Whether it's a simple formatting mistake or a more complex syntax issue, knowing how to fix #VALUE errors in Excel is essential for anyone who wants to create error-free spreadsheets and ensure the accuracy of their data.
When working with Excel, it is common to encounter errors. One of the most frustrating errors is #VALUE, which is raised when a formula or function is unable to process data. This error can be caused by several factors including incorrect syntax, mismatched cell references, or hidden characters. In this article, we will explore the various causes of the #VALUE error and provide tips on how to fix it.
When is #VALUE error raised in Excel?
The #VALUE! error in Excel is commonly caused by the following reasons:
- Unexpected data type. If an Excel function requires a specific data type, such as a number or text, and a cell contains a different data type.
- Incorrect formula syntax. When the function's arguments are incorrect, missing or in wrong order.
- Spaces. If a formula refers to a cell that contains a space character. Visually, such cells look absolutely empty.
- Invisible characters. Sometimes, cells may contain hidden or non-printing characters that prevent a formula from calculating correctly.
- Dates formatted as text. When dates are input in the format that Excel does not understand, they are treated as text strings rather than valid dates.
- Ranges have incompatible dimensions. When formula references a few ranges that are not of the same size or shape, Excel cannot calculate the formula and throws an error.
As you see, the #VALUE error in Excel can be caused by a variety of factors. By understanding the root cause, you can more easily find the right remedy to fix it.

How to troubleshoot and fix #VALUE error in Excel
Once you identify the cause of the error, use the appropriate troubleshooting steps to resolve the issue.
Check if data type is valid
To avoid the #VALUE error in Excel, verify that the data type in the referred cell is correct. If a formula or function requires numeric data, make sure the cell contains a number and not text.
A typical example is math operations such as addition and multiplication. When one of the values that you add up or multiply is non-numeric, a #VALUE error occurs:

To fix the error, you can use one of these options:
- Enter the missing numeric values.
- Use Excel functions that automatically ignore text values.
- Write an IF statement that corresponds to your business logic.
In this example, you can use the PRODUCT function:
=PRODUCT(B3, C3)
If one of the referenced cells contains text, logical value, or is empty, that cell is ignored. The result is as if you multiply the other value by 1.
Alternatively, you can build an IF statement like this:
=IF(AND(ISNUMBER(B3), ISNUMBER(C3)), B3*C3, 0)
This formula multiplies two cells only if both values are numeric and returns zero if either cell contains a non-numeric value. For this particular case, it makes perfect sense.

Remove spaces and hidden characters
In some formulas, a cell with errant spaces or invisible characters may also cause a #VALUE! error, as shown in the screenshot below:

Visually, cells such as D3, B7 and C14 may appear to be completely empty. However, they do contain one or more spaces or non-printing characters. In Excel, a space character is considered text, and it can potentially trigger the #VALUE! error. In fact, it is just another case of the previous example, so it can be fixed in a similar manner:
- Ensure that the problematic cells are really empty. To do this, select the cell and press the Delete key to remove any hidden character in it.
- Use an Excel function that ignores text values, such as the SUM function instead of the arithmetic operation of addition.

Verify that referred ranges are compatible
Many Excel functions that accept multiple ranges in their arguments require those ranges to be of the same size and shape. If not, a formula raises the #VALUE error.
For example, the dynamic array FILTER function results in a #VALUE error when the include and array arguments have incompatible dimensions. For example:
=FILTER(A3:B20, A3:A22="Apple")
Once the range references are changed accordingly, the error is gone:
=FILTER(A3:B20, A3:A20="Apple")

Make sure dates are not stored as text
In Excel, dates are typically stored as numeric values. However, some dates in your worksheet may be stored as text strings instead. When this happens, Excel will return the #VALUE! error if you try to perform calculations or operations on these dates, as text values cannot be added, subtracted or somehow else calculated.
To resolve this issue, you need to convert text-formatted dates to valid Excel dates.

Check formula syntax
Another possible cause of a #VALUE error in Excel could be a syntax error in your formula. Excel's Formula Auditing tools can help you identify and correct such issues.
- Select the cell with the formula that is producing the #VALUE error.
- On the Formulas tab, in the Formula Auditing group, click on Evaluate Formula or Error Checking.
Excel will step through the formula one section at a time, showing the result of each step. If there is a syntax error, Excel will highlight the specific part of the formula is causing the error. Once you have detected the syntax error, correct it and re-evaluate the formula to ensure that it is now working as expected.
For example, consider the following formula in the dataset below:
=SORT(CHOOSECOLS(A3:B20, 3))
The #VALUE error occurs because the col_num argument (3) of the CHOOSECOLS function is greater than the total number of columns in the referred array (2).

Setting the last argument to 2 resolves the issue and returns the desired result – the Total column sorted from smallest to largest:

#VALUE error in Excel XLOOKUP and VLOOKUP
The VLOOKUP function and its modern successor XLOOKUP are commonly used in Excel to search and retrieve matching data. However, both functions can produce the #VALUE error under certain circumstances.
One common cause of the #VALUE error in XLOOKUP is when the dimensions of the lookup and return arrays are incomparable. For example, you cannot search in a horizontal array and return values from a vertical array. Also, the lookup array cannot be bigger or smaller than the return array. If there is any mismatch in the size of these arrays, XLOOKUP will not be able to perform the lookup and return the #VALUE error.
For example, the below XLOOKUP formula returns a #VALUE error because the lookup and return arrays contain a different number of rows:
=XLOOKUP(D3, A3:A20, B3:B22)
Adjusting the return_array reference resolves the error:
=XLOOKUP(D3, A3:A20, B3:B20)

In VLOOKUP, two common reasons for the #VALUE error are when the lookup value exceeds 255 characters and when the col_index_num argument is less than 1. For more information, please see #VALUE error in VLOOKUP.
Get rid of #VALUE error using IFERROR function
To eliminate the #VALUE error in your Excel sheets, you can use the IFERROR function in Excel 2007 - 365 or the IF ISERROR combination in earlier versions.
Suppose you are using a DATEDIF formula to find the difference between the dates in B3 and C3:
=DATEDIF(B3, C3, "d")
If one or both dates are invalid, the formula results in a #VALUE error. To fix it, wrap your core formula in the IFERROR function like this:
=IFERROR(DATEDIF(B3, C3, "d"), "Invalid date!")
If Excel doesn't recognize the referenced cell value as a date, the IFERROR function will explicitly point it out.

