目前常见的激光点云分割算法有基于平面拟合的方法和基于激光点云数据特点的方法两类。具体如下:
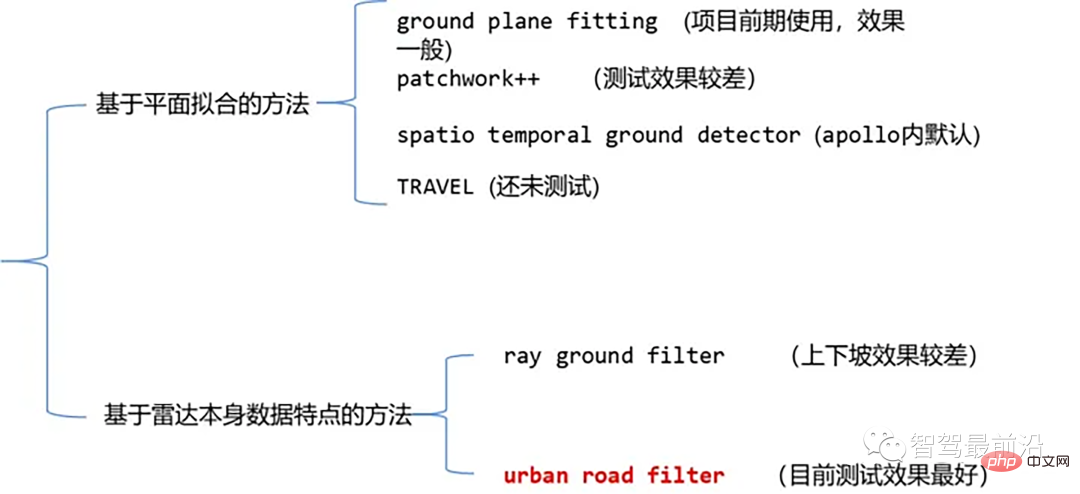
点云地面分割算法
01 基于平面拟合的方法-Ground Plane Fitting
算法思想:一种简单的处理方法就是沿着x方向(车头的方向)将空间分割成若干个子平面,然后对每个子平面使用地面平面拟合算法(GPF)从而得到能够处理陡坡的地面分割方法。该方法是在单帧点云中拟合全局平面,在点云数量较多时效果较好,点云稀疏时极易带来漏检和误检,比如16线激光雷达。
算法伪代码:
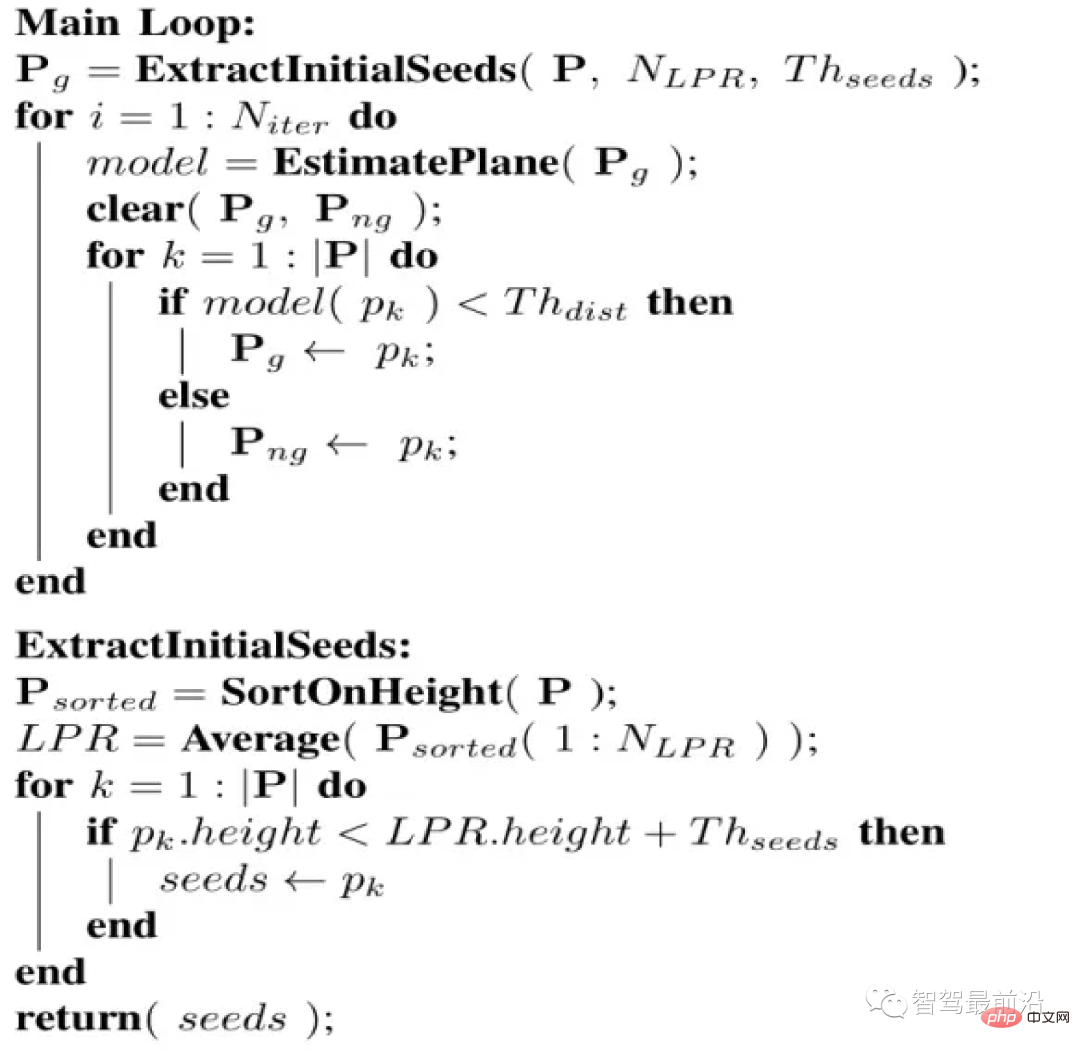
伪代码
算法流程是对于给定的点云 P ,分割的最终结果为两个点云集合,地面点云 和非地面点云。此算法有四个重要参数,如下:
- Niter : 进行奇异值分解(SVD)的次数,也即进行优化拟合的次数
- NLPR : 用于选取LPR的最低高度点的数量
- Thseed : 用于选取种子点的阈值,当点云内的点的高度小于LPR的高度加上此阈值时,我们将该点加入种子点集
- Thdist : 平面距离阈值,我们会计算点云中每一个点到我们拟合的平面的正交投影的距离,而这个平面距离阈值,就是用来判定点是否属于地面
种子点集的选择
我们首先选取一个种子点集(seed point set),这些种子点来源于点云中高度(即z值)较小的点,种子点集被用于建立描述地面的初始平面模型,那么如何选取这个种子点集呢?我们引入最低点代表(Lowest Point Representative, LPR)的概念。LPR就是NLPR个最低高度点的平均值,LPR保证了平面拟合阶段不受测量噪声的影响。

