多個SOTA ! OV-Uni3DETR:提高3D檢測在類別、場景和模態之間的普遍性(清華&港大)
- WBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWB轉載
- 2024-04-11 19:46:18633瀏覽
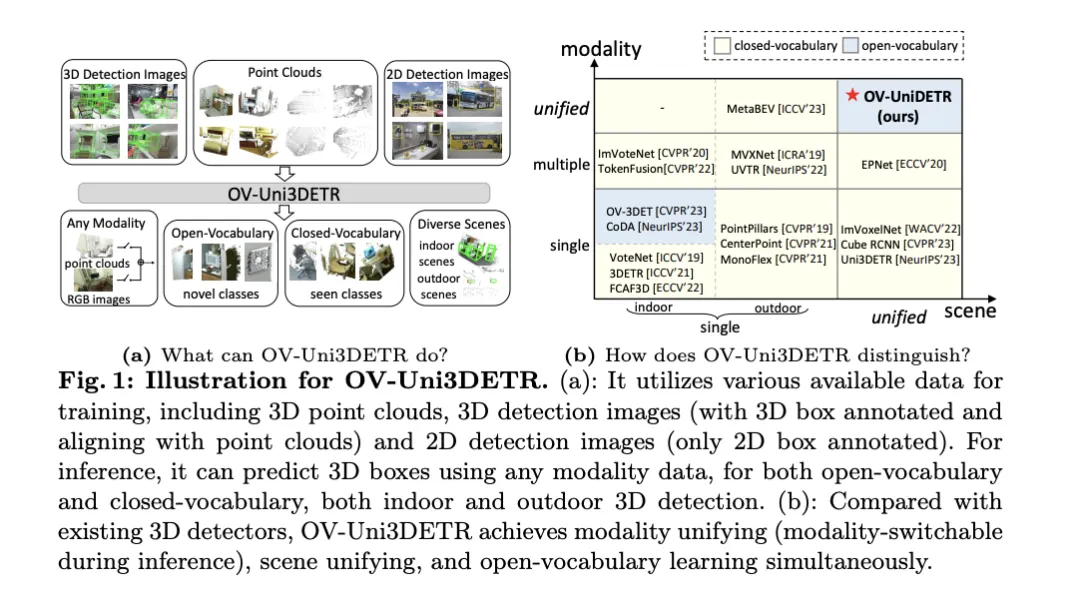
這篇論文討論了3D目標偵測的領域,特別是針對Open-Vocabulary的3D目標偵測。在傳統的3D目標偵測任務中,系統需要在預測真實場景中物件的定位3D邊界框和語意類別標籤,這通常依賴點雲或RGB影像。儘管2D目標檢測技術因其普遍性和速度展現出色,但相關研究表明,3D通用檢測的發展相比之下顯得滯後。目前,大多數3D目標偵測方法仍依賴完全監督學習,並受到特定輸入模式下完全標註資料的限制,只能識別經過訓練過程中出現的類別,無論是在室內或室外場景。
這篇論文指出,3D通用目標偵測面臨的挑戰主要包括:現有的3D偵測器只能在封閉詞彙匯總的情況下工作,因此只能偵測已經見過的類別。緊迫需要Open-Vocabulary的3D目標偵測,以識別和定位訓練過程中未取得的新類別目標實例。現有的3D檢測資料集在大小和類別上與2D資料集相比都有限制,這限制了在定位新目標方面的泛化能力。此外,3D領域缺乏預先訓練的圖像-文字模型,這進一步加劇了Open-Vocabulary 3D檢測的挑戰。同時,缺乏一種針對多模態3D檢測的統一架構,現有的3D檢測器大多設計用於特定的輸入模態(點雲、RGB影像或二者),這阻礙了有效利用來自不同模態和場景(室內或室外)的有效訊息,從而限制了對新目標的泛化能力。
為了解決上述問題,論文提出了一個名為OV-Uni3DETR的統一多模態3D偵測器。此偵測器在訓練期間能夠利用多模態和多來源數據,包括點雲、具有精確3D框標註的點雲和點雲對齊的3D檢測影像,以及僅包含2D框標註的2D偵測影像。透過這種多模態學習方式,OV-Uni3DETR能夠在推理時處理任何模態的數據,實現測試時的模態切換,並在檢測基礎類別和新類別上表現出色。統一的結構進一步促使OV-Uni3DETR能夠在室內和室外場景中進行檢測,具備Open-Vocabulary能力,從而顯著提高3D檢測器在類別、場景和模態之間的普適性。
在此外,針對如何泛化偵測器以識別新類別的問題,以及如何從沒有3D框標註的大量2D檢測影像中學習的問題,論文提出了一種稱為週期模態傳播的方法-透過這種方法,2D和3D模態之間傳播知識以解決這兩個挑戰。透過這種方法,2D檢測器的豐富語義知識可以傳播到3D領域,以協助發現新的框,並3D檢測器的幾何知識則可用於在2D檢測圖像中定位目標,並透過匹配利匹配分類標籤。
論文的主要貢獻包括提出了一個能夠在不同模態和多樣化場景中檢測任何類別目標的統一Open-Vocabulary 3D檢測器OV-Uni3DETR;提出了一個針對室內和室外場景的統一多模態架構;以及提出了2D和3D模態之間知識傳播循環的概念。透過這些創新,OV-Uni3DETR在多個3D檢測任務上實現了最先進的性能,並在Open-Vocabulary設定下顯著超過了先前的方法。這些成果表明,OV-Uni3DETR為3D基礎模型的未來發展邁出了重要一步。
