Android動畫合集之屬性動畫-初見
本節引言:
本節帶給的是Android動畫中的第三種動畫-屬性動畫(Property Animation), 記得上一節8.4.2 Android動畫合集之補間動畫為Fragment 設定過渡動畫的時候,說過,App包和V4包下的Fragment調用setCustomAnimations()對應的 動畫類型是不一樣的,v4包下的是Animation,而app包下的是Animator;
Animation一般動畫就是我們前面學的幀動畫和補間動畫! Animator則是本節要講的屬性動畫!
關於屬性動畫,大牛郭大叔已經寫了三篇非常好的總結文,寫得非常贊,就沒必要重複造輪子了, 不過這裡還是過一遍,大部分內容參考的下面三篇文章:
Android屬性動畫完全解析(上),初識屬性動畫的基本用法
Android屬性動畫完全解析(中),ValueAnimator和ObjectAnimator的高級用法
#Android屬性動畫完全解析(下),Interpolator和ViewPropertyAnimator的用法
寫的非常好,或者說你可以直接跳過本文去看上面的三篇文章~
當然,你願意看我叨叨逼的話,也很歡迎,好了,開始本節內容吧~
1.屬性動畫概念叨著逼
不BB,直接上圖,就是這麼暴力~

##2.ValueAnimator簡單使用
使用流程:
- 1.呼叫ValueAnimator的
- ofInt() ,ofFloat()或ofObject()靜態方法建立ValueAnimator實例 2.呼叫實例的setXxx方法設定動畫持續時間,插值方式,重複次數等3.呼叫實例的
- addUpdateListener新增AnimatorUpdateListener監聽器,在該監聽器中 可以取得ValueAnimator計算出來的值,你可以值套用到指定物件上~ 4.呼叫實例的
- start()方法開啟動畫! 另外我們可以看到ofInt和ofFloat都有這樣的參數:float/int... values代表可以多個值!
使用範例:

#程式碼實作:
佈局文件:activity_main.xml,非常簡單,四個按鈕,一個ImageView
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:id="@+id/ly_root" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="vertical"> <Button android:id="@+id/btn_one" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="动画1" /> <Button android:id="@+id/btn_two" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="动画2" /> <Button android:id="@+id/btn_three" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="动画3" /> <Button android:id="@+id/btn_four" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="动画4" /> <ImageView android:id="@+id/img_babi" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_gravity="center" android:background="@mipmap/img_babi" /></LinearLayout>
接著到MainActivity.java, 首先需要一個修改View位置的方法,這裡呼叫moveView()設定左邊和上邊的起始座標以及寬高!
接著定義了四個動畫,分別是:直線移動,縮放,旋轉加透明,以及圓形旋轉!
然後透過按鈕觸發對應的動畫~
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements View.OnClickListener {
private Button btn_one;
private Button btn_two;
private Button btn_three;
private Button btn_four;
private LinearLayout ly_root;
private ImageView img_babi;
private int width;
private int height;
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
bindViews();
}
private void bindViews() {
ly_root = (LinearLayout) findViewById(R.id.ly_root);
btn_one = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn_one);
btn_two = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn_two);
btn_three = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn_three);
btn_four = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn_four);
img_babi = (ImageView) findViewById(R.id.img_babi);
btn_one.setOnClickListener(this);
btn_two.setOnClickListener(this);
btn_three.setOnClickListener(this);
btn_four.setOnClickListener(this);
img_babi.setOnClickListener(this);
}
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
switch (v.getId()) {
case R.id.btn_one:
lineAnimator();
break;
case R.id.btn_two:
scaleAnimator();
break;
case R.id.btn_three:
raAnimator();
break;
case R.id.btn_four:
circleAnimator();
break;
case R.id.img_babi:
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "不愧是coder-pig~", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
break;
}
}
//定义一个修改ImageView位置的方法
private void moveView(View view, int rawX, int rawY) {
int left = rawX - img_babi.getWidth() / 2;
int top = rawY - img_babi.getHeight();
int width = left + view.getWidth();
int height = top + view.getHeight();
view.layout(left, top, width, height);
}
//定义属性动画的方法:
//按轨迹方程来运动
private void lineAnimator() {