种子点的选择
输入是一帧点云,这个点云内的点已经沿着z方向(即高度)做了排序,取 num_lpr_ 个最小点,求得高度平均值 lpr_height(即LPR),选取高度小于 lpr_height + th_seeds_的点作为种子点。
具体代码实现如下
/*
@brief Extract initial seeds of the given pointcloud sorted segment.
This function filter ground seeds points accoring to heigt.
This function will set the `g_ground_pc` to `g_seed_pc`.
@param p_sorted: sorted pointcloud
@param ::num_lpr_: num of LPR points
@param ::th_seeds_: threshold distance of seeds
@param ::
*/
void PlaneGroundFilter::extract_initial_seeds_(const pcl::PointCloud &p_sorted)
{
// LPR is the mean of low point representative
double sum = 0;
int cnt = 0;
// Calculate the mean height value.
for (int i = 0; i 平面模型
接下来我们建立一个平面模型,点云中的点到这个平面的正交投影距离小于阈值Thdist,则认为该点属于地面,否则属于非地面。采用一个简单的线性模型用于平面模型估计,如下:
ax+by+cz+d=0
即:

其中
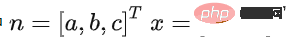
,通过初始点集的协方差矩阵C来求解n,从而确定一个平面,种子点集作为初始点集,其协方差矩阵为
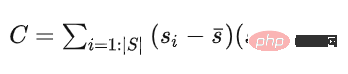
这个协方差矩阵 C 描述了种子点集的散布情况,其三个奇异向量可以通过奇异值分解(SVD)求得,这三个奇异向量描述了点集在三个主要方向的散布情况。由于是平面模型,垂直于平面的法向量 n 表示具有最小方差的方向,可以通过计算具有最小奇异值的奇异向量来求得。
那么在求得了 n 以后, d 可以通过代入种子点集的平均值 ,s(它代表属于地面的点) 直接求得。整个平面模型计算代码如下:
/*
@brief The function to estimate plane model. The
