Rumah >pembangunan bahagian belakang >Tutorial Python >Tutorial terperinci tentang melukis graf tiga dimensi dalam python
Tutorial terperinci tentang melukis graf tiga dimensi dalam python
- WBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBke hadapan
- 2022-08-30 12:04:2010920semak imbas
[Cadangan berkaitan: Tutorial video Python3]
Artikel ini hanya meringkaskan kaedah lukisan yang paling asas.
1. Permulaan
Diandaikan bahawa pakej alat matplotlib telah dipasang.
Gunakan matplotlib.figure.Rajah untuk mencipta bingkai plot:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D fig = plt.figure() ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='3d')
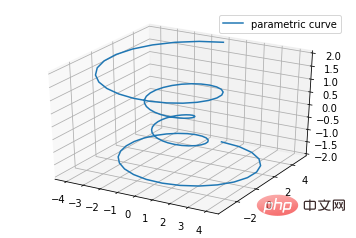
2. Plot garisan (Plot garis)
Penggunaan Asas:
ax.plot(x,y,z,label=' ')
kod:
import matplotlib as mpl from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt mpl.rcParams['legend.fontsize'] = 10 fig = plt.figure() ax = fig.gca(projection='3d') theta = np.linspace(-4 * np.pi, 4 * np.pi, 100) z = np.linspace(-2, 2, 100) r = z**2 + 1 x = r * np.sin(theta) y = r * np.cos(theta) ax.plot(x, y, z, label='parametric curve') ax.legend() plt.show()
3 Petak serakan (Petak serakan)
Penggunaan asas: <.>
ax.scatter(xs, ys, zs, s=20, c=None, depthshade=True, *args, *kwargs)
- xs, ys, zs: data input;
- s: saiz titik taburan
- c: warna, contohnya, c = 'r' adalah merah ;
- depthshase: ketelusan, Benar adalah lutsinar, lalai ialah Benar, Salah adalah legap
- *args dan pembolehubah sambungan lain, seperti maker = 'o', kemudian hasil serakan ialah 'o' Shape
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
def randrange(n, vmin, vmax):
'''
Helper function to make an array of random numbers having shape (n, )
with each number distributed Uniform(vmin, vmax).
'''
return (vmax - vmin)*np.random.rand(n) + vmin
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='3d')
n = 100
# For each set of style and range settings, plot n random points in the box
# defined by x in [23, 32], y in [0, 100], z in [zlow, zhigh].
for c, m, zlow, zhigh in [('r', 'o', -50, -25), ('b', '^', -30, -5)]:
xs = randrange(n, 23, 32)
ys = randrange(n, 0, 100)
zs = randrange(n, zlow, zhigh)
ax.scatter(xs, ys, zs, c=c, marker=m)
ax.set_xlabel('X Label')
ax.set_ylabel('Y Label')
ax.set_zlabel('Z Label')
plt.show()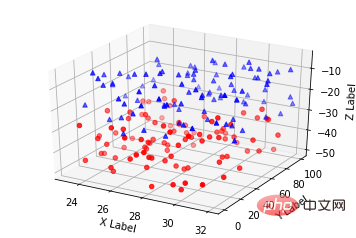
ax.plot_wireframe(X, Y, Z, *args, **kwargs)
- X, Y, Z: data input
- rstride: panjang langkah baris
- cstride: panjang langkah lajur
- rcount: bilangan baris Had atas
- akaun: Had atas bilangan lajur
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import axes3d import matplotlib.pyplot as plt fig = plt.figure() ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='3d') # Grab some test data. X, Y, Z = axes3d.get_test_data(0.05) # Plot a basic wireframe. ax.plot_wireframe(X, Y, Z, rstride=10, cstride=10) plt.show()
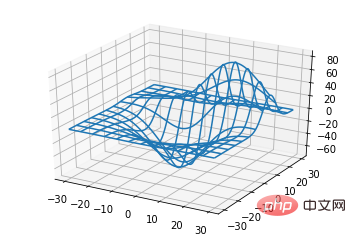
ax.plot_surface(X, Y, Z, *args, **kwargs)
- X, Y, Z: data
- rstride, cstride, rcount, ccount: sama seperti definisi plot Wireframe
- warna: warna permukaan
- cmap: lapisan
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib import cm
from matplotlib.ticker import LinearLocator, FormatStrFormatter
import numpy as np
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.gca(projection='3d')