width = ly_root.getWidth();
height = ly_root.getHeight();
ValueAnimator xValue = ValueAnimator.ofInt(height,0,height / 4,height / 2,height / 4 * 3 ,height);
xValue.setDuration(3000L);
xValue.addUpdateListener(new ValueAnimator.AnimatorUpdateListener() {
@Override
public void onAnimationUpdate(ValueAnimator animation) {
// 轨迹方程 x = width / 2
int y = (Integer) animation.getAnimatedValue();
int x = width / 2;
moveView(img_babi, x, y);
}
});
xValue.setInterpolator(new LinearInterpolator());
xValue.start();
}
//缩放效果
private void scaleAnimator(){
//这里故意用两个是想让大家体会下组合动画怎么用而已~
final float scale = 0.5f;
AnimatorSet scaleSet = new AnimatorSet();
ValueAnimator valueAnimatorSmall = ValueAnimator.ofFloat(1.0f, scale);
valueAnimatorSmall.setDuration(500);
ValueAnimator valueAnimatorLarge = ValueAnimator.ofFloat(scale, 1.0f);
valueAnimatorLarge.setDuration(500);
valueAnimatorSmall.addUpdateListener(new ValueAnimator.AnimatorUpdateListener() {
@Override
public void onAnimationUpdate(ValueAnimator animation) {
float scale = (Float) animation.getAnimatedValue();
img_babi.setScaleX(scale);
img_babi.setScaleY(scale);
}
});
valueAnimatorLarge.addUpdateListener(new ValueAnimator.AnimatorUpdateListener() {
@Override
public void onAnimationUpdate(ValueAnimator animation) {
float scale = (Float) animation.getAnimatedValue();
img_babi.setScaleX(scale);
img_babi.setScaleY(scale);
}
});
scaleSet.play(valueAnimatorLarge).after(valueAnimatorSmall);
scaleSet.start();
//其实可以一个就搞定的
// ValueAnimator vValue = ValueAnimator.ofFloat(1.0f, 0.6f, 1.2f, 1.0f, 0.6f, 1.2f, 1.0f);
// vValue.setDuration(1000L);
// vValue.addUpdateListener(new ValueAnimator.AnimatorUpdateListener() {
// @Override
// public void onAnimationUpdate(ValueAnimator animation) {
// float scale = (Float) animation.getAnimatedValue();
// img_babi.setScaleX(scale);
// img_babi.setScaleY(scale);
// }
// });
// vValue.setInterpolator(new LinearInterpolator());
// vValue.start();
}
//旋转的同时透明度变化
private void raAnimator(){
ValueAnimator rValue = ValueAnimator.ofInt(0, 360);
rValue.setDuration(1000L);
rValue.addUpdateListener(new ValueAnimator.AnimatorUpdateListener() {
@Override
public void onAnimationUpdate(ValueAnimator animation) {
int rotateValue = (Integer) animation.getAnimatedValue();
img_babi.setRotation(rotateValue);
float fractionValue = animation.getAnimatedFraction();
img_babi.setAlpha(fractionValue);
}
});
rValue.setInterpolator(new DecelerateInterpolator());
rValue.start();
}
//圆形旋转
protected void circleAnimator() {
width = ly_root.getWidth();
height = ly_root.getHeight();
final int R = width / 4;
ValueAnimator tValue = ValueAnimator.ofFloat(0,
(float) (2.0f * Math.PI));
tValue.setDuration(1000);
tValue.addUpdateListener(new ValueAnimator.AnimatorUpdateListener() {
@Override
public void onAnimationUpdate(ValueAnimator animation) {
// 圆的参数方程 x = R * sin(t) y = R * cos(t)
float t = (Float) animation.getAnimatedValue();
int x = (int) (R * Math.sin(t) + width / 2);
int y = (int) (R * Math.cos(t) + height / 2);
moveView(img_babi, x, y);
}
});
tValue.setInterpolator(new DecelerateInterpolator());
tValue.start();
}
}好的,使用的流程非常簡單,先建立ValueAnimator對象,呼叫ValueAnimator.ofInt/ofFloat 取得,然後設定動畫持續時間,addUpdateListener新增AnimatorUpdateListener事件監聽, 然後使用參數animation的getAnimatedValue()得到目前的值,然後我們可以拿著這個值 來修改View的一些屬性,從而形成所謂的動畫效果,接著設定setInterpolator動畫渲染模式, 最後呼叫start()開始動畫的播放~
臥槽,直線方程,圓的參數方程,我都開始方了,這不是高數的東西麼,
掛科學渣連三角函數都忘了...