model parameter `normal_` and `d_`, and `th_dist_d_`
is set here.
The main step is performed SVD(UAV) on covariance matrix.
Taking the sigular vector in U matrix according to the smallest
sigular value in A, as the `normal_`. `d_` is then calculated
according to mean ground points.
@param g_ground_pc:global ground pointcloud ptr.
*/
void PlaneGroundFilter::estimate_plane_(void)
{
// Create covarian matrix in single pass.
// TODO: compare the efficiency.
Eigen::Matrix3f cov;
Eigen::Vector4f pc_mean;
pcl::computeMeanAndCovarianceMatrix(*g_ground_pc, cov, pc_mean);
// Singular Value Decomposition: SVD
JacobiSVD svd(cov, Eigen::DecompositionOptions::ComputeFullU);
// use the least singular vector as normal
normal_ = (svd.matrixU().col(2));
// mean ground seeds value
Eigen::Vector3f seeds_mean = pc_mean.head();
// according to normal.T*[x,y,z] = -d
d_ = -(normal_.transpose() * seeds_mean)(0, 0);
// set distance threhold to `th_dist - d`
th_dist_d_ = th_dist_ - d_;
// return the equation parameters
}优化平面主循环
extract_initial_seeds_(laserCloudIn);
g_ground_pc = g_seeds_pc;
// Ground plane fitter mainloop
for (int i = 0; i clear();