# Make data.
X = np.arange(-5, 5, 0.25)
Y = np.arange(-5, 5, 0.25)
X, Y = np.meshgrid(X, Y)
R = np.sqrt(X**2 + Y**2)
Z = np.sin(R)
# Plot the surface.
surf = ax.plot_surface(X, Y, Z, cmap=cm.coolwarm,
linewidth=0, antialiased=False)
# Customize the z axis.
ax.set_zlim(-1.01, 1.01)
ax.zaxis.set_major_locator(LinearLocator(10))
ax.zaxis.set_major_formatter(FormatStrFormatter('%.02f'))
# Add a color bar which maps values to colors.
fig.colorbar(surf, shrink=0.5, aspect=5)
plt.show()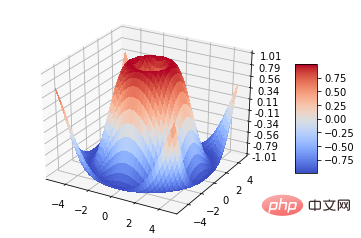
ax.plot_trisurf(*args, **kwargs)
- X, Y, Z: data
- Parameter lain serupa dengan plot permukaan
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np n_radii = 8 n_angles = 36 # Make radii and angles spaces (radius r=0 omitted to eliminate duplication). radii = np.linspace(0.125, 1.0, n_radii) angles = np.linspace(0, 2*np.pi, n_angles, endpoint=False) # Repeat all angles for each radius. angles = np.repeat(angles[..., np.newaxis], n_radii, axis=1) # Convert polar (radii, angles) coords to cartesian (x, y) coords. # (0, 0) is manually added at this stage, so there will be no duplicate # points in the (x, y) plane. x = np.append(0, (radii*np.cos(angles)).flatten()) y = np.append(0, (radii*np.sin(angles)).flatten()) # Compute z to make the pringle surface. z = np.sin(-x*y) fig = plt.figure() ax = fig.gca(projection='3d') ax.plot_trisurf(x, y, z, linewidth=0.2, antialiased=True) plt.show()
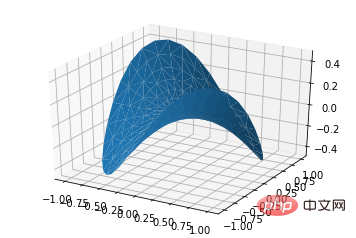
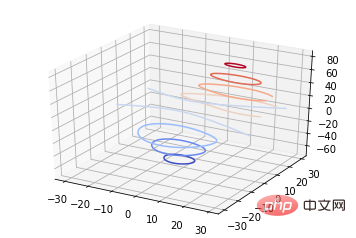
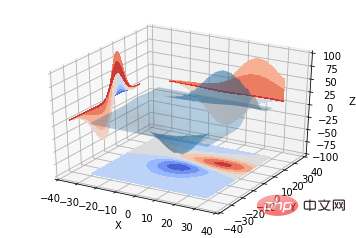
ax.contour(X, Y, Z, *args, **kwargs)kod:
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import axes3d import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from matplotlib import cm fig = plt.figure() ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='3d') X, Y, Z = axes3d.get_test_data(0.05) cset = ax.contour(X, Y, Z, cmap=cm.coolwarm) ax.clabel(cset, fontsize=9, inline=1) plt.show()
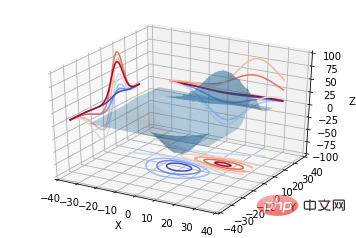