Tip. To quickly find all #VALUE errors in a worksheet, you can utilize the Go to Special feature or the Find and Replace dialog box. We discussed these options in detail when locating #NAME errors. For #VALUE errors, the steps are essentially the same.
That's how to detect and fix the #VALUE error in Excel. By understanding the causes and using the appropriate troubleshooting techniques, you can quickly get your spreadsheet back on track.
Practice workbook for download
#VALUE error in Excel - examples (.xlsx file)
以上是#excel中的价值错误:原因和修复的详细内容。更多信息请关注PHP中文网其他相关文章!
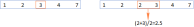
 Google电子表格Countif函数带有公式示例Apr 11, 2025 pm 12:03 PM
Google电子表格Countif函数带有公式示例Apr 11, 2025 pm 12:03 PMGoogle主张Countif:综合指南 本指南探讨了Google表中的多功能Countif函数,展示了其超出简单单元格计数的应用程序。 我们将介绍从精确和部分比赛到Han的各种情况
 Excel共享工作簿:如何为多个用户共享Excel文件Apr 11, 2025 am 11:58 AM
Excel共享工作簿:如何为多个用户共享Excel文件Apr 11, 2025 am 11:58 AM本教程提供了共享Excel工作簿,涵盖各种方法,访问控制和冲突解决方案的综合指南。 现代Excel版本(2010年,2013年,2016年及以后)简化了协作编辑,消除了M的需求
 如何将Excel转换为JPG-保存.xls或.xlsx作为图像文件Apr 11, 2025 am 11:31 AM
如何将Excel转换为JPG-保存.xls或.xlsx作为图像文件Apr 11, 2025 am 11:31 AM本教程探讨了将.xls文件转换为.jpg映像的各种方法,包括内置的Windows工具和免费的在线转换器。 需要创建演示文稿,安全共享电子表格数据或设计文档吗?转换哟
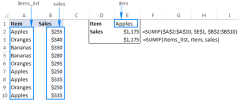 excel名称和命名范围:如何定义和使用公式Apr 11, 2025 am 11:13 AM
excel名称和命名范围:如何定义和使用公式Apr 11, 2025 am 11:13 AM本教程阐明了Excel名称的功能,并演示了如何定义单元格,范围,常数或公式的名称。 它还涵盖编辑,过滤和删除定义的名称。 Excel名称虽然非常有用,但通常是泛滥的
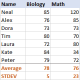 标准偏差Excel:功能和公式示例Apr 11, 2025 am 11:01 AM
标准偏差Excel:功能和公式示例Apr 11, 2025 am 11:01 AM本教程阐明了平均值的标准偏差和标准误差之间的区别,指导您掌握标准偏差计算的最佳Excel函数。 在描述性统计中,平均值和标准偏差为interinsi
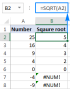 Excel中的平方根:SQRT功能和其他方式Apr 11, 2025 am 10:34 AM
Excel中的平方根:SQRT功能和其他方式Apr 11, 2025 am 10:34 AM该Excel教程演示了如何计算正方根和n根。 找到平方根是常见的数学操作,Excel提供了几种方法。 计算Excel中正方根的方法: 使用SQRT函数:
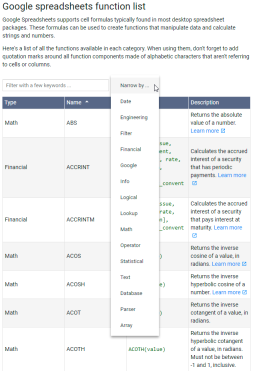 Google表基础知识:了解如何使用Google电子表格Apr 11, 2025 am 10:23 AM
Google表基础知识:了解如何使用Google电子表格Apr 11, 2025 am 10:23 AM解锁Google表的力量:初学者指南 本教程介绍了Google Sheets的基础,这是MS Excel的强大而多才多艺的替代品。 了解如何轻松管理电子表格,利用关键功能并协作


热AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智能驱动的应用程序,用于创建逼真的裸体照片

AI Clothes Remover
用于从照片中去除衣服的在线人工智能工具。

Undress AI Tool
免费脱衣服图片

Clothoff.io
AI脱衣机

Video Face Swap
使用我们完全免费的人工智能换脸工具轻松在任何视频中换脸!

热门文章

热工具

Dreamweaver Mac版
视觉化网页开发工具

mPDF
mPDF是一个PHP库,可以从UTF-8编码的HTML生成PDF文件。原作者Ian Back编写mPDF以从他的网站上“即时”输出PDF文件,并处理不同的语言。与原始脚本如HTML2FPDF相比,它的速度较慢,并且在使用Unicode字体时生成的文件较大,但支持CSS样式等,并进行了大量增强。支持几乎所有语言,包括RTL(阿拉伯语和希伯来语)和CJK(中日韩)。支持嵌套的块级元素(如P、DIV),

SublimeText3 Linux新版
SublimeText3 Linux最新版

Atom编辑器mac版下载
最流行的的开源编辑器

PhpStorm Mac 版本
最新(2018.2.1 )专业的PHP集成开发工具