1,盒模型常用属性
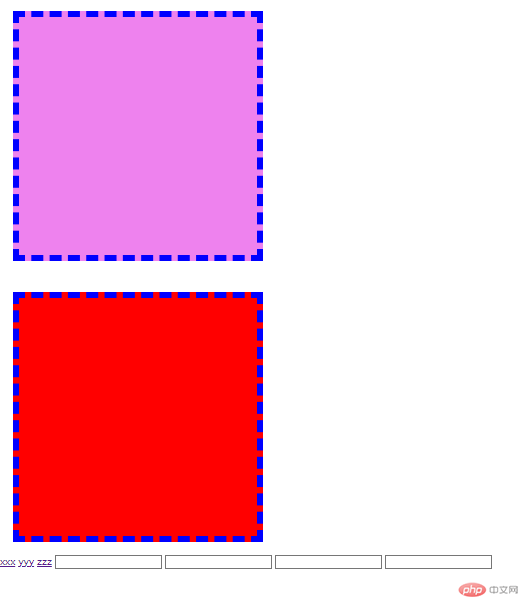
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="zh-CN"><head> <meta charset="UTF-8" /> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" /> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" /> <title>盒模型</title></head><body> <div class="box"></div> <div class="box"></div> <style> .box { width: 400px; height: 400px; background-color: violet; /* border: 10px solid black; */ /* padding: 20px; */ /* background-clip: content-box; */ box-sizing: border-box; } /* 10px+20px+400px=430px+30=460px */ /* 我的本意是想要得到一个400*400的盒子,但是最终计算结果却包括了内边距padding和边框border */ /* 10+20=30 , 400-30=370 */ /* 将左右多出来的padding,border全减去 */ /* .box { width: 140px; height: 140px; background-color: violet; border: 10px solid black; padding: 20px; background-clip: content-box; } */ .box { /* 四值:完整语法, 上向下左,顺时针方向 */ padding: 5px 10px 15px 20px; padding: 5px 20px 15px 20px; /* 三值语法: 左右相等,而上下不等 */ padding: 5px 20px 15px; /* 双值语法: 左右相同,上下也相同,但并不是同一个值*/ padding: 15px 20px 15px 20px; padding: 15px 20px; /* 三值与双值的记忆方法: 第二个位置的值一定表示的是左右 */ /* 单值: 四个方向全相同 */ padding: 20px; } .box { /* 边框与padding,margin类似,但又有显著的不同, 因为边框是可见的 */ /* border-right-width: 10px; border-right-style: solid; border-right-color: blue; */ /* border-right: 10px solid blue; border-left: 10px solid blue; border-top: 10px solid blue; border-bottom: 10px solid blue; */ border: 10px dashed blue; } .box { margin: 20px; } .box:last-of-type { background-color: red; margin-top: 50px; /* margin会在垂直方向出现折叠,谁大用谁的 */ } /* 页面中所有元素,都是一个矩形块 */ /* 矩形块在一个二维平面中,只有"垂直","水平"二种排列方式 */ /* 与这种排列方式对应的,就只有二种元素类型: 块元素, 行内元素 */ /* div: 块元素 */ </style> <a href="">xxx</a> <a href="">yyy</a> <a href="">zzz</a> <input type="text" /> <input type="text" /> <input type="text" /> <input type="text" /> <!-- 布局前提: 是在一个"宽度受限,而高度无限的空间内" --> <!-- 布局时,必须将width,height其中一个限制死,否则无法完成布局 --> <!-- 根据人类的观看习惯, 通常是将宽度限制,而高度随内容舒展 --></body></html>
2,媒体查询
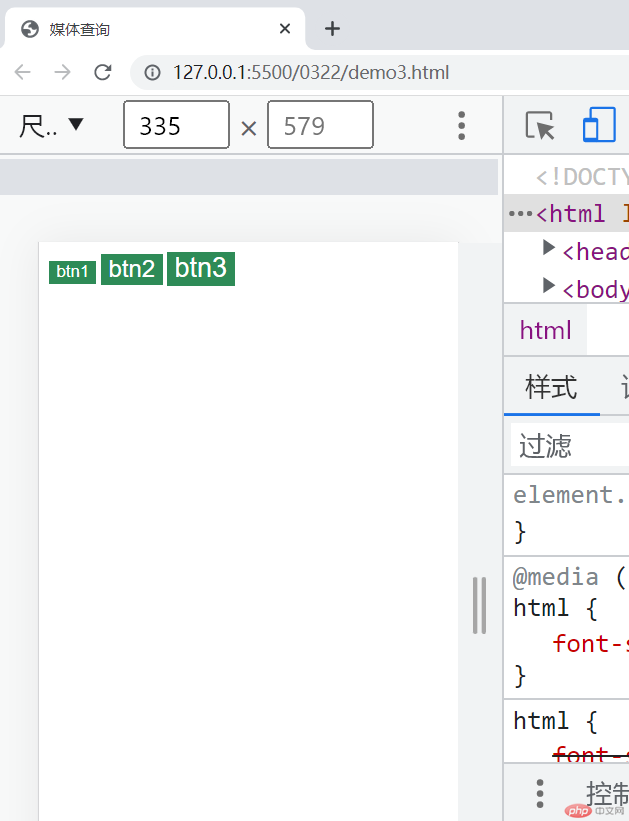