g_not_ground_pc->clear();
//pointcloud to matrix
MatrixXf points(laserCloudIn_org.points.size(), 3);
int j = 0;
for (auto p : laserCloudIn_org.points)
{
points.row(j++) points.push_back(laserCloudIn_org[r]);
}
}
}得到这个初始的平面模型以后,我们会计算点云中每一个点到该平面的正交投影的距离,即 points * normal_,并且将这个距离与设定的阈值(即th_dist_d_) 比较,当高度差小于此阈值,我们认为该点属于地面,当高度差大于此阈值,则为非地面点。经过分类以后的所有地面点被当作下一次迭代的种子点集,迭代优化。
02 基于雷达数据本身特点的方法-Ray Ground Filter
代码
https://www.php.cn/link/a8d3b1e36a14da038a06f675d1693dd8
算法思想
Ray Ground Filter算法的核心是以射线(Ray)的形式来组织点云。将点云的 (x, y, z)三维空间降到(x,y)平面来看,计算每一个点到车辆x正方向的平面夹角 θ, 对360度进行微分,分成若干等份,每一份的角度为0.2度。
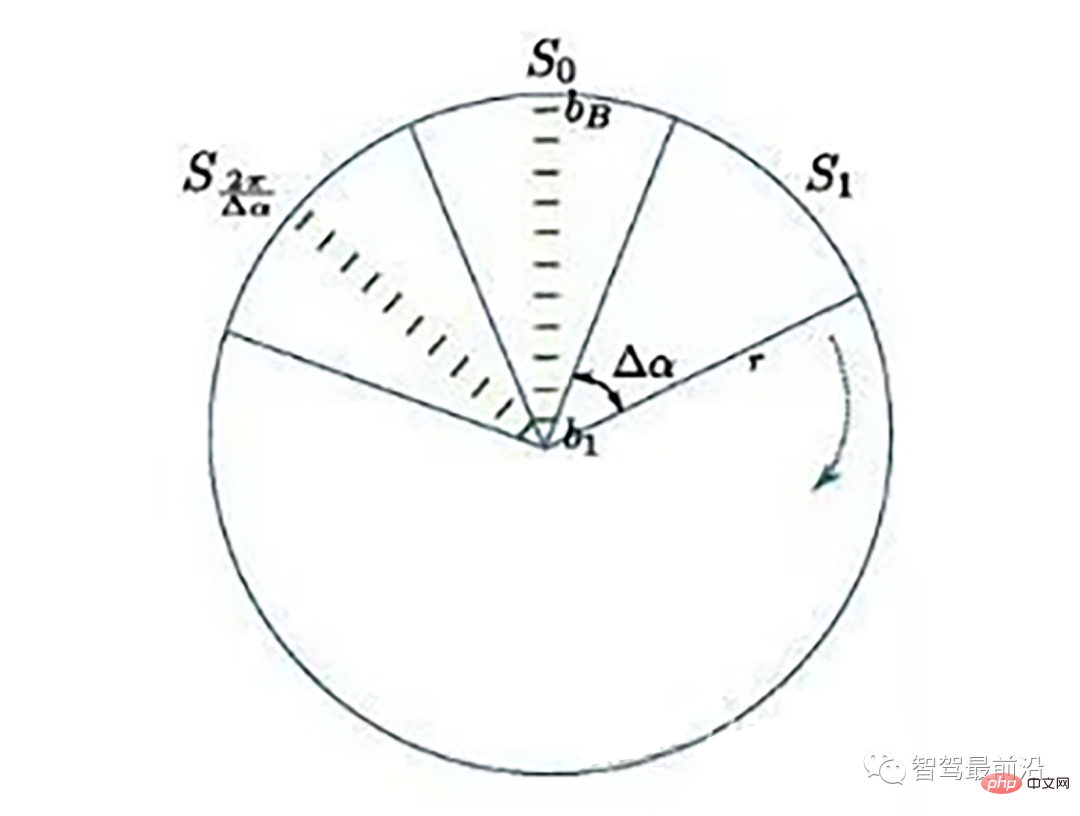
激光线束等间隔划分示意图(通常以激光雷达角度分辨率划分)
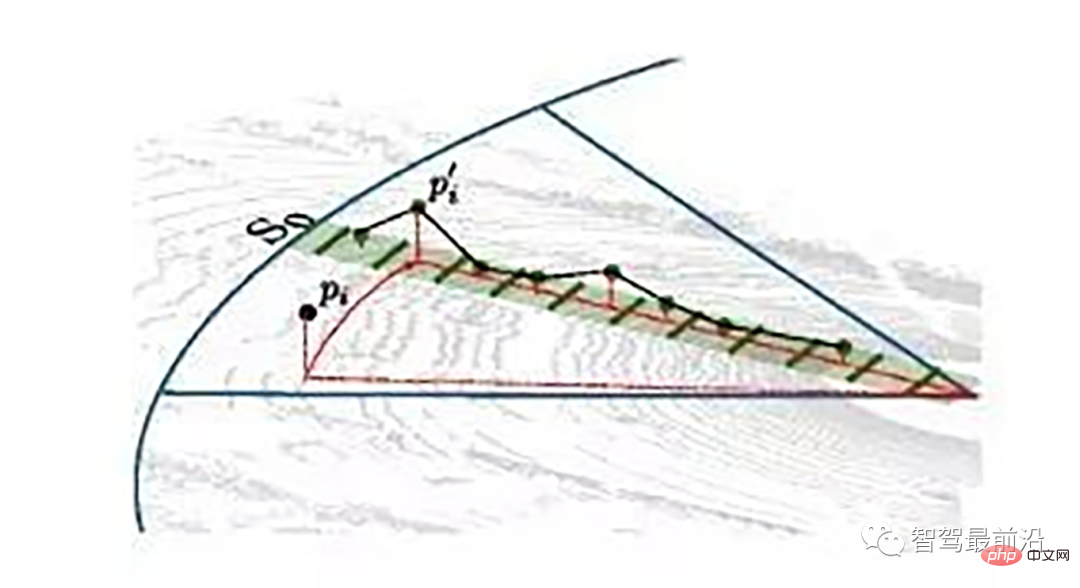
同一角度范围内激光线束在水平面的投影以及在Z轴方向的高度折线示意图
为了方便对同一角度的线束进行处理,要将原来直角坐标系的点云转换成柱坐标描述的点云数据结构。对同一夹角的线束上的点按照半径的大小进行排序,通过前后两点的坡度是否大于我们事先设定的坡度阈值,从而判断点是否为地面点。
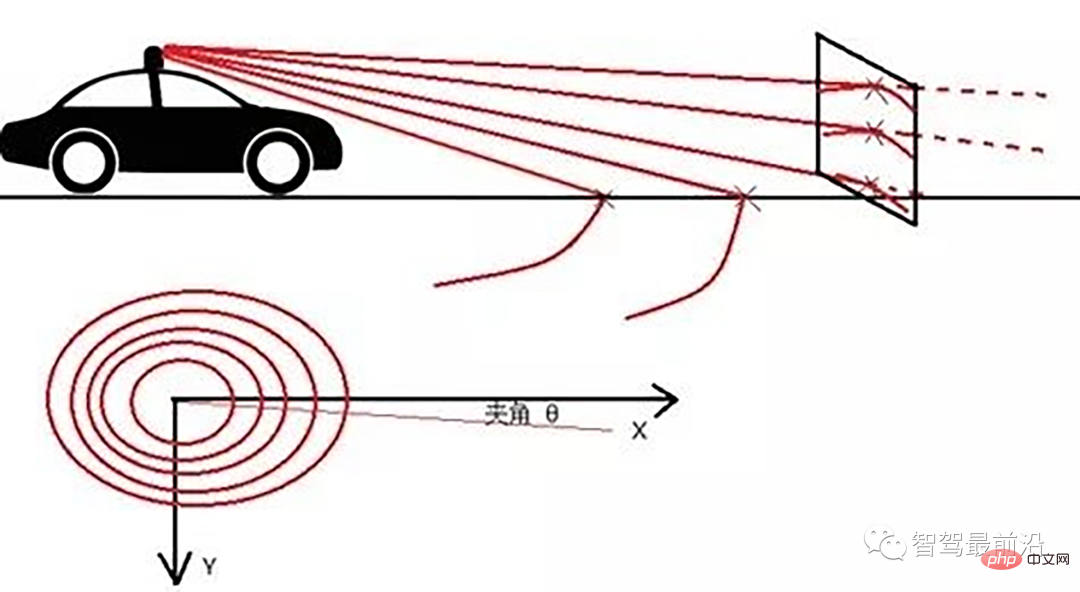
线激光线束纵截面与俯视示意图(n=4)
通过如下公式转换成柱坐标的形式:
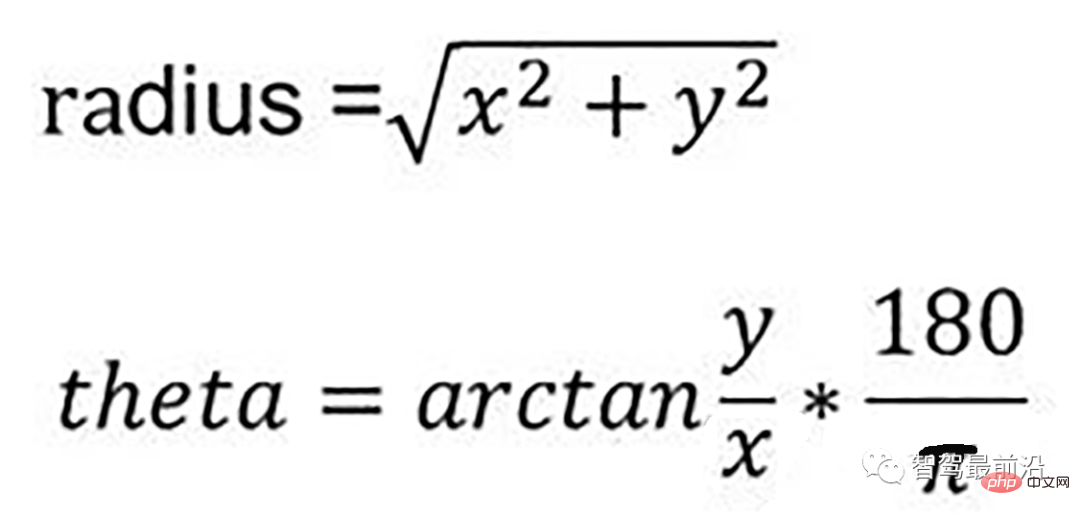
转换成柱坐标的公式
radius表示点到lidar的水平距离(半径),theta是点相对于车头正方向(即x方向)的夹角。对点云进行水平角度微分之后,可得到1800条射线,将这些射线中的点按照距离的远近进行排序。通过两个坡度阈值以及当前点的半径求得高度阈值,通过判断当前点的高度(即点的z值)是否在地面加减高度阈值范围内来判断当前点是为地面。
伪代码

