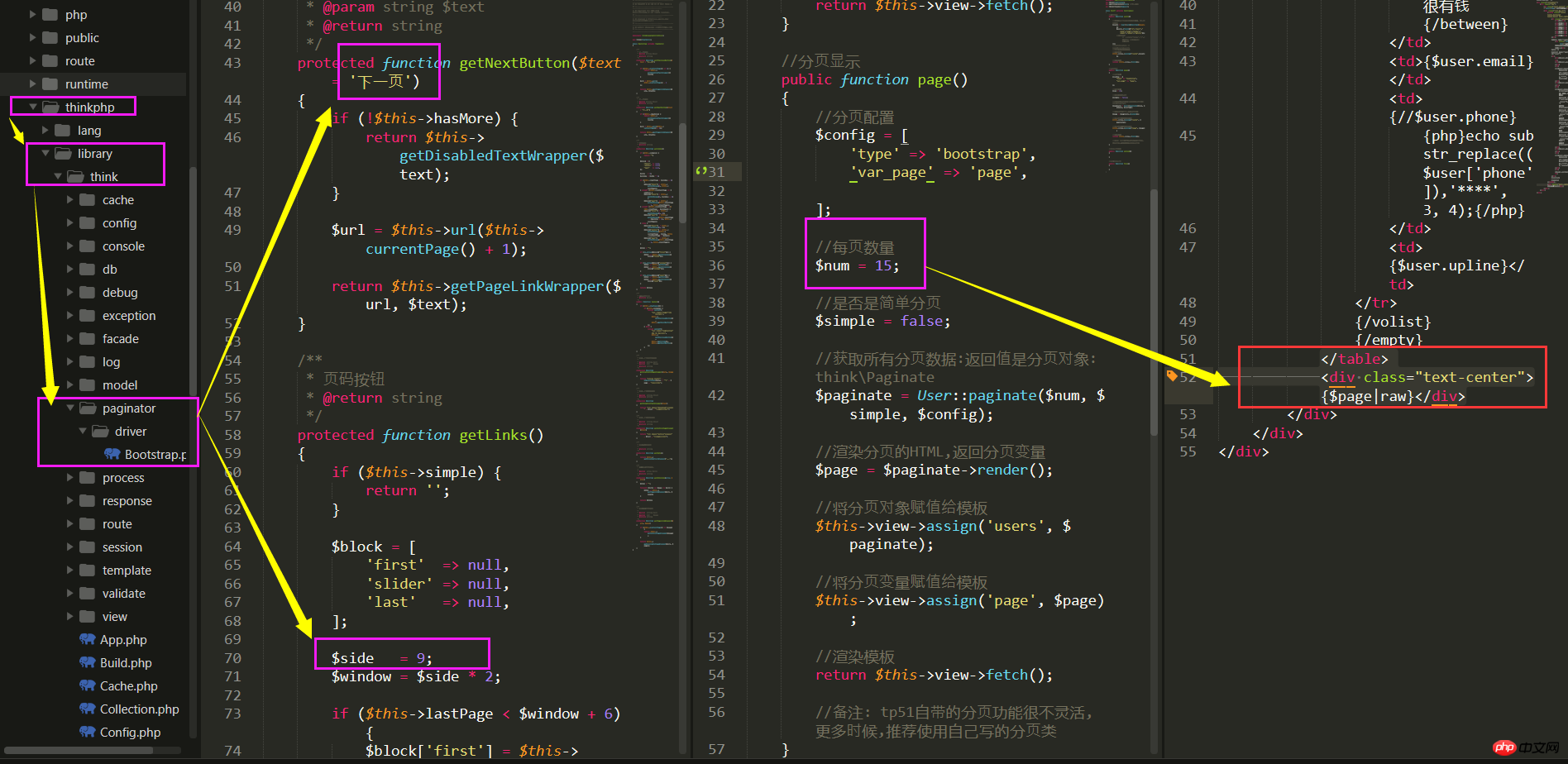
视图文件:tp51/application/index/view/staff/page.html
</table> //在表格标签外面添加分页查询
<div class="text-center">{$page|raw}</div>
文件上传
控制器文件:tp51/application/index/controller/staff.php
//1.渲染一个文件上传的表单
public function upload()
{
return $this->view->fetch();
}视图文件:tp51/application/index/view/staff/upload.html
<div class="upbox" style="width: 400px;height: 200px;text-align: center;border: 2px solid red;"> <h3>文件上传</h3> <form action="upfile" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data"> <input type="file" name="file"> <button>提交</button> </form> </div>
处理文件上传
控制器文件:tp51/application/index/controller/staff.php
public function file()
{
//1.获取上传的文件信息(Request请求对象中的file(),返回文件对象think/File)
$file = Request::file('file');
//2.将文件从临时目录移到到服务器上的指定目录
if (is_null($file)) {
$this->error('没有选择任何文件');
}
//3.判断上传文件
$rule = ['size'=>2097152, 'ext'=>'jpg,jpeg,png,gif'];
if($file->check($rule)) {
$fileInfo = $file->move('uptemp');
$res = '<h3 style="color:green;">上传成功</h3>文件名是:'.$fileInfo->getSaveName();
} else {
$res = '<h3 style="color:red;">上传失败</h3>'.$file->getError();
}
return $res;
}视图文件:tp51/application/index/view/staff/upfile.html 为空即可

