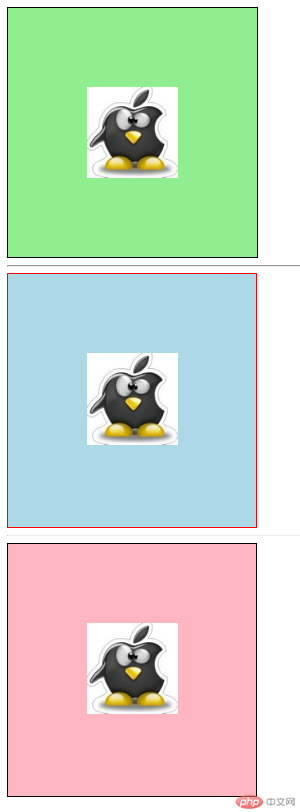
1、内边距
/*实现图片居中显示*/
实例
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="static/css/style1.css">
<title>内边距(padding)——图片居中</title>
<style>
/****方案一****/
.box1{
width:300px;
height: 300px;
background-color: lightgreen;
border:1px solid black;
}
/*使用padding让图片居中显示*/
/* 容器300*300,图片200*200,最直观的想法是添加50px的内边距 */
.box1 {
padding: 95px;
}
/* 会发现,内边距会增加盒子填充厚度,将盒子撑大 */
/*如果想保持原来盒子大小,只能手工修改box1的宽高*/
.box1 {
width: 110px;
height: 110px;
}
/*********************** 方案2: 宽度分离 *********************/
/* 给box2认一个干爹,添加一个父级盒子wrap, 这时box2就是儿子了, width就有效了*/
.wrap{
width:300px;
}
.box2{
background-color: lightblue;
border:1px solid red;
padding:95px;
}
/*********************** 方案3: box-sizing 盒尺寸 *********************/
/*经过前面学习, 知道了在默认情况下, 宽度是作用到盒中的内容上的*/
/*而一个盒子有content,padding,border,margin四部分组成,所以改变宽度会造成盒子大小不确定*/
/*方案2: 是将width宽度直接作用到了外部盒子上, 而box2此时就自动变成了warp的内容,所以会应用到width*/
.box3{
width:300px;
background-color: lightpink;
border: 1px solid black;
padding: 95px;
/*让宽度width作用到边框级,作用到内容级仍会撑开盒子的*/
box-sizing: border-box;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<!--将一张图片居中显示-->
<div class="box1">
<img src="http://himg.bdimg.com/sys/portrait/item/c42773636c69753132de0c.jpg" alt="小姐姐" >
</div>
<hr>
<div class="wrap">
<div class="box2">
<img src="http://himg.bdimg.com/sys/portrait/item/c42773636c69753132de0c.jpg" alt="小姐姐" >
</div>
</div>
<hr>
<div class="box3">
<img src="http://himg.bdimg.com/sys/portrait/item/c42773636c69753132de0c.jpg" alt="小姐姐" >
</div>
</body>
</html>运行实例 »
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
2、外边距
实例
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>外边距margin</title>
<style>
/********** 同级塌陷 **********/
.box1{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: lightblue;
}
.box2{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: lightcoral;
}
.box1{
margin-bottom: 30px;
}
.box2{
margin-top: 30px;
}
/* 按正常思维,现在二个盒子上下应该有60px外边距,但是页面却未发生变化 */
/* 说明二个盒子之间的外边距仍是30,肯定有一个外边距没有生效,究竟是哪一个呢? */
/* 现在将box1的margin-bottom改为50px */
.box1 {
margin-bottom: 50px;
}
/* 发现变宽了, 看样子是box1生效了, box2无效 */
/* 再把box2的margin改为80px */
.box2 {
margin-top: 80px;
}
/* 发现上下间距又变宽了,再次检查发现box2的margin生效了,box1的margin失效了 */
/* 从而得出一个结论: 当二个盒子上下排列时,外边距会出现塌陷现象,小的会陷到大的里面去,简称:"同级塌陷" */
/* 下面演示当二个盒子相互潜逃,为父子关系时,设置了margin会出现哪些问题? */
/********** 嵌套传递 **********/
.box3{
width:200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: lightcoral;
}
.box4{
width:100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: lightgreen;
}
/* 我们的任务是:使box4离box3顶部之间有50px的间距,通过margin-top来实现 */
.box4{
/*margin-top: 50px;*/
}
/* 我们的任务是:使box4离box3顶部之间有50px的间距,通过margin-top来实现 */
/* 结果发现不对, 外边距跑到了外部盒子box3上面去了,这就是外边距的"嵌套传递"现象 */
/* 当给一个子盒子添加margin时,这个margin会自动传递到父级盒子上 */
/* 所以,正确的做法是,给父级盒子添加内边距来实现 */
/* 先复位 */
.box3{
padding-top: 50px;