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="zh-CN"><head> <meta charset="UTF-8" /> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" /> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" /> <title>媒体查询</title></head><body> <!-- 媒体: 显示/输出信息的介质/载体, 屏幕, 打印机 --> <!-- 查询: 根据当前媒体宽度的变化来选择不同的页面或显示效果 --> <button class="btn samll">btn1</button> <button class="btn middle">btn2</button> <button class="btn large">btn3</button></body><style> /* em: 默认元素字号,16px, */ /* rem: 根元素的字号, 16px */ html { font-size: 10px; /* 1rem = 10px; */ } /* 按钮基本样式 */ .btn { background-color: seagreen; color: white; border: none; outline: none; } .btn:hover { cursor: pointer; opacity: 0.8; transition: 0.3s; padding: 0.4rem 0.8rem; } .btn.small { /* font-size: 12px; */ font-size: 1.2rem; } .btn.middle { /* font-size: 16px; */ font-size: 1.6rem; } .btn.large { /* font-size: 18px; */ font-size: 1.8rem; } /* 最大374px时生效,是不是当小于374px才有效果 */ @media (max-width: 374px) { html { font-size: 12px; } } /* 374px - 414px 之间 */ @media (min-width: 375px) and (max-width: 413px) { html { font-size: 14px; } } /* >414px 之间 */ @media (min-width: 414px) { html { font-size: 16px; } } /* 以上是一个由小到大的匹配过程: 移动优先 */ /* 以上是一个由大到小的匹配过程: PC优先 */</style></html>
3,em,rem的用法和差别
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="zh-CN"><head> <meta charset="UTF-8" /> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" /> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" /> <title>常用单位</title></head><body> <!-- px: 像素,绝对单位, 1in = 96px --> <!-- em,rem,vh,vw: 相对单位 --> <div> <span>Hello</span> </div> <style> html { font-size: 10px; /* 在根元素中设置的字号,在其它地方引用是使用rem,并且这个值是不变的 */ /* 因为一个页面,只有一个根元素, html */ /* 1rem = 10px */ } div { /* font-size: 32px; */ /* 1em = 16px */ /* 32px = 2em */ font-size: 3rem; } div span { /* font-size: 2em; */ /* 2em = 2*16=32px */ /* 但是 em在父元素中被重新定义了, 1em = 30px */ /* 2em = 60px */ /* em总是随着自身或父元素的字号发生变化,在布局时会显得非常的混乱 */ /* font-size: 20px; */ font-size: 2rem; } </style></body></html>



