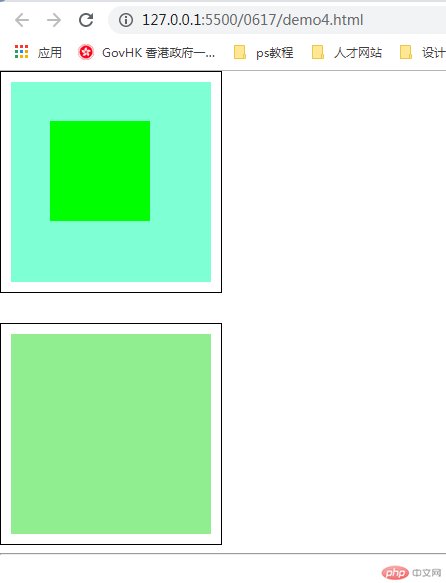
1.盒模型常用的属性
知识点: width,height,padding,marign,border,position
实例
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>盒/框模型常用属性</title>
<style>
.box {
/* 宽、高:内容区 */
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
}
.box.one {
/* 内边距 */
padding: 10px;
/* 加1px的实线边框 */
border: 1px solid #000000;
/* 背景色 */
background-color: aquamarine;
/* 对背景进行裁切 默认是 border-box (边框级别),content-box(内容区) */
background-clip: content-box;
/* 顺序按照上、右、下、左 来设置 */
/* margin: top right bottom left; */
/* 外边距 */
margin: 0 0 20px 0;
/* 作用同上 */
margin-bottom: 20px;
}
.box.two {
/* 内边距 */
padding: 10px;
/* 加1px的实线边框 */
border: 1px solid #000000;
/* 背景色 */
background-color: lightgreen;
/* 对背景进行裁切 默认是 border-box (边框级别),content-box(内容区) */
background-clip: content-box;
/* 当两个盒子在垂直方向上,外边距会产生折叠 */
margin-top: 30px;
}
.box.parent {
background-color: lightpink;
/* 一旦一个元素被添加了position 且值非static 那么它就是定位元素 */
position: relative;
/* 从左边向右移动30px */
/* 相对定位是相对自己做了偏移,这个元素在文档流中的位置不释放 */
left: 30px;
top: 40px;
}
.son {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: lime;
/* 绝对定位 */
/* 如果没有定位父级元素,会向上一级找,直到找到,就是body元素 */
position: absolute;
/* 固定定位 会忽略定位父级 总是相对于body定位*/
position: fixed;
left: 50px;
top: 50px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 块级元素默认垂直排列 -->
<div class="box one"></div>
<div class="box two"></div>
<hr />
<!-- 嵌套关系-->
<div class="box parent">
<div class="box son"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>运行实例 »
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
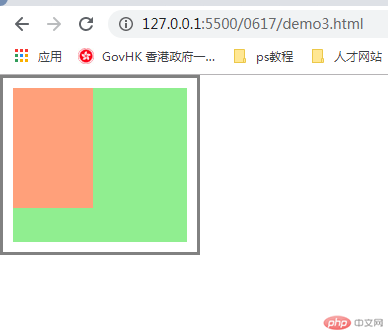
2.元素大小的重新计算: box-sizing的用法
知识点:box-sizing: border-box, content-box,
实例
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>元素用户自定义元素大小的计算方式</title>
<style>
/* 常用样式初始化 */
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
.box {
width: 200px;
height: 180px;
background-color: lightgreen;
border: 3px solid rgb(129, 129, 129);
background-clip: content-box;
padding: 10px;
/* box-sizing: 重新计算盒大小 content-box默认是以内容区为准*/
box-sizing: content-box;
/* border-box: 有效范围到边框 */
box-sizing: border-box;
}
.box2 {
width: 80px;
height: 120px;
background-color: lightsalmon;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box">
<div class="box2"></div>
</div>
<!-- width: content_width + padding_left/rigth + border_left/right -->
<!-- 宽: 200 + 20 + 6 =226-->
</body>
</html>运行实例 »
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
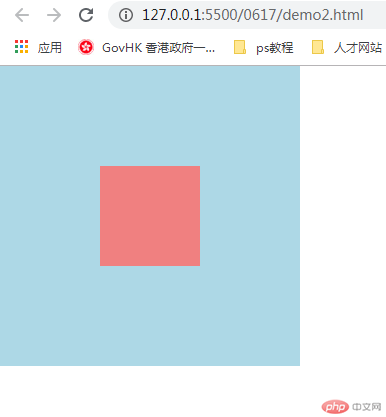
3.元素的水平与垂直居中
知识点:position: left,top,right,bottom; marign:auto;
实例
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>margin:auto 块元素的垂直居中</title>
<style>
.container {
width: 300px;
height: 300px;
background-color: lightblue;
position: relative;
}
.container .item {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: lightcoral;
/* 水平居中 */
/* 让浏览器自动计算左右外边距 */
/* margin-left: auto;
margin-right: auto; */
/* 垂直居中 */
/* 不能用margin-top:auto 和 margin-bottom:auto 来垂直居中 */
/* 通过绝对定位来实现垂直居中 */
position: absolute;
/* 让当前元素绝对定位的上下文充满整个父级容器 */
/* 左上角开始 */
top: 0;
left: 0;
/* 右下角结束 */
right: 0;
bottom: 0;
margin: auto;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<div class="item"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>运行实例 »
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例