OV-Uni3DETR方法詳解
Multi-Modal Learning
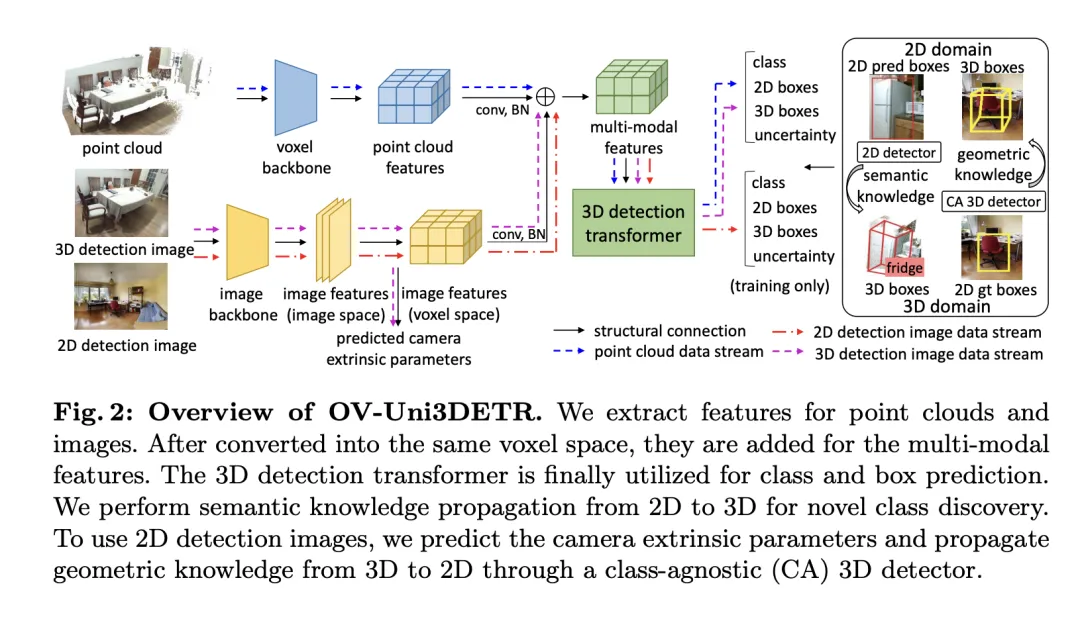
#本文介紹了一個多模式學習框架,專門針對3D目標偵測任務,透過整合雲端資料和影像資料來增強偵測效能。這種框架能夠處理在推理時可能缺少的某些感測器模態,也就是兼備測驗時模態切換的能力。透過特定的網路結構提取並整合來自兩種不同模態的特徵,包括3D點雲特徵和2D影像特徵,這些特徵經過元素化處理和相機參數映射後,被融合用於後續的目標偵測任務。
關鍵的技術點包括使用3D卷積和批量歸一化來規範化和整合不同模式的特徵,防止在特徵層級上的不一致性導致某一模式被忽略。此外,採用隨機切換模式的訓練策略,確保模型能夠靈活地處理只來自單一模式的數據,從而提高模型的穩健性和適應性。
最終,該架構利用複合損失函數,結合了類別預測、2D和3D邊界框回歸的損失,以及一個用於加權回歸損失的不確定性預測,來優化整個檢測流程。這種多模態學習方法不僅提高了對現有類別的檢測性能,而且透過融合不同類型的數據,增強了對新類別的泛化能力。多模態架構最終預測類別標籤、4維2D框和7維3D框,用於2D和3D目標偵測。對於3D框回歸,使用L1損失和解耦IoU損失;對於2D框回歸,使用L1損失和GIoU損失。在Open-Vocabulary設定中,有新類別樣本,增加了訓練樣本的難度。因此,引入了不確定性預測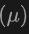 ,並用它來加權L1回歸損失。目標偵測學習的損失為:
,並用它來加權L1回歸損失。目標偵測學習的損失為:
對於某些3D場景,可能存在多視圖影像,而不是單一的單眼影像。對於它們中的每一個,提取圖像特徵並使用各自的投影矩陣投影到體素空間。體素空間中的多個影像特徵被求和以獲取多模態特徵。這種方法透過結合不同模態的訊息,提高了模型對新類別的泛化能力,並增強了在多樣化輸入條件下的適應性。
Knowledge Propagation: 2D—3D
#在介紹的多模態學習基礎上,文中針對Open-Vocabulary的3D偵測執行了一種稱為「知識傳播: 」的方法。 Open-Vocabulary學習的核心問題是識別訓練過程中未經人工標註的新類別。由於取得點雲資料的難度,預先訓練的視覺-語言模型尚未在點雲領域開發。點雲資料與RGB影像之間的模態差異限制了這些模型在3D檢測中的表現。
」的方法。 Open-Vocabulary學習的核心問題是識別訓練過程中未經人工標註的新類別。由於取得點雲資料的難度,預先訓練的視覺-語言模型尚未在點雲領域開發。點雲資料與RGB影像之間的模態差異限制了這些模型在3D檢測中的表現。
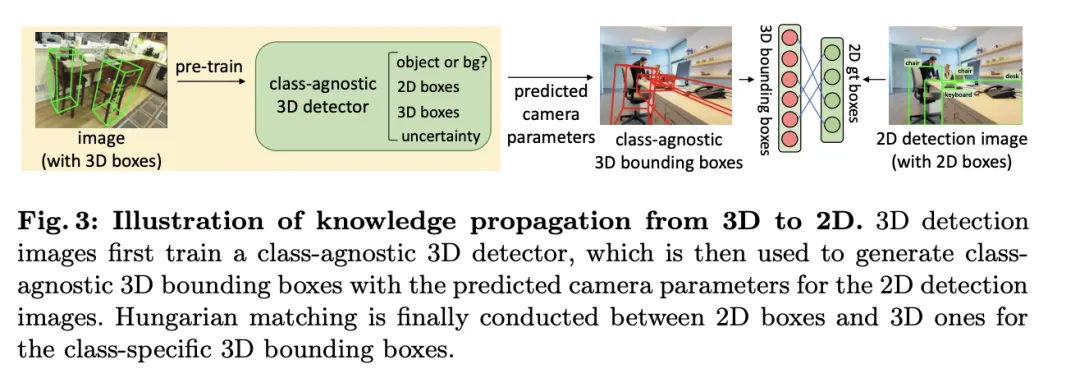