伪代码
- local_max_slope_ :设定的同条射线上邻近两点的坡度阈值。
- general_max_slope_ :整个地面的坡度阈值
遍历1800条射线,对于每一条射线进行如下操作:
1.计算当前点和上一个点的水平距离pointdistance
2.根据local_max_slope_和pointdistance计算当前的坡度差阈值height_threshold
3.根据general_max_slope_和当前点的水平距离计算整个地面的高度差阈值general_height_threshold
4.若当前点的z坐标小于前一个点的z坐标加height_threshold并大于前一个点的z坐标减去height_threshold:
5.若当前点z坐标小于雷达安装高度减去general_height_threshold并且大于相加,认为是地面点
6.否则:是非地面点。
7.若pointdistance满足阈值并且前点的z坐标小于雷达安装高度减去height_threshold并大于雷达安装高度加上height_threshold,认为是地面点。
/*!
*
* @param[in] in_cloud Input Point Cloud to be organized in radial segments
* @param[out] out_organized_points Custom Point Cloud filled with XYZRTZColor data
* @param[out] out_radial_divided_indices Indices of the points in the original cloud for each radial segment
* @param[out] out_radial_ordered_clouds Vector of Points Clouds, each element will contain the points ordered
*/
void PclTestCore::XYZI_to_RTZColor(const pcl::PointCloud::Ptr in_cloud,
PointCloudXYZIRTColor &out_organized_points,
std::vector &out_radial_divided_indices,
std::vector &out_radial_ordered_clouds)
{
out_organized_points.resize(in_cloud->points.size());
out_radial_divided_indices.clear();
out_radial_divided_indices.resize(radial_dividers_num_);
out_radial_ordered_clouds.resize(radial_dividers_num_);
for (size_t i = 0; i points.size(); i++)
{
PointXYZIRTColor new_point;
//计算radius和theta
//方便转到柱坐标下。
auto radius = (float)sqrt(
in_cloud->points[i].x * in_cloud->points[i].x + in_cloud->points[i].y * in_cloud->points[i].y);
auto theta = (float)atan2(in_cloud->points[i].y, in_cloud->points[i].x) * 180 / M_PI;
if (theta points[i];
new_point.radius = radius;
new_point.theta = theta;
new_point.radial_div = radial_div;
new_point.concentric_div = concentric_div;
new_point.original_index = i;
out_organized_points[i] = new_point;
//radial divisions更加角度的微分组织射线
out_radial_divided_indices[radial_div].indices.push_back(i);
out_radial_ordered_clouds[radial_div].push_back(new_point);
} //end for
//将同一根射线上的点按照半径(距离)排序
#pragma omp for
for (size_t i = 0; i 03 基于雷达数据本身特点的方法-urban road filter
原文
Real-Time LIDAR-Based Urban Road and Sidewalk Detection for Autonomous Vehicles
代码
https://www.php.cn/link/305fa4e2c0e76dd586553d64c975a626
z_zero_method
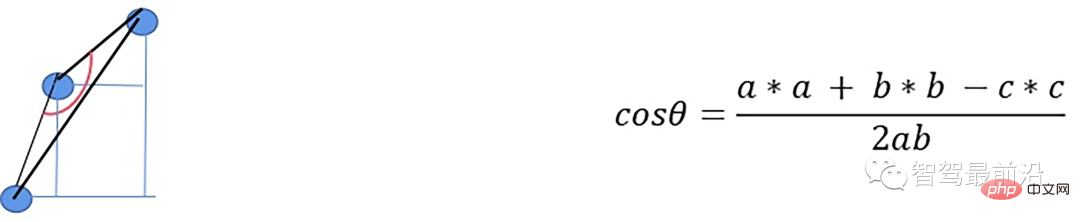
z_zero_method
首先将数据组织成[channels][thetas]
对于每一条线,对角度进行排序
- 以当前点p为中心,向左选k个点,向右选k个点
- 分别计算左边及右边k个点与当前点在x和y方向差值的均值
- 同时计算左边及右边k个点的最大z值max1及max2
- 根据余弦定理求解余弦角
如果余弦角度满足阈值且max1减去p.z满足阈值或max2减去p.z满足阈值且max2-max1满足阈值,认为此点为障碍物,否则就认为是地面点。
x_zero_method
X-zero和Z-zero方法可以找到避开测量的X和Z分量的人行道,X-zero和Z-zero方法都考虑了体素的通道数,因此激光雷达必须与路面平面不平行,这是上述两种算法以及整个城市道路滤波方法的已知局限性。X-zero方法去除了X方向的值,使用柱坐标代替。
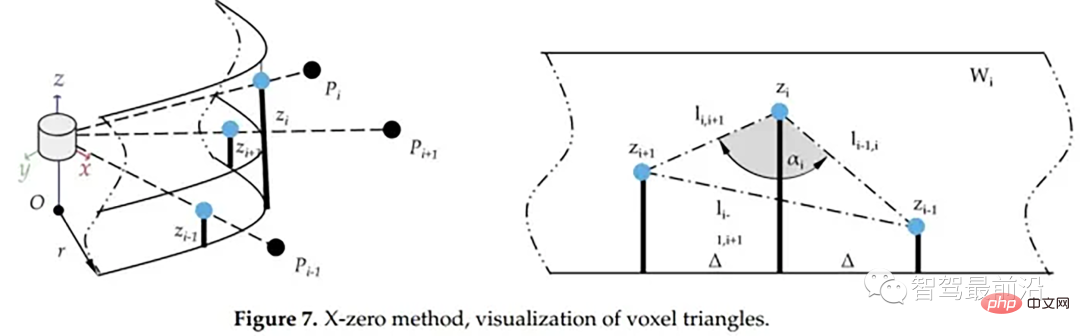
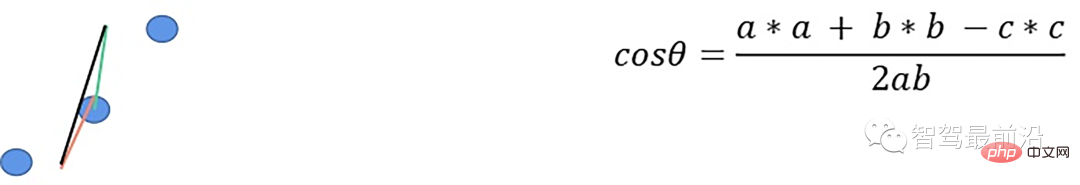
x_zero_method
首先将数据组织成[channels][thetas]
对于每一条线,对角度进行排序
- 以当前点p为中心,向右选第k/2个点p1和第k个点p2
- 分别计算p及p1、p1及p2、p及p2间z方向的距离
- 根据余弦定理求解余弦角
如果余弦角度满足阈值且p1.z-p.z满足阈值或p1.z-p2.z满足阈值且p.z-p2.z满足阈值,认为此点为障碍物
star_search_method
该方法将点云划分为矩形段,这些形状的组合像一颗星;这就是名字的来源,从每个路段提取可能的人行道起点,其中创建的算法对基于Z坐标的高度变化不敏感,这意味着在实践中,即使当激光雷达相对于路面平面倾斜时,该算法也会表现良好,在柱坐标系中处理点云。
具体实现:
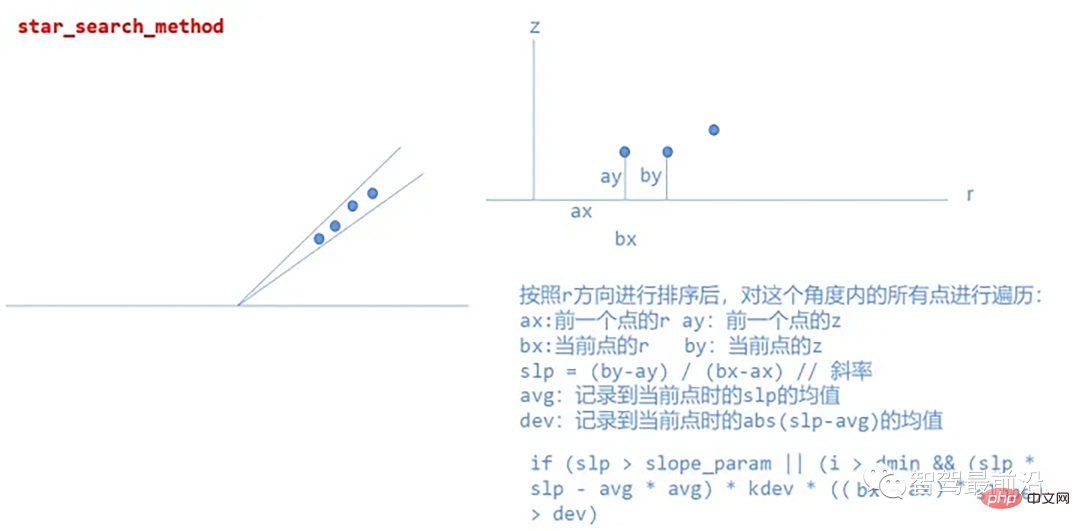
star_search_method
以上是「深度解析」:探究自动驾驶中的激光雷达点云分割算法的详细内容。更多信息请关注PHP中文网其他相关文章!
 大多数使用的10个功率BI图 - 分析VidhyaApr 16, 2025 pm 12:05 PM
大多数使用的10个功率BI图 - 分析VidhyaApr 16, 2025 pm 12:05 PM用Microsoft Power BI图来利用数据可视化的功能 在当今数据驱动的世界中,有效地将复杂信息传达给非技术观众至关重要。 数据可视化桥接此差距,转换原始数据i
