如果你正在访问一个网站,而你登录以后,又去浏览其他网站。如果其他网站可以读取到你之前正在访问的网站的Cookie,你又没有退出登录,那么其他网站就可以冒充你,为所欲为。这个过程,就叫做跨站请求伪造。那么如何避免这种不安全的操作呢,我们可以使用“同源策略”。“同源策略”的目的,是为了保证用户信息的安全,防止恶意的网站窃取数据。目前,所有浏览器都实行这个政策。即A网页设置的 Cookie,B网页不能打开,除非这两个网页”同源”。所谓”同源”指的是”三个相同”:
协议相同域名相同端口相同
举例来说,https://www.php.cn/course/type/3.html这个网址,协议是https://,域名是www.php.cn,端口是80(默认端口可以省略)。它的同源情况如下:
https://www.php.cn/wenda.html:同源http://php.cn/other.html:不同源(协议不同)https://www.php.net/other.html:不同源(域名不同)https://www.php.cn:81/course/type/3.html:不同源(端口不同)
同源策略规定,AJAX请求只能发给同源的网址,否则就报错。我们可以用以下两种方法规避这个限制。
一、跨域资源共享 CORS。
CORS是一个W3C标准,全称是”跨域资源共享”(Cross-origin resource sharing)。它允许浏览器向跨域服务器,发出XMLHttpRequest请求,从而克服了AJAX只能同源使用的限制。CORS需要浏览器和服务器同时支持。整个CORS通信过程,都是浏览器自动完成,不需要用户参与。
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8" /><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" /><title>Document</title></head><body><button>跨域请求-CORS</button><h2></h2><script>var btn = document.querySelector("button");btn.addEventListener("click",function () {// 1. 创建Ajax对象var xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();// 2. 监听请求xhr.onreadystatechange = function () {if (xhr.readyState === 4 && xhr.status === 200) {console.log(xhr.responseText);document.querySelector("h2").innerHTML = xhr.responseText;}};// 3. 初始化请求参数xhr.open("GET", "http://php.edu/0522/test1.php", true);//"test1.php"在另外一个服务器上// 4. 发送请求xhr.send(null);},false);</script></body></html>
输出效果:
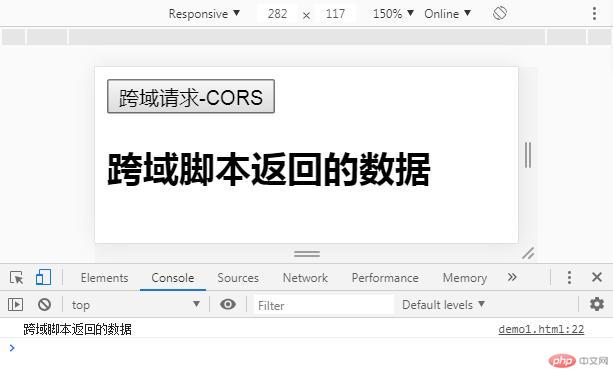
test1.php
<?phpheader('Access-Control-Allow-Origin:http://js.edu');header('content-type:text/html;charset-utf-8');echo '跨域脚本返回的数据';flush();
二、跨域资源共享 JSONP。
JSONP是服务器与客户端跨域通信的常用方法。它的基本思想是,网页通过添加一个<script>元素,向服务器请求JSON数据,这种做法不受同源策略限制,服务器收到请求后,将数据放在一个指定名字的回调函数里传回来。
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8" /><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" /><title>跨域请求-JSONP</title></head><body><button>跨域请求-JSONP</button><script>// 1. 准备好回调处理函数function handle(jsonData) {console.log(jsonData);var data = JSON.parse(jsonData);console.log(data);// 将接口返回的数据渲染到页面中var ul = document.createElement("ul");ul.innerHTML += "<li>" + data.title + "</li>";ul.innerHTML += "<li>姓名:" + data.user.name + "</li>";ul.innerHTML += "<li>邮箱:" + data.user.email + "</li>";document.body.appendChild(ul);}// 2. 点击按钮发起一个基于JSONP的跨域请求var btn = document.querySelector("button");btn.addEventListener("click",function () {var script = document.createElement("script");script.src = "http://php.edu/0522/test2.php?jsonp=handle&id=3";document.head.appendChild(script);},false);</script></body></html>
test2.php
<?php//这里返回的是json,json只支持utf8header('content-type:text/html;charset=utf-8');$callback = $_GET['jsonp'];$id = $_GET['id'];//模仿接口,根据查询条件返回不同的内容$users = [0=>'{"name":"admin","email":"admin@php.cn"}',1=>'{"name":"lulu","email":"lulu@php.cn"}',2=>'{"name":"anna","email":"anna@php.cn"}',];if (array_key_exists(($id-1),$users)) {$user = $users[$id-1];}$json = '{"title":"用户信息表","user":'.$user.'}';echo $callback . '('. json_encode($json) . ')';
输出效果:
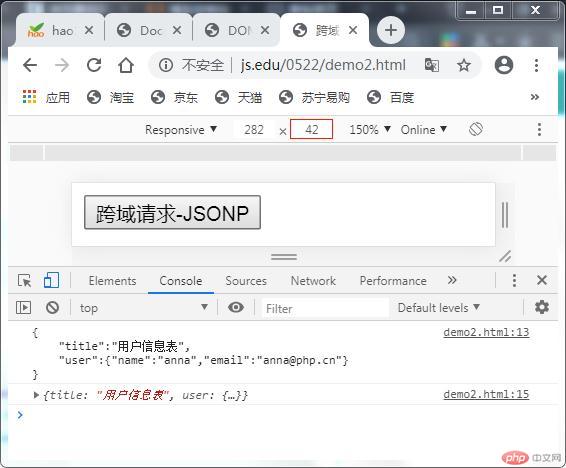
三、总结
1.同源策略是针对脚本发出请求的,不针对标签,所以比如img标签可以跨域。
2.JSONP只能发送GET请求,而CORS支持所有类型的HTTP请求。
3.实现CORS通信的关键是服务器,只要服务器实现了CORS接口,就可以跨域通信。
4.CORS与JSONP的使用目的相同,但是比JSONP更强大。
5.JSONP支持老式浏览器,以及可以向不支持CORS的网站请求数据。