範例參考自github:MoveViewValueAnimator
3.ObjectAnimator簡單使用
比起ValueAnimator,ObjectAnimator顯得更為易用,透過該類別我們可以直接對任意物件的任意屬性進行動畫操作!沒錯,是任意對象,不單單只是View對象,
不斷地將物件中的某個屬性值進行賦值,然後根據物件屬性值的改變再來決定如何展現
出來!例如為TextView設定如下動畫:ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(textview, "alpha", 1f, 0f);
這裡就是不斷改變alpha的值,從1f - 0f,然後物件根據屬性值的變化來刷新介面顯示,從而
展現出淡入淡出的效果,而在TextView類別中並沒有alpha這個屬性,ObjectAnimator內部機制是:尋找傳輸的屬性名稱對應的get和set方法~,而非找這個屬性值! 不信的話你可以到TextView的源碼裡找找是否有alpha這個屬性!
好的,下面我們利用ObjectAnimator來實現四種補間動畫的效果吧~
運行效果圖:
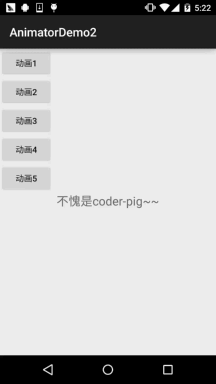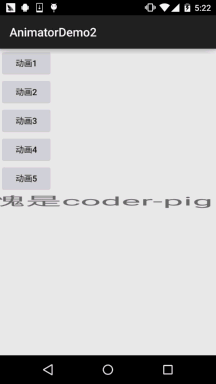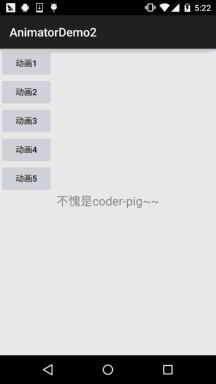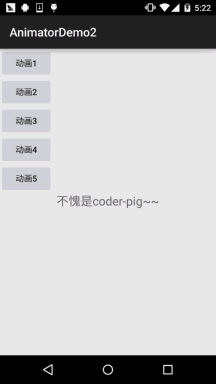
程式碼實作:
佈局直接用的上面那個佈局,加了個按鈕,把ImageView換成了TextView,這裡就不貼程式碼了, 直接上MainActivity.java部分的程式碼,其實都是大同小異的~
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements View.OnClickListener {
private Button btn_one;
private Button btn_two;
private Button btn_three;
private Button btn_four;
private Button btn_five;
private LinearLayout ly_root;
private TextView tv_pig;
private int height;
private ObjectAnimator animator1;
private ObjectAnimator animator2;
private ObjectAnimator animator3;
private ObjectAnimator animator4;
private AnimatorSet animSet;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
bindViews();
initAnimator();
}
private void bindViews() {
ly_root = (LinearLayout) findViewById(R.id.ly_root);
btn_one = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn_one);
btn_two = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn_two);
btn_three = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn_three);
btn_four = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn_four);
btn_five = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn_five);
tv_pig = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.tv_pig);
height = ly_root.getHeight();
btn_one.setOnClickListener(this);
btn_two.setOnClickListener(this);
btn_three.setOnClickListener(this);
btn_four.setOnClickListener(this);
btn_five.setOnClickListener(this);
tv_pig.setOnClickListener(this);
}
//初始化动画
private void initAnimator() {
animator1 = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(tv_pig, "alpha", 1f, 0f, 1f, 0f, 1f);
animator2 = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(tv_pig, "rotation", 0f, 360f, 0f);
animator3 = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(tv_pig, "scaleX", 2f, 4f, 1f, 0.5f, 1f);
animator4 = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(tv_pig, "translationY", height / 8, -100, height / 2);
}
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
switch (v.getId()) {
case R.id.btn_one:
animator1.setDuration(3000l);
animator1.start();
break;
case R.id.btn_two:
animator2.setDuration(3000l);
animator2.start();
break;
case R.id.btn_three:
animator3.setDuration(3000l);
animator3.start();
break;
case R.id.btn_four:
animator4.setDuration(3000l);
animator4.start();
break;
case R.id.btn_five:
//将前面的动画集合到一起~
animSet = new AnimatorSet();
animSet.play(animator4).with(animator3).with(animator2).after(animator1);
animSet.setDuration(5000l);
animSet.start();
break;
case R.id.tv_pig:
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "不愧是coder-pig~", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
break;
}
}
}用法也非常簡單,上面涉及到的組合動畫我們下面講~
#4.組合動畫與AnimatorListener
從上面兩個例子我們都體驗了一把組合動畫,用到了AnimatorSet這個類別!