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import axes3d from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import axes3d import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from matplotlib import cm fig = plt.figure() ax = fig.gca(projection='3d') X, Y, Z = axes3d.get_test_data(0.05) ax.plot_surface(X, Y, Z, rstride=8, cstride=8, alpha=0.3) cset = ax.contour(X, Y, Z, zdir='z', offset=-100, cmap=cm.coolwarm) cset = ax.contour(X, Y, Z, zdir='x', offset=-40, cmap=cm.coolwarm) cset = ax.contour(X, Y, Z, zdir='y', offset=40, cmap=cm.coolwarm) ax.set_xlabel('X') ax.set_xlim(-40, 40) ax.set_ylabel('Y') ax.set_ylim(-40, 40) ax.set_zlabel('Z') ax.set_zlim(-100, 100) plt.show()
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import axes3d import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from matplotlib import cm fig = plt.figure() ax = fig.gca(projection='3d') X, Y, Z = axes3d.get_test_data(0.05) ax.plot_surface(X, Y, Z, rstride=8, cstride=8, alpha=0.3) cset = ax.contourf(X, Y, Z, zdir='z', offset=-100, cmap=cm.coolwarm) cset = ax.contourf(X, Y, Z, zdir='x', offset=-40, cmap=cm.coolwarm) cset = ax.contourf(X, Y, Z, zdir='y', offset=40, cmap=cm.coolwarm) ax.set_xlabel('X') ax.set_xlim(-40, 40) ax.set_ylabel('Y') ax.set_ylim(-40, 40) ax.set_zlabel('Z') ax.set_zlim(-100, 100) plt.show()
ax.bar(left, height, zs=0, zdir='z', *args, **kwargs
- x, y, zs = z, data
- zdir : Arah planarisasi carta bar boleh difahami secara terperinci mengikut kod.
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='3d')
for c, z in zip(['r', 'g', 'b', 'y'], [30, 20, 10, 0]):
xs = np.arange(20)
ys = np.random.rand(20)
# You can provide either a single color or an array. To demonstrate this,
# the first bar of each set will be colored cyan.
cs = [c] * len(xs)
cs[0] = 'c'
ax.bar(xs, ys, zs=z, zdir='y', color=cs, alpha=0.8)
ax.set_xlabel('X')
ax.set_ylabel('Y')
ax.set_zlabel('Z')
plt.show()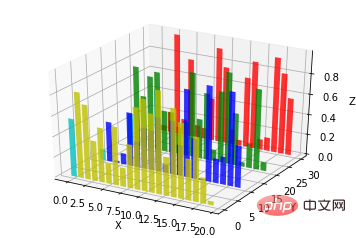
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.gca(projection='3d')
# Plot a sin curve using the x and y axes.
x = np.linspace(0, 1, 100)
y = np.sin(x * 2 * np.pi) / 2 + 0.5
ax.plot(x, y, zs=0, zdir='z', label='curve in (x,y)')
# Plot scatterplot data (20 2D points per colour) on the x and z axes.
colors = ('r', 'g', 'b', 'k')
x = np.random.sample(20*len(colors))
y = np.random.sample(20*len(colors))
c_list = []
for c in colors:
c_list.append([c]*20)
