1.设置弹性元素的增长因子
实例
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>设置弹性元素的增长因子</title>
<style>
.container{
width: 500px;
background:lightblue;
}
.flex{
display: flex;
}
.item{
border:1px solid green;
background:pink;
width: 100px;
padding: 10px;
}
.demo1 > .item{
flex-grow: 0;
}
.demo2 > .item:first-of-type{
flex-grow:0;
}
.demo2 > .item:nth-child(2){
flex-grow:0;
}
.demo2 > .item:last-of-type{
flex-grow:1;
}
.demo3 > .item:first-of-type{
flex-grow:1;
}
.demo3 > .item:nth-child(2){
flex-grow:1;
}
.demo3 > .item:last-of-type{
flex-grow:3;
}
.demo4 > .item:first-of-type{
flex-grow:0.6;
}
.demo4 > .item:nth-child(2){
flex-grow:0.7;
}
.demo4 > .item:last-of-type{
flex-grow:0.9;
}
.demo5 > .item:first-of-type{
width: 130px;
flex-grow:1;
}
.demo5 > .item:nth-child(2){
width: 140px;
flex-grow:1;
}
.demo5 > .item:last-of-type{
width: 160px;
flex-grow:4;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>flex-grow: 设置弹性元素增长因子</h1>
<h3>(1): 所有弹性元素不增长,以原始宽度显示,增长因子为: 0(默认)</h3>
<div class="container flex demo1">
<span class="item">item1</span>
<span class="item">item2</span>
<span class="item">item3</span>
</div>
<h3>(2): 将全部剩余空间分配给指定弹性元素</h3>
<div class="container flex demo2">
<span class="item">item1</span>
<span class="item">item2</span>
<span class="item">item3</span>
</div>
<h3>(3): 全部剩余空间按增长因子在不同弹性元素分配</h3>
<div class="container flex demo3">
<span class="item">item1</span>
<span class="item">item2</span>
<span class="item">item3</span>
</div>
<h3>(4): 增长因子支持小数, 因为是按增长比例分配</h3>
<div class="container flex demo4">
<span class="item">item1</span>
<span class="item">item2</span>
<span class="item">item3</span>
</div>
<h3>(5): 每个弹性元素宽度不同时, 同样适用以上分配规律</h3>
<div class="container flex demo5">
<span class="item">item1</span>
<span class="item">item2</span>
<span class="item">item3</span>
</div>
</body>
</html>运行实例 »
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
运行结果图:

手写代码:


2.设置弹性元素的缩减因子
实例
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>设置弹性元素的缩减因子</title>
<style>
.container{
width: 500px;
background:lightblue;
}
.flex{
display: flex;
}
.item{
border:1px solid green;
background:pink;
width: 200px;
padding: 10px;
}
.demo1 > .item{
flex-shrink: 0;
}
.demo2 > .item:first-of-type{
flex-shrink:0;
}
.demo2 > .item:nth-child(2){
flex-shrink: 0
}
.demo2 > .item:last-of-type{
flex-shrink:1;
}
.demo3 > .item:first-of-type{
flex-shrink:2;
}
.demo3 > .item:nth-child(2){
flex-shrink:1;
}
.demo3 > .item:last-of-type{
flex-shrink:3;
}
.demo4 > .item:first-of-type{
flex-shrink:0.6;
}
.demo4 > .item:nth-child(2){
flex-shrink:0.7;
}
.demo4 > .item:last-of-type{
flex-shrink:0.9;
}
.demo5 > .item:first-of-type{
width: 100px;
flex-shrink:1;
}
.demo5 > .item:nth-child(2){
width: 140px;
flex-shrink:1;
}
.demo5 > .item:last-of-type{
width: 160px;
flex-shrink:4;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>flex-shrink: 设置弹性元素缩减因子</h1>
<h3>(1): 所有弹性元素不缩减,以原始宽度显示,缩减因子为: 0</h3>
<div class="container flex demo1">
<span class="item">item1</span>
<span class="item">item2</span>
<span class="item">item3</span>
</div>
<h3>(2): 所有弹性元素自适应容器宽度且不换行,缩减因子: 1 (默认)</h3>
<div class="container flex demo2">
<span class="item">item1</span>
<span class="item">item2</span>
<span class="item">item3</span>
</div>
<h3>(3): 当三个弹性元素的缩减因为子不相等时</h3>
<div class="container flex demo3">
<span class="item">item1</span>
<span class="item">item2</span>
<span class="item">item3</span>
</div>
<h3>(4): 缩减因子也可以是小数,只要大于就可以</h3>
<div class="container flex demo4">
<span class="item">item1</span>
<span class="item">item2</span>
<span class="item">item3</span>
</div>
<h3>(5): 每个弹性元素宽度不同时, 同样适用以上分配规律</h3>
<div class="container flex demo5">
<span class="item">item1</span>
<span class="item">item2</span>
<span class="item">item3</span>
</div>
</body>
</html>运行实例 »
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
运行结果图:

手写代码:

3.设置弹性元素的基准尺寸
实例
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>设置弹性元素的基准尺寸</title>
<style>
.container{
width: 500px;
background:lightblue;
}
.flex{
display: flex;
}
.item{
border:1px solid green;
background:pink;
padding: 10px;
}
.demo1 > .item{
flex-basis: content;
}
.demo2 > .item{
width: 100px;
}
.demo3 > .item{
flex-basis:auto;
}
.demo4 > .item{
width: 100px;
flex-basis:140px;
}
.demo5 > .item:first-of-type{
flex-basis:30%;
}
.demo5 > .item:nth-child(2){
flex-basis:45%;
}
.demo5 > .item:last-of-type{
flex-basis:25%;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>flex-basis: 设置弹性元素的基准尺寸</h1>
<h3>(1): 在未设置弹性元素宽度时, 以内容宽度显示</h3>
<div class="container flex demo1">
<span class="item">item1</span>
<span class="item">item2</span>
<span class="item">item3</span>
</div>
<h3>(2): 存在自定义元素宽度时,则以该宽度显示</h3>
<div class="container flex demo2">
<span class="item">item1</span>
<span class="item">item2</span>
<span class="item">item3</span>
</div>
<h3>(3): 自动状态下, 由浏览器根据预设值自行判定</h3>
<div class="container flex demo3">
<span class="item">item1</span>
<span class="item">item2</span>
<span class="item">item3</span>
</div>
<h3>(4): 当元素存在自定义宽度与基准宽度时, 以基准宽度为准</h3>
<div class="container flex demo4">
<span class="item">item1</span>
<span class="item">item2</span>
<span class="item">item3</span>
</div>
<h3>(5): 元素基准宽度支持百分比设置</h3>
<div class="container flex demo5">
<span class="item">item1</span>
<span class="item">item2</span>
<span class="item">item3</span>
</div>
</body>
</html>运行实例 »
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
运行结果图:

手写代码:

4.简化弹性元素的基本设置
实例
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>简化弹性元素的基本设置</title>
<style>
.container{
width: 500px;
background:lightblue;
}
.flex{
display: flex;
}
.item{
border:1px solid green;
background:pink;
padding: 10px;
}
.demo1 > .item{
width: 100px;
height:60px;
flex:initial;
flex:0 1 auto;
}
.demo2 > .item{
width: 100px;
height: 60px;
flex:auto;
}
.demo3 > .item{
width: 100px;
height: 60px;
flex:none;
flex:0 0 auto;
}
.demo4 > .item{
width: 100px;
height: 60px;
flex: 1;
}
.demo5 > .item{
width: 100px;
height: 60px;
flex: 1 0 200px;
}
.demo6 > .item{
width: 100px;
height: 60px;
}
.demo6 > .item:first-of-type{
flex:1 1 50%;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>简化弹性元素的基本设置</h1>
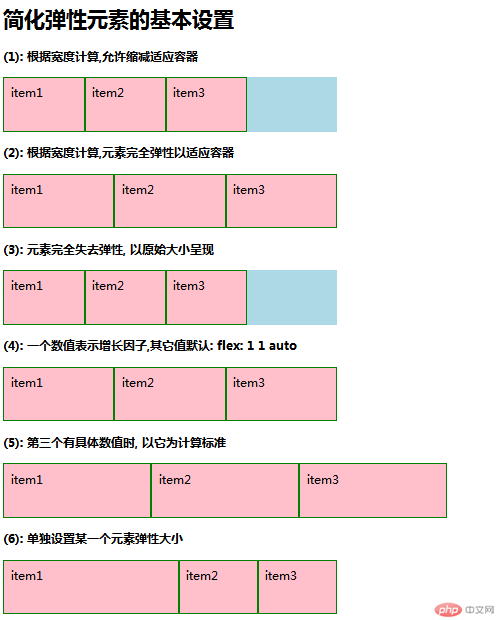
<h3>(1): 根据宽度计算,允许缩减适应容器</h3>
<div class="container flex demo1">
<span class="item">item1</span>
<span class="item">item2</span>
<span class="item">item3</span>
</div>
<h3>(2): 根据宽度计算,元素完全弹性以适应容器</h3>
<div class="container flex demo2">
<span class="item">item1</span>
<span class="item">item2</span>
<span class="item">item3</span>
</div>
<h3>(3): 元素完全失去弹性, 以原始大小呈现</h3>
<div class="container flex demo3">
<span class="item">item1</span>
<span class="item">item2</span>
<span class="item">item3</span>
</div>
<h3>(4): 一个数值表示增长因子,其它值默认: flex: 1 1 auto</h3>
<div class="container flex demo4">
<span class="item">item1</span>
<span class="item">item2</span>
<span class="item">item3</span>
</div>
<h3>(5): 第三个有具体数值时, 以它为计算标准</h3>
<div class="container flex demo5">
<span class="item">item1</span>
<span class="item">item2</span>
<span class="item">item3</span>
</div>
<h3>(6): 单独设置某一个元素弹性大小</h3>
<div class="container flex demo6">
<span class="item">item1</span>
<span class="item">item2</span>
<span class="item">item3</span>
</div>
</body>
</html>运行实例 »
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
运行结果图:
手写代码:

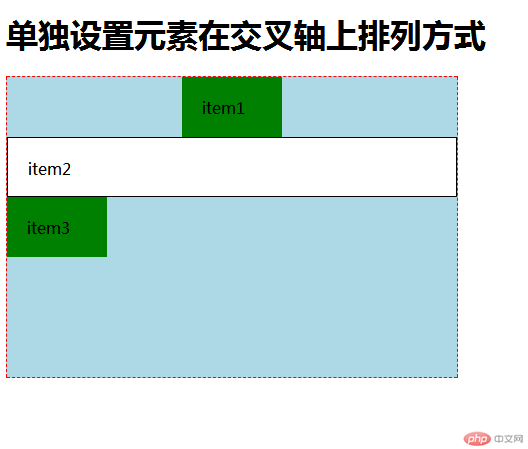
5.单独设置元素在交叉轴上排列方式
实例
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>单独设置元素在交叉轴上排列方式</title>
<style>
.container{
width: 450px;
height: 300px;
background:lightblue;
border:1px dashed red;
flex-flow: column nowrap;
align-items:flex-end;
}
.flex{
display:flex;
}
.item{
padding: 20px;
background:green;
box-sizing: border-box;
width: 100px;
height: 60px;
}
.item:first-of-type{
align-self: center;
}
.item:nth-child(2){
align-self:stretch;
width: 100%;
background:white;
border:1px solid black;
}
.item:last-of-type{
align-self: flex-start;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>单独设置元素在交叉轴上排列方式</h1>
<div class="container flex">
<span class="item">item1</span>
<span class="item">item2</span>
<span class="item">item3</span>
</div>
</body>
</html>运行实例 »
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
运行结果图:
手写代码:

6.移动端首页
当元素没有内容时候,设置height:100%,该元素不会被撑开,此时高度为0,但是设置height:100vh,该元素会被撑开屏幕高度一致。
实例
<!DOCTYPE html>
<head>
<title>移动端首页</title>
<style>
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
body {
height: 100vh;
display: flex;
flex-flow: column nowrap;
}
header, footer {
min-height: 100px;
background: pink;
flex: 0 0 auto;
}
main {
height: 90vh;
background: lightgreen;
flex: 1;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<header>头部</header>
<main>主体</main>
<footer>底部</footer>
</body>
</html>运行实例 »
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
运行结果图:

手写代码:


