本文介绍了实现一个稀疏混合专家语言模型(MoE)的方法,详细解释了模型的实施过程,包括采用稀疏混合专家取代传统的前馈神经网络,实现 top-k 门控和带噪声的 top-k 门控,以及采用 Kaiming He 初始化技术。作者还说明了从 makemore 架构保持不变的元素,比如数据集处理、分词预处理和语言建模任务。最后还提供了一个 GitHub 仓库链接,用于实现模型的整个过程,是一本不可多得的实战教科书。
内容简介
混合专家模型(MoE)在发布后开始受到广泛关注,特别是在稀疏化的混合专家语言模型中。虽然大部分组件与传统的transformers相似,但稀疏混合专家语言模型的训练稳定性存在一些问题,尽管看上去相对简单。
这种可配置的小规模稀疏 MoE 实施方法在Hugging Face的一篇博客中被介绍了出来,这对于想要进行新方法快速试验的研究者来说可能非常有帮助。博客还提供了基于PyTorch的详细代码,可以在此链接找到:https://github.com/AviSoori1x/makeMoE/tree/main。这样的小规模实现有助于研究者们在这个领域进行快速试验。
本站对此进行了整理,以飨读者。
本文在 makemore 架构的基础上,进行了几处更改:
使用稀疏混合专家代替单独的前馈神经网络;
Top-k 门控和有噪声的 Top-k 门控;
参数初始化使用了 Kaiming He 初始化方法,但本文重点是可自定义初始化方法,包括选择 Xavier/Glorot 等初始化方法。
同时,以下模块与 makemore 保持一致:
数据集、预处理(分词)部分以及 Andrej 最初选择的语言建模任务 - 生成莎士比亚文风的文本内容
Casusal 自注意力机制
训练循环
推理逻辑
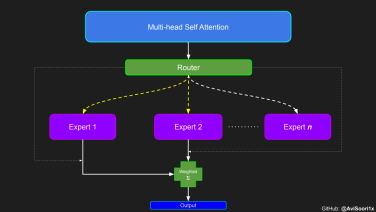
接下来逐步介绍实施方案,先从注意力机制开始。
因果缩放点积注意力机制
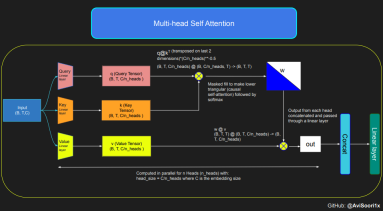
下面这段代码展示了自注意力机制的基本概念,并且侧重于使用经典的缩放点积自注意力(scaled dot product self-attention.)实现。在这一自注意力变体机制中,查询矩阵、键矩阵和值矩阵都来自相同的输入序列。同时为了确保自回归语言生成过程的完整性,特别是在纯解码器模型中,使用了一种掩码机制。
这种掩码机制非常关键,因为它可以掩盖当前 token 所处位置之后的任何信息,从而引导模型只关注序列的前面部分。这种了遮挡 token 后面内容的注意力被称为因果自注意力。值得注意的是,稀疏混合专家模型并不局限于仅有解码器的 Transformer 架构。事实上,这一领域的许多重要的成果都是围绕 T5 架构展开的,T5 架构也包含了 Transformer 模型中的编码器和解码器组件。
#This code is borrowed from Andrej Karpathy's makemore repository linked in the repo.The self attention layers in Sparse mixture of experts models are the same asin regular transformer modelstorch.manual_seed(1337)B,T,C = 4,8,32 # batch, time, channelsx = torch.randn(B,T,C)# let's see a single Head perform self-attentionhead_size = 16key = nn.Linear(C, head_size, bias=False)query = nn.Linear(C, head_size, bias=False)value = nn.Linear(C, head_size, bias=False)k = key(x) # (B, T, 16)q = query(x) # (B, T, 16)wei =q @ k.transpose(-2, -1) # (B, T, 16) @ (B, 16, T) ---> (B, T, T)tril = torch.tril(torch.ones(T, T))#wei = torch.zeros((T,T))wei = wei.masked_fill(tril == 0, float('-inf'))wei = F.softmax(wei, dim=-1) #B,T,Tv = value(x) #B,T,Hout = wei @ v # (B,T,T) @ (B,T,H) -> (B,T,H)out.shape
torch.Size([4, 8, 16])
然后,因果自注意力和多头因果自注意力的代码可整理如下。多头自注意力并行应用多个注意力头,每个注意力头单独关注通道的一个部分(嵌入维度)。多头自注意力从本质上改善了学习过程,并由于其固有的并行能力提高了模型训练的效率。下面这段代码使用了 dropout 来进行正则化,来防止过拟合。
#Causal scaled dot product self-Attention Headn_embd = 64n_head = 4n_layer = 4head_size = 16dropout = 0.1class Head(nn.Module):""" one head of self-attention """def __init__(self, head_size):super().__init__()self.key = nn.Linear(n_embd, head_size, bias=False)self.query = nn.Linear(n_embd, head_size, bias=False)self.value = nn.Linear(n_embd, head_size, bias=False)self.register_buffer('tril', torch.tril(torch.ones(block_size, block_size)))self.dropout = nn.Dropout(dropout)def forward(self, x):B,T,C = x.shapek = self.key(x) # (B,T,C)q = self.query(x) # (B,T,C)# compute attention scores ("affinities")wei = q @ k.transpose(-2,-1) * C**-0.5 # (B, T, C) @ (B, C, T) -> (B, T, T)wei = wei.masked_fill(self.tril[:T, :T] == 0, float('-inf')) # (B, T, T)wei = F.softmax(wei, dim=-1) # (B, T, T)wei = self.dropout(wei)# perform the weighted aggregation of the valuesv = self.value(x) # (B,T,C)out = wei @ v # (B, T, T) @ (B, T, C) -> (B, T, C) return out多头自注意力的实现方式如下:
#Multi-Headed Self Attentionclass MultiHeadAttention(nn.Module):""" multiple heads of self-attention in parallel """def __init__(self, num_heads, head_size):super().__init__()self.heads = nn.ModuleList([Head(head_size) for _ in range(num_heads)])self.proj = nn.Linear(n_embd, n_embd)self.dropout = nn.Dropout(dropout)def forward(self, x):out = torch.cat([h(x) for h in self.heads], dim=-1)out = self.dropout(self.proj(out)) return out
创建一个专家模块
即一个简单的多层感知器
在稀疏混合专家架构中,每个 transformer 区块内的自注意力机制保持不变。不过,每个区块的结构发生了巨大的变化:标准的前馈神经网络被多个稀疏激活的前馈网络(即专家网络)所取代。所谓「稀疏激活」,是指序列中的每个 token 只被分配给有限数量的专家(通常是一个或两个)。
这有助于提高训练和推理速度,因为每次前向传递都会激活少数专家。不过,所有专家都必须存在 GPU 内存中,因此当参数总数达到数千亿甚至数万亿时,就会产生部署方面的问题。

#Expert moduleclass Expert(nn.Module):""" An MLP is a simple linear layer followed by a non-linearity i.e. each Expert """def __init__(self, n_embd):super().__init__()self.net = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(n_embd, 4 * n_embd),nn.ReLU(),nn.Linear(4 * n_embd, n_embd),nn.Dropout(dropout),)def forward(self, x): return self.net(x)
Top-k 门控的一个例子

门控网络,也称为路由,确定哪个专家网络接收来自多头注意力的 token 的输出。举个例子解释路由的机制,假设有 4 个专家,token 需要被路由到前 2 个专家中。首先需要通过线性层将 token 输入到门控网络中。该层将对应于(Batch size,Tokens,n_embed)的输入张量从(2,4,32)维度,投影到对应于(Batch size、Tokens,num_expert)的新形状:(2、4,4)。其中 n_embed 是输入的通道维度,num_experts 是专家网络的计数。
接下来,沿最后一个维度,找出最大的前两个值及其相应的索引。
#Understanding how gating worksnum_experts = 4top_k=2n_embed=32#Example multi-head attention output for a simple illustrative example, consider n_embed=32, context_length=4 and batch_size=2mh_output = torch.randn(2, 4, n_embed)topkgate_linear = nn.Linear(n_embed, num_experts) # nn.Linear(32, 4)logits = topkgate_linear(mh_output)top_k_logits, top_k_indices = logits.topk(top_k, dim=-1)# Get top-k expertstop_k_logits, top_k_indices
#output:(tensor([[[ 0.0246, -0.0190],[ 0.1991,0.1513],[ 0.9749,0.7185],[ 0.4406, -0.8357]], [[ 0.6206, -0.0503],[ 0.8635,0.3784],[ 0.6828,0.5972],[ 0.4743,0.3420]]], grad_fn=<TopkBackward0>), tensor([[[2, 3],[2, 1],[3, 1],[2, 1]], [[0, 2], [0, 3], [3, 2], [3, 0]]]))
通过仅保留沿最后一个维度进行比较的前 k 大的值,来获得稀疏门控的输出。用负无穷值填充其余部分,在使用 softmax 激活函数。负无穷会被映射至零,而最大的前两个值会更加突出,且和为 1。要求和为 1 是为了对专家输出的内容进行加权。
zeros = torch.full_like(logits, float('-inf')) #full_like clones a tensor and fills it with a specified value (like infinity) for masking or calculations.sparse_logits = zeros.scatter(-1, top_k_indices, top_k_logits)sparse_logits
#outputtensor([[[ -inf,-inf,0.0246, -0.0190], [ -inf,0.1513,0.1991,-inf], [ -inf,0.7185,-inf,0.9749], [ -inf, -0.8357,0.4406,-inf]],[[ 0.6206,-inf, -0.0503,-inf], [ 0.8635,-inf,-inf,0.3784], [ -inf,-inf,0.5972,0.6828], [ 0.3420,-inf,-inf,0.4743]]], grad_fn=<ScatterBackward0>)
gating_output= F.softmax(sparse_logits, dim=-1)gating_output
#ouputtensor([[[0.0000, 0.0000, 0.5109, 0.4891], [0.0000, 0.4881, 0.5119, 0.0000], [0.0000, 0.4362, 0.0000, 0.5638], [0.0000, 0.2182, 0.7818, 0.0000]],[[0.6617, 0.0000, 0.3383, 0.0000], [0.6190, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.3810], [0.0000, 0.0000, 0.4786, 0.5214], [0.4670, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.5330]]], grad_fn=<SoftmaxBackward0>)
使用有噪声的 top-k 门控以实现负载平衡
# First define the top k router moduleclass TopkRouter(nn.Module):def __init__(self, n_embed, num_experts, top_k):super(TopkRouter, self).__init__()self.top_k = top_kself.linear =nn.Linear(n_embed, num_experts) def forward(self, mh_ouput):# mh_ouput is the output tensor from multihead self attention blocklogits = self.linear(mh_output)top_k_logits, indices = logits.topk(self.top_k, dim=-1)zeros = torch.full_like(logits, float('-inf'))sparse_logits = zeros.scatter(-1, indices, top_k_logits)router_output = F.softmax(sparse_logits, dim=-1) return router_output, indices
接下来使用下面这段代码来测试程序:
#Testing this out:num_experts = 4top_k = 2n_embd = 32mh_output = torch.randn(2, 4, n_embd)# Example inputtop_k_gate = TopkRouter(n_embd, num_experts, top_k)gating_output, indices = top_k_gate(mh_output)gating_output.shape, gating_output, indices#And it works!!
#output(torch.Size([2, 4, 4]), tensor([[[0.5284, 0.0000, 0.4716, 0.0000],[0.0000, 0.4592, 0.0000, 0.5408],[0.0000, 0.3529, 0.0000, 0.6471],[0.3948, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.6052]], [[0.0000, 0.5950, 0.4050, 0.0000], [0.4456, 0.0000, 0.5544, 0.0000], [0.7208, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.2792], [0.0000, 0.0000, 0.5659, 0.4341]]], grad_fn=<SoftmaxBackward0>), tensor([[[0, 2],[3, 1],[3, 1],[3, 0]], [[1, 2], [2, 0], [0, 3], [2, 3]]]))
尽管最近发布的 mixtral 的论文没有提到这一点,但本文的作者相信有噪声的 Top-k 门控机制是训练 MoE 模型的一个重要工具。从本质上讲,不会希望所有的 token 都发送给同一组「受欢迎」的专家网络。人们需要的是能在开发和探索之间取得良好平衡。为此,为了负载平衡,从门控的线性层向 logits 激活函数添加标准正态噪声是有帮助的,这使训练更有效率。
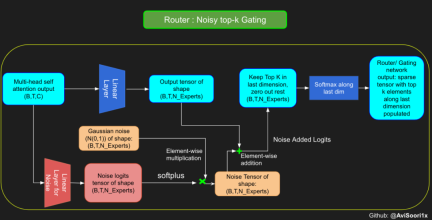
#Changing the above to accomodate noisy top-k gatingclass NoisyTopkRouter(nn.Module):def __init__(self, n_embed, num_experts, top_k):super(NoisyTopkRouter, self).__init__()self.top_k = top_k#layer for router logitsself.topkroute_linear = nn.Linear(n_embed, num_experts)self.noise_linear =nn.Linear(n_embed, num_experts)def forward(self, mh_output):# mh_ouput is the output tensor from multihead self attention blocklogits = self.topkroute_linear(mh_output)#Noise logitsnoise_logits = self.noise_linear(mh_output)#Adding scaled unit gaussian noise to the logitsnoise = torch.randn_like(logits)*F.softplus(noise_logits)noisy_logits = logits + noisetop_k_logits, indices = noisy_logits.topk(self.top_k, dim=-1)zeros = torch.full_like(noisy_logits, float('-inf'))sparse_logits = zeros.scatter(-1, indices, top_k_logits)router_output = F.softmax(sparse_logits, dim=-1) return router_output, indices
再次尝试代码:
#Testing this out, again:num_experts = 8top_k = 2n_embd = 16mh_output = torch.randn(2, 4, n_embd)# Example inputnoisy_top_k_gate = NoisyTopkRouter(n_embd, num_experts, top_k)gating_output, indices = noisy_top_k_gate(mh_output)gating_output.shape, gating_output, indices#It works!!
#output(torch.Size([2, 4, 8]), tensor([[[0.4181, 0.0000, 0.5819, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000],[0.4693, 0.5307, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000],[0.0000, 0.4985, 0.5015, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000],[0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.2641, 0.0000, 0.7359, 0.0000, 0.0000]], [[0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.6301, 0.0000, 0.3699, 0.0000, 0.0000], [0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.4766, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.5234], [0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.6815, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.3185, 0.0000], [0.4482, 0.5518, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000]]], grad_fn=<SoftmaxBackward0>), tensor([[[2, 0],[1, 0],[2, 1],[5, 3]], [[3, 5], [7, 3], [3, 6], [1, 0]]]))
创建稀疏化的混合专家模块
在获得门控网络的输出结果之后,对于给定的 token,将前 k 个值选择性地与来自相应的前 k 个专家的输出相乘。这种选择性乘法的结果是一个加权和,该加权和构成 SparseMoe 模块的输出。这个过程的关键和难点是避免不必要的乘法运算,只为前 k 名专家进行正向转播。为每个专家执行前向传播将破坏使用稀疏 MoE 的目的,因为这个过程将不再是稀疏的。
class SparseMoE(nn.Module):def __init__(self, n_embed, num_experts, top_k):super(SparseMoE, self).__init__()self.router = NoisyTopkRouter(n_embed, num_experts, top_k)self.experts = nn.ModuleList([Expert(n_embed) for _ in range(num_experts)])self.top_k = top_kdef forward(self, x):gating_output, indices = self.router(x)final_output = torch.zeros_like(x)# Reshape inputs for batch processingflat_x = x.view(-1, x.size(-1))flat_gating_output = gating_output.view(-1, gating_output.size(-1))# Process each expert in parallelfor i, expert in enumerate(self.experts):# Create a mask for the inputs where the current expert is in top-kexpert_mask = (indices == i).any(dim=-1)flat_mask = expert_mask.view(-1)if flat_mask.any():expert_input = flat_x[flat_mask]expert_output = expert(expert_input)# Extract and apply gating scoresgating_scores = flat_gating_output[flat_mask, i].unsqueeze(1)weighted_output = expert_output * gating_scores# Update final output additively by indexing and addingfinal_output[expert_mask] += weighted_output.squeeze(1) return final_output
运行以下代码来用样本测试上述实现,可以看到确实如此!
import torchimport torch.nn as nn#Let's test this outnum_experts = 8top_k = 2n_embd = 16dropout=0.1mh_output = torch.randn(4, 8, n_embd)# Example multi-head attention outputsparse_moe = SparseMoE(n_embd, num_experts, top_k)final_output = sparse_moe(mh_output)print("Shape of the final output:", final_output.shape)Shape of the final output: torch.Size([4, 8, 16])
需要强调的是,如上代码所示,从路由 / 门控网络输出的 top_k 本身也很重要。索引确定了被激活的专家是哪些, 对应的值又决定了权重大小。下图进一步解释了加权求和的概念。
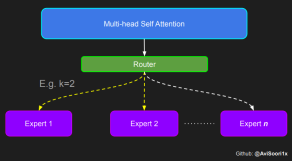
模块整合
将多头自注意力和稀疏混合专家相结合,形成稀疏混合专家 transformer 块。就像在 vanilla transformer 块中一样,也要使用残差以确保训练稳定,并避免梯度消失等问题。此外,要采用层归一化来进一步稳定学习过程。
#Create a self attention + mixture of experts block, that may be repeated several number of timesclass Block(nn.Module):""" Mixture of Experts Transformer block: communication followed by computation (multi-head self attention + SparseMoE) """def __init__(self, n_embed, n_head, num_experts, top_k):# n_embed: embedding dimension, n_head: the number of heads we'd likesuper().__init__()head_size = n_embed // n_headself.sa = MultiHeadAttention(n_head, head_size)self.smoe = SparseMoE(n_embed, num_experts, top_k)self.ln1 = nn.LayerNorm(n_embed)self.ln2 = nn.LayerNorm(n_embed)def forward(self, x):x = x + self.sa(self.ln1(x))x = x + self.smoe(self.ln2(x)) return x
最后,将所有内容整合在一起,形成稀疏混合专家语言模型。
class SparseMoELanguageModel(nn.Module):def __init__(self):super().__init__()# each token directly reads off the logits for the next token from a lookup table self.token_embedding_table = nn.Embedding(vocab_size, n_embed) self.position_embedding_table = nn.Embedding(block_size, n_embed)self.blocks = nn.Sequential(*[Block(n_embed, n_head=n_head, num_experts=num_experts,top_k=top_k) for _ in range(n_layer)])self.ln_f = nn.LayerNorm(n_embed) # final layer normself.lm_head = nn.Linear(n_embed, vocab_size)def forward(self, idx, targets=None):B, T = idx.shape# idx and targets are both (B,T) tensor of integerstok_emb = self.token_embedding_table(idx) # (B,T,C)pos_emb = self.position_embedding_table(torch.arange(T, device=device)) # (T,C)x = tok_emb + pos_emb # (B,T,C)x = self.blocks(x) # (B,T,C)x = self.ln_f(x) # (B,T,C)logits = self.lm_head(x) # (B,T,vocab_size)if targets is None:loss = Noneelse:B, T, C = logits.shapelogits = logits.view(B*T, C)targets = targets.view(B*T)loss = F.cross_entropy(logits, targets)return logits, lossdef generate(self, idx, max_new_tokens):# idx is (B, T) array of indices in the current contextfor _ in range(max_new_tokens):# crop idx to the last block_size tokensidx_cond = idx[:, -block_size:]# get the predictionslogits, loss = self(idx_cond)# focus only on the last time steplogits = logits[:, -1, :] # becomes (B, C)# apply softmax to get probabilitiesprobs = F.softmax(logits, dim=-1) # (B, C)# sample from the distributionidx_next = torch.multinomial(probs, num_samples=1) # (B, 1)# append sampled index to the running sequenceidx = torch.cat((idx, idx_next), dim=1) # (B, T+1) return idx
参数初始化对于深度神经网络的高效训练非常重要。由于专家中存在 ReLU 激活,因此这里使用了 Kaiming He 初始化。也可以尝试在 transformer 中更常用的 Glorot 初始化。杰里米 - 霍华德(Jeremy Howard)的《Fastai》第 2 部分有一个从头开始实现这些功能的精彩讲座:https://course.fast.ai/Lessons/lesson17.html
Glorot 参数初始化通常被用于 transformer 模型,因此这是一个可能提高模型性能的方法。
def kaiming_init_weights(m):if isinstance (m, (nn.Linear)): init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight)model = SparseMoELanguageModel()model.apply(kaiming_init_weights)
本文作者使用 mlflow 跟踪并记录重要指标和训练超参数。
#Using MLFlowm = model.to(device)# print the number of parameters in the modelprint(sum(p.numel() for p in m.parameters())/1e6, 'M parameters')# create a PyTorch optimizeroptimizer = torch.optim.AdamW(model.parameters(), lr=learning_rate)#mlflow.set_experiment("makeMoE")with mlflow.start_run():#If you use mlflow.autolog() this will be automatically logged. I chose to explicitly log here for completenessparams = {"batch_size": batch_size , "block_size" : block_size, "max_iters": max_iters, "eval_interval": eval_interval,"learning_rate": learning_rate, "device": device, "eval_iters": eval_iters, "dropout" : dropout, "num_experts": num_experts, "top_k": top_k }mlflow.log_params(params)for iter in range(max_iters):# every once in a while evaluate the loss on train and val setsif iter % eval_interval == 0 or iter == max_iters - 1:losses = estimate_loss()print(f"step {iter}: train loss {losses['train']:.4f}, val loss {losses['val']:.4f}")metrics = {"train_loss": losses['train'], "val_loss": losses['val']}mlflow.log_metrics(metrics, step=iter)# sample a batch of dataxb, yb = get_batch('train')# evaluate the losslogits, loss = model(xb, yb)optimizer.zero_grad(set_to_none=True)loss.backward()optimizer.step()8.996545 M parametersstep 0: train loss 5.3223, val loss 5.3166step 100: train loss 2.7351, val loss 2.7429step 200: train loss 2.5125, val loss 2.5233...step 4999: train loss 1.5712, val loss 1.7508
记录训练和验证损失可以很好地指示训练的进展情况。该图显示,可能应该在 4500 次时停止(当验证损失稍微增加时)