 AI的专家系统Apr 16, 2025 pm 12:00 PM
AI的专家系统Apr 16, 2025 pm 12:00 PM专家系统:深入研究AI的决策能力 想象一下,从医疗诊断到财务计划,都可以访问任何事情的专家建议。 这就是人工智能专家系统的力量。 这些系统模仿Pro
 三个最好的氛围编码器分解了这项代码中的AI革命Apr 16, 2025 am 11:58 AM
三个最好的氛围编码器分解了这项代码中的AI革命Apr 16, 2025 am 11:58 AM首先,很明显,这种情况正在迅速发生。各种公司都在谈论AI目前撰写的代码的比例,并且这些代码的比例正在迅速地增加。已经有很多工作流离失所
 跑道AI的Gen-4:AI蒙太奇如何超越荒谬Apr 16, 2025 am 11:45 AM
跑道AI的Gen-4:AI蒙太奇如何超越荒谬Apr 16, 2025 am 11:45 AM从数字营销到社交媒体的所有创意领域,电影业都站在技术十字路口。随着人工智能开始重塑视觉讲故事的各个方面并改变娱乐的景观
 如何注册5天ISRO AI免费课程? - 分析VidhyaApr 16, 2025 am 11:43 AM
如何注册5天ISRO AI免费课程? - 分析VidhyaApr 16, 2025 am 11:43 AMISRO的免费AI/ML在线课程:通向地理空间技术创新的门户 印度太空研究组织(ISRO)通过其印度遥感研究所(IIR)为学生和专业人士提供了绝佳的机会
 AI中的本地搜索算法Apr 16, 2025 am 11:40 AM
AI中的本地搜索算法Apr 16, 2025 am 11:40 AM本地搜索算法:综合指南 规划大规模活动需要有效的工作量分布。 当传统方法失败时,本地搜索算法提供了强大的解决方案。 本文探讨了爬山和模拟
 OpenAI以GPT-4.1的重点转移,将编码和成本效率优先考虑Apr 16, 2025 am 11:37 AM
OpenAI以GPT-4.1的重点转移,将编码和成本效率优先考虑Apr 16, 2025 am 11:37 AM该版本包括三种不同的型号,GPT-4.1,GPT-4.1 MINI和GPT-4.1 NANO,标志着向大语言模型景观内的特定任务优化迈进。这些模型并未立即替换诸如
 提示:chatgpt生成假护照Apr 16, 2025 am 11:35 AM
提示:chatgpt生成假护照Apr 16, 2025 am 11:35 AMChip Giant Nvidia周一表示,它将开始制造AI超级计算机(可以处理大量数据并运行复杂算法的机器),完全是在美国首次在美国境内。这一消息是在特朗普总统SI之后发布的


热AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智能驱动的应用程序,用于创建逼真的裸体照片

AI Clothes Remover
用于从照片中去除衣服的在线人工智能工具。

Undress AI Tool
免费脱衣服图片

Clothoff.io
AI脱衣机

AI Hentai Generator
免费生成ai无尽的。

热门文章

热工具

Atom编辑器mac版下载
最流行的的开源编辑器

安全考试浏览器
Safe Exam Browser是一个安全的浏览器环境,用于安全地进行在线考试。该软件将任何计算机变成一个安全的工作站。它控制对任何实用工具的访问,并防止学生使用未经授权的资源。

禅工作室 13.0.1
功能强大的PHP集成开发环境

SublimeText3 英文版
推荐:为Win版本,支持代码提示!

记事本++7.3.1
好用且免费的代码编辑器






