1. 值传递与引用传递
1.1 值传递
- 值传递发生在基本数据类型中
let a = 10;let b = a;console.log(a, b); //10 10a = 5;console.log(a, b); //5 10
1.2 引用传递
- 发生在引用类型,数组,对象
let s1 = {x: 1,y: 1};console.log(s1);// {x:1, y:1}let s2 = s1;console.log(s2);// {x:1, y:1}console.log(s1 === s2);// trues1.x = 10;console.log(s1);// {x:10, y:1}console.log(s2);// {x:10, y:1}
1.3 传参
- 函数中,始终是值传递
- 传入对象,更新对象的属性仍属于值传递,因为对象没有被改变
//基本类型const f1 = x => x = 10;let p = 5;f1(p);console.log(p);//对象const f2 = (obj) => { obj.age = 22; obj = {}; };let o = {age: 10,id: 0001}console.log(o);// {age:10, id:1}f2(o);console.log(o);// {age:22, id:1}
*
- 深拷贝:值传递
- 浅拷贝:引用传递
2. 模板字面量
- 字符串字面量+变量插值(嵌入到字符串)
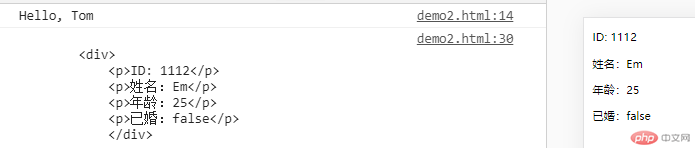
let name = "Tom";let greet = `Hello, ${name}`;console.log(greet);let stu = {id: 1112,name: "Em",age: 25,married: false}let stuInfo = `<div><p>ID: ${stu.id}</p><p>姓名:${stu.name}</p><p>年龄:${stu.age}</p><p>已婚:${stu.married}</p></div>`;console.log(stuInfo);document.write(stuInfo);
2.1 标签函数
- 第一个参数:字符串本身元素组成的数组
- 第二个及以后:插值/插值组成的数组
//少量参数let sum = (strs, a, b) => {console.log(strs);console.log(a, b);}let a = 5;let b = 10;let c = 20;sum`${a}+${b}=`;//多个参数sum = (strs, ...arr) => {console.log(strs);console.log(arr);}sum`${a}+${b}+${c}=`;

3. 解构
3.1 数组解构
let arr = [1, 2, 3];let [a, b] = arr;console.log(a, b);// 1 2let c;[a, b, c] = arr;console.log(c);// 3arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7];[a, b, ...c] = arr;console.log(a, b, ...c);// 1 2 3 4 5 6 7[, , , , , c,] = arr;console.log(c);// 6// let [x, y] = [8, 9];x = 80;y = 90;console.log(x, y);// 80 90[y, x] = [x, y];console.log(x, y)// 90 80
3.2 对象解构
let stu = { name: "Tom", age: 22 };({ name, age } = stu);// let { name, age } = stu;console.log(name, age)// Tom 22
3.3 参数解构
let sum = ([a, b]) => a + b;console.log(sum([60, 60]));// 120let stu1 = ({ name, age }) => [name, age];console.log(stu1({ name: "Em", age: 25 }));//["Em", 25]
3.4 对象简化
- 如果对象的属性与变量作用域相同且同名,可以写作:
x = 90, y = 80;let user = {x,y}console.log(user);// {x: 90, y: 80}
4 bind() call() apply() 函数
- 默认的this关键字指向window
- 在对象中作为属性的函数里,this指向的是当前的对象
- 这三个函数用来改变this关键字的指向
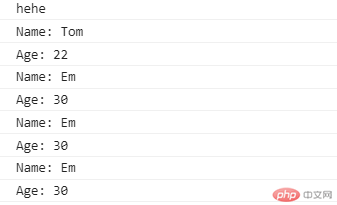
let stu = {name: "Em",age: 30}let name = "hehe";let obj = {name: "Tom",age: 22,foo: function () {console.log("Name: " + this.name);console.log("Age: " + this.age);}}console.log(this.name);obj.foo();obj.foo.bind(stu)();obj.foo.call(stu);obj.foo.apply(stu);
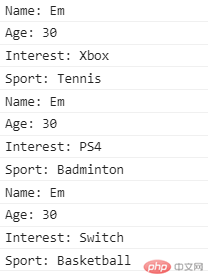
- 若函数有参数需传入:
obj = {name: "Tom",age: 22,foo: function (i, s) {console.log("Name: " + this.name);console.log("Age: " + this.age);console.log("Interest: " + i);console.log("Sport: " + s);}}obj.foo.bind(stu, "Xbox", "Tennis")();obj.foo.apply(stu, ["PS4", "Badminton"]);obj.foo.call(stu, "Switch", "Basketball");
5. 访问器属性 Getter Setter
- 方法以属性的方式使用
- 简化语法
let item = {name: "unknown",price: 0,amount: 0,set setName(name) {this.name = name;},set setPrice(price) {this.price = price;},get addItem() {this.amount++;},get getName() {return this.name;},get getPrice() {return this.price;},get getAmount() {return this.amount;}}item.addItem;console.log(item.getAmount);item.setName = "iPad";console.log(item.getName);item.setPrice = "199";console.log(item.getPrice);//1//iPad//199
6. 流程控制
6.1 if 语句
- 语法
if(true) return a = 1;else return a = 2;
- 当只有执行语句只有一行时,{}括号可以省略,多行时不可以
let a = 1;if (a > 60)console.log(true);elseconsole.log(false);// false
- 多个分支时
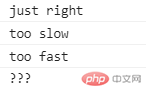
let foo = (speed) => {if (speed < 60 && speed >= 0) {console.log("too slow");} else if (speed >= 60 && speed <= 100) {console.log("just right");} else if (speed > 100 && speed < 200) {console.log("too fast");} else {console.log("???");}}let currentSpeed = 80;foo(currentSpeed);currentSpeed = 30;foo(currentSpeed);currentSpeed = 150;foo(currentSpeed);currentSpeed = -1;foo(currentSpeed);
6.2 switch 语句
- 语法
switch(true) {case a:...;break;case b:...;break;default:...;break;}
*case 也可以是表达式表示多个值,如:
case a>0&&a<10:
console.log(true);
但多用于单个值的判断
let animal = "cat";switch (animal) {case "cat":console.log("猫");break;case "dog":console.log("狗");break;default:break;}//猫
6.3 三元运算符
- 用于简化双分支
currentSpeed = 2000;animal = "cat";console.log(currentSpeed <= 200 ? "OK" : "Boom");//Boomconsole.log(animal === "cat" ? true : false);//true