# By using zdir='y', the y value of these points is fixed to the zs value 0
# and the (x,y) points are plotted on the x and z axes.
ax.scatter(x, y, zs=0, zdir='y', c=c_list, label='points in (x,z)')
# Make legend, set axes limits and labels
ax.legend()
ax.set_xlim(0, 1)
ax.set_ylim(0, 1)
ax.set_zlim(0, 1)
ax.set_xlabel('X')
ax.set_ylabel('Y')
ax.set_zlabel('Z')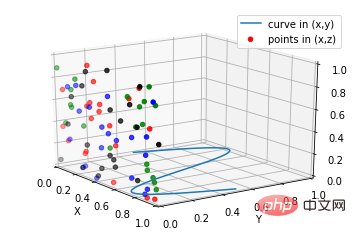
subplot(2,2,1) subplot(2,2,2) subplot(2,2,[3,4])Python:
subplot(2,2,1) subplot(2,2,2) subplot(2,1,2)kod:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d.axes3d import Axes3D, get_test_data
from matplotlib import cm
import numpy as np
# set up a figure twice as wide as it is tall
fig = plt.figure(figsize=plt.figaspect(0.5))
#===============
# First subplot
#===============
# set up the axes for the first plot
ax = fig.add_subplot(2, 2, 1, projection='3d')
# plot a 3D surface like in the example mplot3d/surface3d_demo
X = np.arange(-5, 5, 0.25)
Y = np.arange(-5, 5, 0.25)
X, Y = np.meshgrid(X, Y)
R = np.sqrt(X**2 + Y**2)
Z = np.sin(R)
surf = ax.plot_surface(X, Y, Z, rstride=1, cstride=1, cmap=cm.coolwarm,
linewidth=0, antialiased=False)
ax.set_zlim(-1.01, 1.01)
fig.colorbar(surf, shrink=0.5, aspect=10)
#===============
# Second subplot
#===============
# set up the axes for the second plot
ax = fig.add_subplot(2,1,2, projection='3d')
# plot a 3D wireframe like in the example mplot3d/wire3d_demo
X, Y, Z = get_test_data(0.05)
ax.plot_wireframe(X, Y, Z, rstride=10, cstride=10)
plt.show()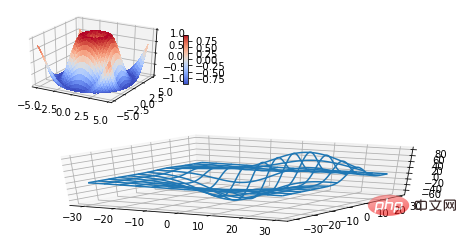
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.gca(projection='3d')
# Demo 1: zdir
zdirs = (None, 'x', 'y', 'z', (1, 1, 0), (1, 1, 1))
xs = (1, 4, 4, 9, 4, 1)
ys = (2, 5, 8, 10, 1, 2)
zs = (10, 3, 8, 9, 1, 8)
for zdir, x, y, z in zip(zdirs, xs, ys, zs):
label = '(%d, %d, %d), dir=%s' % (x, y, z, zdir)
ax.text(x, y, z, label, zdir)
# Demo 2: color
ax.text(9, 0, 0, "red", color='red')
# Demo 3: text2D
# Placement 0, 0 would be the bottom left, 1, 1 would be the top right.
ax.text2D(0.05, 0.95, "2D Text", transform=ax.transAxes)
# Tweaking display region and labels
ax.set_xlim(0, 10)
ax.set_ylim(0, 10)
ax.set_zlim(0, 10)
ax.set_xlabel('X axis')
ax.set_ylabel('Y axis')
ax.set_zlabel('Z axis')
plt.show()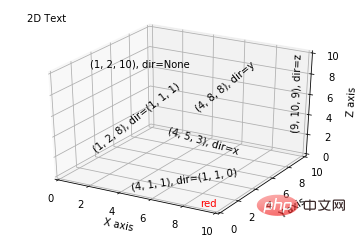
Tutorial video Python3 ]
Atas ialah kandungan terperinci Tutorial terperinci tentang melukis graf tiga dimensi dalam python. Untuk maklumat lanjut, sila ikut artikel berkaitan lain di laman web China PHP!
Kenyataan:
Artikel ini dikembalikan pada:jb51.net. Jika ada pelanggaran, sila hubungi admin@php.cn Padam
Artikel sebelumnya:Objek jenis data tutorial NumPy PythonArtikel seterusnya:Objek jenis data tutorial NumPy Python
Artikel berkaitan
Lihat lagi- Membawa anda memahami Penyelia alat pengurusan proses Python
- Perangkak Python merangkak data halaman web dan menghuraikan data
- Analisis terperinci Python bagi aplikasi kod np.where().
- Definisi parameter kelas Python dan kaedah pengembangan data nyah picit/kembang
- Penjelasan terperinci tentang penciptaan tatasusunan dalam tutorial Python NumPy