height: 150px;
}
/* 下面演示margin的自动挤压,这是布局中使用非常广泛 */
/********** 自动挤压 **********/
.box5 {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: lightgreen;
}
/*margin的默认值*/
.box5{
/*margin-left: auto;*/
/*margin-right: auto;*/
margin: 0 auto;
/* 这个"自动挤压"使盒子居中对齐的特征,在页面布局中应用非常多,非常重要,好好理解 */
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<!--
问题:
1、同级塌陷
2、嵌套传递
3、自动挤压
-->
<div class="box1"></div>
<div class="box2"></div>
<hr>
<div class="box3">
<div class="box4"></div>
</div>
<hr>
<div class="box5">BOX5</div>
</body>
</html>运行实例 »
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例

3、浮动与绝对定位
<!--
定位参照物:
1. 相对定位, 是以元素在文档流中的原始位置为参照物进行定位的
2. 绝对定位, 它是脱离了文档流的, 所有必须要有一个定位父级做为参照物
position: absolute; 默认以整个窗口进行绝对定位, 定位父级是<body>
-->
实例
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>绝对定位——登录</title>
<style>
*{
margin:0 auto;
}
.nav{
width: 90%;
height:60px;
background-color: lightcoral;
}
.nav-line-1{
float: right;
margin: 0 5px;
line-height: 60px;
text-align: center;
}
/*遮罩模型*/
.shade{
position: absolute;
/*左上角显示*/
left: 0;
top:0;
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
background-color: black;
opacity: 0.3;
/*display: none;*/
}
.login{
width: 300px;
height: 300px;
background-color: white;
position: absolute;
left:50%;
top:50%;
margin-left: -150px;/* 为了居中 */
margin-top: -150px;/* 为了居中 */
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="nav">
<span class="nav-line-1">购物车</span>
<span class="nav-line-1">Prime</span>
<span class="nav-line-1">我的账户</span>
</div>
<div class="shade" id="shade">
<div class="login">
<button onclick="this.parentNode.parentNode.style.display='none'">X</button>
<h2 style="text-align: center;">请输入账号、密码</h2>
<hr>
<p>
<label for="username">账号:</label>
<input type="text" name="username" id="username" placeholder="长度为4-30个字符">
</p>
<p>
<label for="password">密码:</label>
<input type="password" name="password" id="password" placeholder="长度为6-18个字符">
</p>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>运行实例 »
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例

4、固定定位
实例
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>小广告——固定定位</title>
<style>
body{
height: 2000px;
}
.ads{
width: 270px;
height: 200px;
background-color: lightblue;
position: fixed;/*固定定位*/
right: 0;
bottom: 50%;
margin-bottom: -50px;/* 为了居中 */
}
.ads img{
height: 200px;
/*margin-top: 50px;*/
}
button{
float: right;
margin-top: 10px;
margin-right: 20px;
border: none;
background: none;
font-size: 2em; /*两倍*/
color: red;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>固定定位小案例——广告位</h1>
<div class="ads">
<button onclick="this.parentNode.style.display='none'">X</button>
<img src="http://pic33.nipic.com/20130921/2759550_154636215356_2.jpg" alt="QQ在线客服">
</div>
</body>
</html>运行实例 »
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例