為了解決這個問題,提出利用預訓練的2DOpen-Vocabulary偵測器的語意知識,並為新類別產生對應的3D邊界框。這些產生的3D框將補充訓練時可用類別有限的3D真實標籤。
具體來說,首先使用2DOpen-Vocabulary偵測器產生2D邊界框或實例遮罩。考慮到2D領域可用的資料和標註更為豐富,這些產生的2D框能夠實現更高的定位精度,並涵蓋更廣泛的類別範圍。然後,透過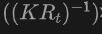 將這些2D框投影到3D空間,以獲得對應的3D框。具體操作是使用
將這些2D框投影到3D空間,以獲得對應的3D框。具體操作是使用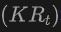
將3D點投影到2D空間,找到2D框內的點,然後對2D框內的這些點進行聚類以消除離群值,從而獲得對應的3D框。由於預先訓練的2D偵測器的存在,未標註的新目標可以在產生的3D框集中被發現。透過這種方式,從2D領域到生成的3D框傳播的豐富語意知識,大大促進了3DOpen-Vocabulary偵測。對於多視圖影像,分別產生3D框並將它們整合在一起以供最終使用。
在推理過程中,當點雲和圖像都可用時,可以以類似的方式提取3D框。這些產生的3D框也可以視為3DOpen-Vocabulary偵測結果的一種形式。將這些3D框加入多模態3D變換器的預測中,以補充可能缺少的目標,並透過3D非極大值抑制(NMS)過濾重疊的邊界框。由預先訓練的2D偵測器所分配的置信度分數透過預定的常數系統地除以,然後重新解釋為對應3D框的置信度得分。
實驗
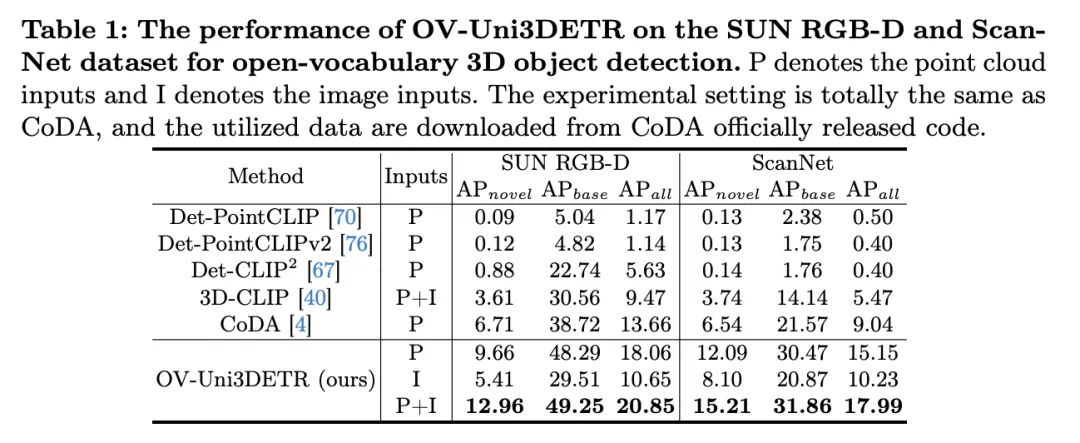
表格展示了OV-Uni3DETR在SUN RGB-D和ScanNet数据集上进行Open-Vocabulary3D目标检测的性能。实验设置与CoDA完全相同,使用的数据来自CoDA官方发布的代码。性能指标包括新类别平均精度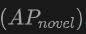 、基类平均精度
、基类平均精度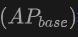 和所有类平均精度
和所有类平均精度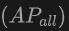 。输入类型包括点云(P)、图像(I)以及它们的组合(P I)。
。输入类型包括点云(P)、图像(I)以及它们的组合(P I)。
分析这些结果,我们可以观察到以下几点:
-
多模态输入的优势:当使用点云和图像的组合作为输入时,OV-Uni3DETR在两个数据集的所有评价指标上都取得了最高分,尤其是在新类别平均精度
 上的提升最为显著。这表明结合点云和图像可以显著提高模型对未见类别的检测能力,以及整体检测性能。
上的提升最为显著。这表明结合点云和图像可以显著提高模型对未见类别的检测能力,以及整体检测性能。 - 对比其他方法:与其他基于点云的方法相比(如Det-PointCLIP、Det-PointCLIPv2、Det-CLIP、3D-CLIP和CoDA),OV-Uni3DETR在所有评价指标上都展现出优异的性能。这证明了OV-Uni3DETR在处理Open-Vocabulary3D目标检测任务上的有效性,尤其是在利用多模态学习和知识传播策略方面。
- 图像与点云输入的比较:仅使用图像(I)作为输入的OV-Uni3DETR虽然在性能上低于使用点云(P)作为输入的情况,但依然表现出不错的检测能力。这证明了OV-Uni3DETR架构的灵活性和对单一模态数据的适应能力,同时也强调了融合多种模态数据对提升检测性能的重要性。
-
在新类别上的表现:OV-Uni3DETR在新类别平均精度
 上的表现尤其值得关注,这对于Open-Vocabulary检测尤为关键。在SUN RGB-D数据集上,使用点云和图像输入时的
上的表现尤其值得关注,这对于Open-Vocabulary检测尤为关键。在SUN RGB-D数据集上,使用点云和图像输入时的 达到了12.96%,在ScanNet数据集上达到了15.21%,这显著高于其他方法,显示了其在识别训练过程中未见过的类别上的强大能力。
达到了12.96%,在ScanNet数据集上达到了15.21%,这显著高于其他方法,显示了其在识别训练过程中未见过的类别上的强大能力。
总的来说,OV-Uni3DETR通过其统一的多模态学习架构,在Open-Vocabulary3D目标检测任务上表现出卓越的性能,尤其是在结合点云和图像数据时,能够有效提升对新类别的检测能力,证明了多模态输入和知识传播策略的有效性和重要性。
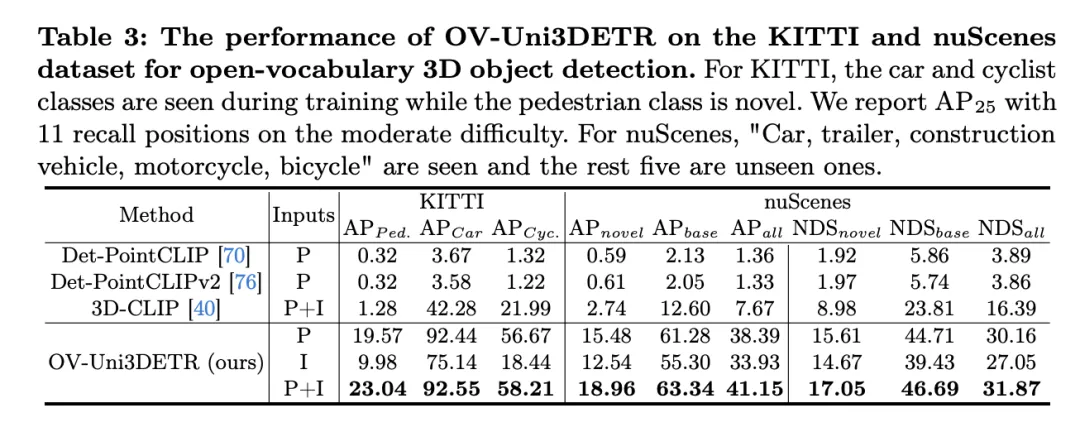
这个表格展示了OV-Uni3DETR在KITTI和nuScenes数据集上进行Open-Vocabulary3D目标检测的性能,涵盖了在训练过程中已见(base)和未见(novel)的类别。对于KITTI数据集,"car"和"cyclist"类别在训练过程中已见,而"pedestrian"类别是新颖的。性能使用在中等难度下的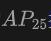
指标来衡量,且采用了11个召回位置。对于nuScenes数据集,"car, trailer, construction vehicle, motorcycle, bicycle"是已见类别,剩余五个为未见类别。除了AP指标外,还报告了NDS(NuScenes Detection Score)来综合评估检测性能。
分析这些结果可以得出以下结论:
- Significant advantages of multi-modal input: Compared with using only point cloud (P) or image (I) as input, when using both point cloud and image (P I ) as input, OV-Uni3DETR achieved the highest scores on all evaluation metrics. This result highlights the significant advantages of multi-modal learning in improving detection capabilities for unseen categories and overall detection performance.
