Django 表單
HTML表單是網站互動性的經典方式。 本章將介紹如何用Django對使用者提交的表單資料進行處理。
HTTP 請求
HTTP協定以"請求-回覆"的方式運作。客戶發送請求時,可以在請求中附加資料。伺服器透過解析請求,就可以獲得客戶傳來的數據,並根據URL來提供特定的服務。
GET 方法
我們在先前的專案中建立一個search.py 文件,用於接收使用者的請求:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from django.http import HttpResponse
from django.shortcuts import render_to_response
# 表单
def search_form(request):
return render_to_response('search_form.html')
# 接收请求数据
def search(request):
request.encoding='utf-8'
if 'q' in request.GET:
message = '你搜索的内容为: ' + request.GET['q'].encode('utf-8')
else:
message = '你提交了空表单'
return HttpResponse(message)在範本目錄template中新增search_form.html表單:
<html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8" /> <title>Search - w3cschool.cc</title> </head> <body> <form action="/search/" method="get"> <input type="text" name="q"> <input type="submit" value="Search"> </form> </body> </html>
urls.py 規則修改為如下形式:
from django.conf.urls import *
from HelloWorld.view import hello
from HelloWorld.testdb import testdb
from HelloWorld import search
urlpatterns = patterns("",
('^hello/$', hello),
('^testdb/$', testdb),
(r'^search-form/$', search.search_form),
(r'^search/$', search.search),
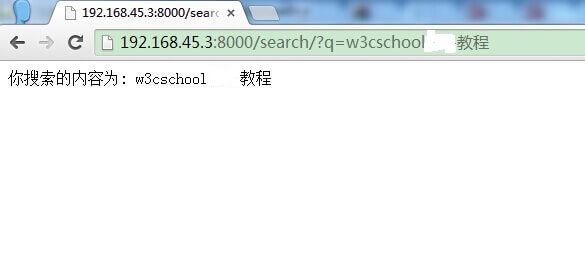
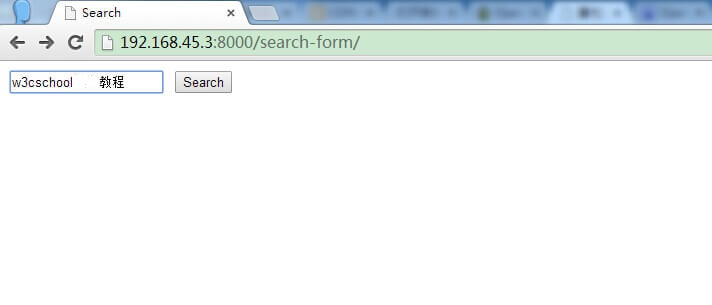
)訪問位址:http://192.168.45.3:8000/search-form/並蒐索,結果如下所示:
POST 方法
上面我們使用了GET方法。視圖顯示和請求處理分成兩個函數處理。
提交資料時較常用POST方法。我們下面使用該方法,並使用一個URL和處理函數,同時顯示視圖和處理請求。
我們在tmplate 建立 post.html:
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<title>Search - w3cschool.cc</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="/search-post/" method="post">
{% csrf_token %}
<input type="text" name="q">
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
</form>
<p>{{ rlt }}</p>
</body>
</html>在範本的結尾,我們增加一個rlt記號,為表格處理結果預留位置。
表格後面還有一個{% csrf_token %}的標籤。 csrf全名為Cross Site Request Forgery。這是Django提供的防止偽裝提交請求的功能。 POST方法提交的表格,必須有此標籤。
在HelloWorld目錄下新search2.py 檔案並使用search_post 函數來處理POST 請求:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from django.shortcuts import render
from django.core.context_processors import csrf
# 接收POST请求数据
def search_post(request):
ctx ={}
ctx.update(csrf(request))
if request.POST:
ctx['rlt'] = request.POST['q']
return render(request, "post.html", ctx)urls.py 規則修改為以下形式:
from django.conf.urls import *
from HelloWorld.view import hello
from HelloWorld.testdb import testdb
from HelloWorld import search
from HelloWorld import search2
urlpatterns = patterns("",
('^hello/$', hello),
('^testdb/$', testdb),
(r'^search-form/$', search.search_form),
(r'^search/$', search.search),
(r'^search-post/$', search2.search_post),
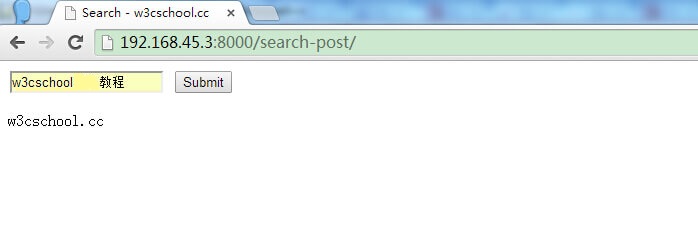
)訪問http: //192.168.45.3:8000/search-post/ 顯示結果如下:
完成上述實例後,我們的目錄結構為:
HelloWorld |-- HelloWorld | |-- __init__.py | |-- __init__.pyc | |-- models.pyc | |-- search.py | |-- search.pyc | |-- search2.py | |-- search2.pyc | |-- settings.py | |-- settings.pyc | |-- testdb.py | |-- testdb.pyc | |-- urls.py | |-- urls.pyc | |-- view.py | |-- view.pyc | |-- wsgi.py | `-- wsgi.pyc |-- TestModel | |-- __init__.py | |-- __init__.pyc | |-- admin.py | |-- models.py | |-- models.pyc | |-- tests.py | `-- views.py |-- manage.py `-- templates |-- base.html |-- hello.html |-- post.html `-- search_form.html 3 directories, 29 files
#Request 物件
每個view函數的第一個參數是一個HttpRequest對象,就像下面這個hello()函數:
from django.http import HttpResponse
def hello(request):
return HttpResponse("Hello world")HttpRequest對象包含當前請求URL的一些資訊:
#屬性 | #描述 |
| path | |
| method
| elif request.method == 'POST':|
| ##GET | 包含所有HTTP GET參數的類別字典物件。參見QueryDict 文件。 |
| POST#### | 包含所有HTTP POST參數的類別字典物件。參見QueryDict 文件。 伺服器收到空的POST請求的情況也是有可能發生的。也就是說,表單form透過HTTP POST方法提交請求,但是表單中可以沒有資料。因此,不能使用語句if request.POST來判斷是否使用HTTP POST方法;應該使用if request.method == "POST" (參見本表的method屬性)。 注意: POST不包括file-upload資訊。參見FILES屬性。 |
REQUEST | #為了方便,該屬性是POST和GET屬性的集合體,但是有特殊性,先找出POST屬性,然後再找GET屬性。借鏡PHP's $_REQUEST。 例如,如果GET = {"name": "john"} 和POST = {"age": '34'},則REQUEST["name"] 的值為"john", REQUEST[" age"]的值是"34". #強烈建議使用GET and POST,因為這兩個屬性更顯式化,寫出的程式碼也更容易理解。 |
COOKIES | #包含所有cookies的標準Python字典物件。 Keys和values都是字串。參見第12章,有關於cookies更詳細的講解。 |
FILES | #包含所有上傳檔案的類別字典物件。 FILES中的每個Key都是<input type="file" name="" />標籤中name屬性的值. FILES中的每個value 同時也是一個標準Python字典對象,包含下面三個Keys:
注意:只有在請求方法是POST,並且請求頁面中<form>有enctype="multipart/form- data"屬性時FILES才擁有資料。否則,FILES 是一個空字典。 |
META | #包含所有可用HTTP頭部資訊的字典。 例如:
|
| ########################## ###HTTP_REFERER: referring頁############HTTP_USER_AGENT: 客戶端的user-agent字串############HTTP_X_BENDER: X-Bender頭訊息#### #####################user#############是個django.contrib.auth.models.User 對象,代表目前登入的用戶。 ######如果存取使用者目前沒有登錄,user將被初始化為django.contrib.auth.models.AnonymousUser的實例。 ### 你可以透過user的is_authenticated()方法來辨別使用者是否登入: if request.user.is_authenticated(): # Do something for logged-in users. else: # Do something for anonymous users. 只有啟動Django中的AuthenticationMiddleware時該屬性才可用 | |
#session | 唯一可讀寫的屬性,代表目前會話的字典物件。只有在啟動Django中的session支援時該屬性才可用。 參見第12章。 |
raw_post_data | #原始HTTP POST數據,未解析過。 高級處理時會有用處。 |
Request物件也有一些有用的方法:
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| __getitem__(key) | 傳回GET/POST的鍵值,先取POST,後取GET。如果鍵不存在拋出 KeyError。 這是我們可以使用字典語法存取HttpRequest物件。 例如,request["foo"]等同於先request.POST["foo"] 然後 request.GET["foo"]的運算。 |
| has_key() | 檢查request.GET or request.POST中是否包含參數指定的Key。 |
| get_full_path() | 傳回包含查詢字串的請求路徑。例如, "/music/bands/the_beatles/?print=true" |
| #is_secure() | 如果請求是安全的,回傳True,就是說,發出的是HTTPS請求。 |
QueryDict物件
在HttpRequest物件中, GET和POST屬性是django.http.QueryDict類別的實例。
QueryDict類似字典的自訂類,用來處理單鍵對應多值的情況。
QueryDict實作所有標準的字典方法。也包含一些特有的方法:
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| 和標準字典的處理有一點不同,就是,如果Key對應多個Value,__getitem__()回傳最後一個value。 | |
| #設定參數指定key的value清單(一個Python list)。注意:它只能在一個mutable QueryDict 物件上被呼叫(就是透過copy()產生的一個QueryDict物件的拷貝). | |
| 如果key對應多個value,get()傳回最後一個value。 | |
| #參數可以是QueryDict,也可以是標準字典。和標準字典的update方法不同,方法加入字典items,而不是取代它們: | |
和標準字典的items()方法有一點不同,該方法使用單值邏輯的__getitem__(): |
此外, QueryDict也有一些方法,如下表:
| #方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
copy() | 傳回物件的拷貝,內部實作是用Python標準函式庫的copy.deepcopy()。該拷貝是mutable(可更改的) — 就是說,可以更改該拷貝的值。 |
getlist(key) | #傳回和參數key對應的所有值,作為一個Python list傳回。如果key不存在,則傳回空list。 It's guaranteed to return a list of some sort.. |
#setlist(key,list_) | 設定key的值為list_ (unlike __setitem__()). |
#appendlist(key,item) | 新增item到和key關聯的內部list. |
setlistdefault(key,list) | 和setdefault有一點不同,它接受list而不是單一value作為參數。 |
lists() | #和items()有一點不同, 它會傳回key的所有值,作為一個list, 例如: >>> q = QueryDict('a=1&a=2&a=3')
>>> q.lists()
[('a', ['1', '2', '3'])] |
urlencode() | 傳回一個以查詢字串格式進行格式化後的字串(e.g., "a=2&b=3&b=5"). |