我們呼叫的play()方法,然後傳入第一個開始執行的動畫,此時他會回傳一個Builder類別給我們:
- after(Animator anim) 將現有動畫插入傳入的動畫之後執行
- after(long delay) 將現有動畫延遲指定毫秒後執行
- before(Animator anim) 將現有動畫插入到傳在入的動畫之前執行
- with(Animator anim) 將現有動畫和傳入的動畫同時執行
AnimatorUpdateListener,當值狀態改變時會回呼onAnimationUpdate
除了這種事件外還有:動畫進行狀態的監聽~ AnimatorListener
,我們可以呼叫- addListener
- 方法 新增監聽器,然後重寫下面四個回呼方法:
- onAnimationStart():動畫開始
- onAnimationRepeat():動畫重複執行
- onAnimationEnd():動畫結束
:動畫取消
#沒錯,加入你真的用AnimatorListener的話,四個方法你都要重寫,當然跟前面的手勢那一節一樣, Android已經提供我們好一個適配器類別:AnimatorListenerAdapter
,該類別中已經把每個接口 方法都實作好了,所以我們這裡只寫一個回呼方法也可以額!
5.使用XML來寫動畫使用XML來寫動畫,畫的時間可能比Java程式碼長一點,但重用起來就輕鬆很多! 對應的XML標籤分別為:<animator><objectAnimator
><- set
- > 相關的屬性解釋如下:
- android:ordering:指定動畫的播放順序:sequentially(順序執行),together(同時執行)
- #android:duration:動畫的持續時間
- android:propertyName="x":這裡的x,還記得上面的"alpha"嗎?載入動畫的那個物件裡需要 定義getx和setx的方法,objectAnimator就是透過這裡來修改物件裡的值的!
- android:valueFrom="1" :動畫起始的初始值
- android:valueTo="0" :動畫結束的最終值
="floatType":變化值的資料類型
##使用範例如下:①
從0到100平滑過渡的動畫###:###<animator xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:valueFrom="0" android:valueTo="100" android:valueType="intType"/>
②將一個視圖的alpha屬性從1變成0:
<objectAnimator xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:valueFrom="1" android:valueTo="0" android:valueType="floatType" android:propertyName="alpha"/>
③set動畫使用示範:
<set android:ordering="sequentially" > <set> <objectAnimator android:duration="500" android:propertyName="x" android:valueTo="400" android:valueType="intType" /> <objectAnimator android:duration="500" android:propertyName="y" android:valueTo="300" android:valueType="intType" /> </set> <objectAnimator android:duration="500" android:propertyName="alpha" android:valueTo="1f" /></set>
載入我們的動畫檔案:
AnimatorSet set = (AnimatorSet)AnimatorInflater.loadAnimator(mContext, R.animator.property_animator); animator.setTarget(view); animator.start();
6.本節範例程式碼下載:
AnimatorDemo1.zip
AnimatorDemo2.zip
本節小結:
好的,本節給大家捋了一捋安卓中屬性動畫的基本用法,不知道你get了沒,內容還是比較簡單 的,而且例子比較有趣,相信大家會喜歡,嗯,就說這麼多,謝謝~
感謝郭神的文章~