- Effectiveness of Open-Vocabulary detection: OV-Uni3DETR shows excellent performance when dealing with unseen categories, especially in the "pedestrian" category of the KITTI dataset and nuScenes data Set on the "novel" category. This shows that the model has strong generalization ability to novel categories and is an effective Open-Vocabulary detection solution.
- Comparison with other methods: Compared with other point cloud-based methods (such as Det-PointCLIP, Det-PointCLIPv2 and 3D-CLIP), OV-Uni3DETR exhibits significant Performance improvements, both in the detection of seen and unseen categories. This demonstrates its advancement in handling Open-Vocabulary3D object detection tasks.
- Comparison of image input and point cloud input: Although the performance of using image input is slightly lower than that of using point cloud input, image input is still able to provide relatively high detection accuracy, which shows that This demonstrates the adaptability and flexibility of the OV-Uni3DETR architecture.
- Comprehensive evaluation index: It can be seen from the results of the NDS evaluation index that OV-Uni3DETR not only performs well in recognition accuracy, but also achieves high results in overall detection quality. scores, especially when combining point cloud and image data.
OV-Uni3DETR demonstrates excellent performance on Open-Vocabulary3D object detection, especially in handling unseen categories and multi-modal data. These results verify the effectiveness of the multi-modal input and knowledge dissemination strategy, as well as the potential of OV-Uni3DETR in improving the generalization ability of 3D object detection tasks.
Discussion
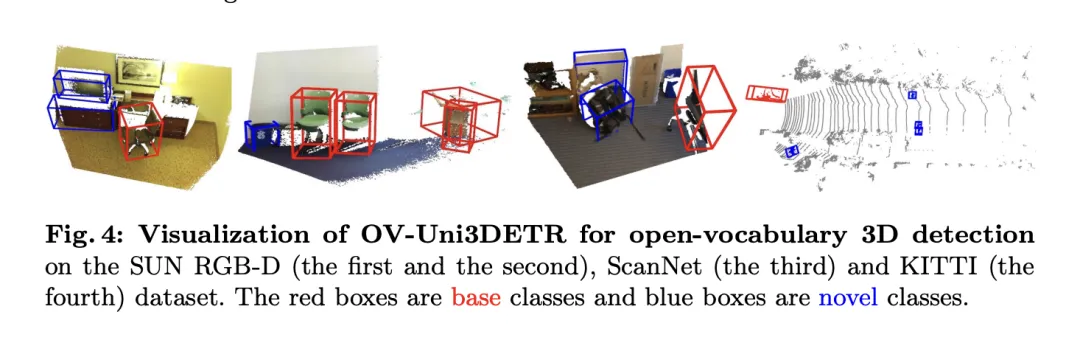
This paper proposes OV-Uni3DETR, a unified multi-modal 3D detector for Open- Vocabulary has brought significant progress in the field of 3D object detection. This method utilizes multi-modal data (point clouds and images) to improve detection performance, and effectively expands the model's recognition capabilities for unseen categories through a 2D to 3D knowledge dissemination strategy. Experimental results on multiple public datasets demonstrate the excellent performance of OV-Uni3DETR on new and base classes, especially when combining point cloud and image inputs, which can significantly improve the detection capabilities of new classes while simultaneously The overall detection performance has also reached a new height.