接下来可以使用这个模型逐字符自回归地生成文本。
# generate from the model. Not great. Not too bad eithercontext = torch.zeros((1, 1), dtype=torch.long, device=device)print(decode(m.generate(context, max_new_tokens=2000)[0].tolist()))
DUKE VINCENVENTIO:If it ever fecond he town sue kigh now,That thou wold'st is steen 't.SIMNA:Angent her; no, my a born Yorthort,Romeoos soun and lawf to your sawe with ch a woft ttastly defy,To declay the soul art; and meart smad.CORPIOLLANUS:Which I cannot shall do from by born und ot cold warrike,What king we best anone wrave's going of heard and goodThus playvage; you have wold the grace....
本文参考内容:
在实施过程中,作者大量参考了以下出版物:
混合专家模型:https://arxiv.org/pdf/2401.04088.pdf
超大型神经网络:稀疏门控混合专家层:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1701.06538.pdf
来自 Andrej Karpathy 的原始 makemore 实现:https://github.com/karpathy/makemore
还可以尝试以下几种方法,来提高模型性能:
提高混合专家模块的效率;
尝试不同的神经网络初始化策略;
从字符级到子词级的分词;
对专家数量和 k 的取值(每个 token 激活的专家数量)进行贝叶斯超参数搜索。这可以归类为神经架构搜索。
优化专家能力。
以上是手把手教你,从零开始实现一个稀疏混合专家架构语言模型(MoE)的详细内容。更多信息请关注PHP中文网其他相关文章!
 每个人都擅长使用AI:关于氛围编码的想法Apr 19, 2025 am 11:17 AM
每个人都擅长使用AI:关于氛围编码的想法Apr 19, 2025 am 11:17 AM您可以查看会议和贸易展览中正在发生的事情。您可以询问工程师在做什么,或咨询首席执行官。 您看的任何地方,事情都以惊人的速度发生变化。 工程师和非工程师 有什么区别
 火箭发射模拟和分析使用Rocketpy -Analytics VidhyaApr 19, 2025 am 11:12 AM
火箭发射模拟和分析使用Rocketpy -Analytics VidhyaApr 19, 2025 am 11:12 AM模拟火箭发射的火箭发射:综合指南 本文指导您使用强大的Python库Rocketpy模拟高功率火箭发射。 我们将介绍从定义火箭组件到分析模拟的所有内容
 5个免费数据分析课程 - 分析VidhyaApr 19, 2025 am 11:11 AM
5个免费数据分析课程 - 分析VidhyaApr 19, 2025 am 11:11 AM踏上数据驱动的职业旅程而不会破坏银行! 本文重点介绍了五个非凡的免费数据分析课程,非常适合两位经验丰富的专业人士,他们寻求扩大技能和好奇的新手渴望探索T
 如何使用OpenAgi构建自主AI代理? - 分析VidhyaApr 19, 2025 am 11:10 AM
如何使用OpenAgi构建自主AI代理? - 分析VidhyaApr 19, 2025 am 11:10 AM利用AI代理商的力量与OpenAgi:综合指南 想象一下不懈的助手,总是可以简化您的任务并提供有见地的建议。这就是AI代理商的承诺,Openagi赋予您建造它们
 GPT-4O MINI:OpenAI的最新模型如何堆叠?Apr 19, 2025 am 11:09 AM
GPT-4O MINI:OpenAI的最新模型如何堆叠?Apr 19, 2025 am 11:09 AMOpenai的最新产品GPT-4O Mini标志着朝着负担得起且可访问的高级AI迈出的重要一步。 这种小型语言模型(SLM)直接挑战诸如Llama 3和Gemma 2之类的竞争对手,具有低潜伏期,成本效益和A
 从技术创新者到医疗保健先驱:Geetha Manjunath博士的AI故事Apr 19, 2025 am 11:02 AM
从技术创新者到医疗保健先驱:Geetha Manjunath博士的AI故事Apr 19, 2025 am 11:02 AMNiramai Analytix的创始人兼首席执行官Geetha Manjunath博士的这一集由“领导数据”的剧集。 Manjunath博士拥有AI和Healthcare的25年以上的经验,并获得了印度科学学院的博士学位和MBA来回。
 用Ollama -Analytics Vidhya简化本地LLM部署Apr 19, 2025 am 11:01 AM
用Ollama -Analytics Vidhya简化本地LLM部署Apr 19, 2025 am 11:01 AM利用Ollama本地开源LLMS的力量:综合指南 运行大型语言模型(LLMS)本地提供无与伦比的控制和透明度,但是设置环境可能令人生畏。 Ollama简化了这个过程
 如何使用Monsterapi微调大语言模型Apr 19, 2025 am 10:49 AM
如何使用Monsterapi微调大语言模型Apr 19, 2025 am 10:49 AM利用微调LLM的功能与Monsterapi:综合指南 想象一个虚拟助手完美理解并预测您的需求。 由于大型语言模型(LLMS)的进步,这已成为现实。 但是,


热AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智能驱动的应用程序,用于创建逼真的裸体照片

AI Clothes Remover
用于从照片中去除衣服的在线人工智能工具。

Undress AI Tool
免费脱衣服图片

Clothoff.io
AI脱衣机

AI Hentai Generator
免费生成ai无尽的。

热门文章

热工具

MinGW - 适用于 Windows 的极简 GNU
这个项目正在迁移到osdn.net/projects/mingw的过程中,你可以继续在那里关注我们。MinGW:GNU编译器集合(GCC)的本地Windows移植版本,可自由分发的导入库和用于构建本地Windows应用程序的头文件;包括对MSVC运行时的扩展,以支持C99功能。MinGW的所有软件都可以在64位Windows平台上运行。

SublimeText3汉化版
中文版,非常好用

EditPlus 中文破解版
体积小,语法高亮,不支持代码提示功能

Atom编辑器mac版下载
最流行的的开源编辑器

禅工作室 13.0.1
功能强大的PHP集成开发环境