In terms of advantages, OV-Uni3DETR first demonstrated the potential of multi-modal learning in improving 3D target detection performance. By integrating point cloud and image data, the model is able to learn complementary features from each modality, enabling more accurate detection on rich scenes and diverse target categories. Secondly, by introducing a 2D to 3D knowledge transfer mechanism, OV-Uni3DETR is able to utilize rich 2D image data and pre-trained 2D detection models to identify and locate new categories that have not been seen during the training process, which greatly improves the generalization of the model. ization ability. In addition, this method shows powerful capabilities in processing Open-Vocabulary detection, bringing new research directions and potential applications to the field of 3D detection.
In terms of shortcomings, although OV-Uni3DETR has demonstrated its advantages in many aspects, there are also some potential limitations. First, although multi-modal learning can improve performance, it also increases the complexity of data acquisition and processing. Especially in practical applications, the synchronization and registration of different modal data may pose challenges. Secondly, although the knowledge dissemination strategy can effectively utilize 2D data to assist 3D detection, this method may rely on high-quality 2D detection models and accurate 3D-2D alignment technology, which may be difficult to guarantee in some complex environments. In addition, for some extremely rare categories, even Open-Vocabulary detection may face recognition accuracy challenges, which requires further research to resolve.
OV-Uni3DETR has made significant progress in Open-Vocabulary3D object detection through its innovative multi-modal learning and knowledge dissemination strategy. Although there are some potential limitations, its advantages demonstrate the great potential of this method in promoting the development and application expansion of 3D inspection technology. Future research can further explore how to overcome these limitations and how to apply these strategies to a wider range of 3D perception tasks.
Conclusion
In this paper, we mainly proposed OV-Uni3DETR, a unified multi-modal open vocabulary 3D detector. With the help of multi-modal learning and cyclic modal knowledge dissemination, our OV-Uni3DETR can well identify and locate new classes, achieving modal unification and scene unification. Experiments demonstrate its strong capabilities in both open and closed vocabulary environments, both indoor and outdoor scenes, and in any modal data input. Targeting unified open-vocabulary 3D detection in multimodal environments, we believe our study will drive subsequent research along the promising but challenging direction of general 3D computer vision.
以上是多個SOTA ! OV-Uni3DETR:提高3D檢測在類別、場景和模態之間的普遍性(清華&港大)的詳細內容。更多資訊請關注PHP中文網其他相關文章!


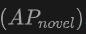 上的提升最为显著。这表明结合点云和图像可以显著提高模型对未见类别的检测能力,以及整体检测性能。
上的提升最为显著。这表明结合点云和图像可以显著提高模型对未见类别的检测能力,以及整体检测性能。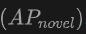 上的表现尤其值得关注,这对于Open-Vocabulary检测尤为关键。在SUN RGB-D数据集上,使用点云和图像输入时的
上的表现尤其值得关注,这对于Open-Vocabulary检测尤为关键。在SUN RGB-D数据集上,使用点云和图像输入时的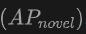 达到了12.96%,在ScanNet数据集上达到了15.21%,这显著高于其他方法,显示了其在识别训练过程中未见过的类别上的强大能力。
达到了12.96%,在ScanNet数据集上达到了15.21%,这显著高于其他方法,显示了其在识别训练过程中未见过的类别上的强大能力。