Vue 구성 요소와 통신하는 8가지 방법 소개(컬렉션)
- 青灯夜游앞으로
- 2020-07-09 15:20:044131검색

vue는 데이터 기반 뷰 업데이트를 위한 프레임워크이므로 vue에서는 구성 요소 간의 데이터 통신이 매우 중요합니다. 그렇다면 구성 요소 간의 데이터 통신은 어떻게 발생합니까? 우선, Vue의 컴포넌트들 사이에 어떤 관계가 존재하는지 알아야 그들의 통신 방식을 더 쉽게 이해할 수 있습니다.
vue 컴포넌트의 관계 설명:
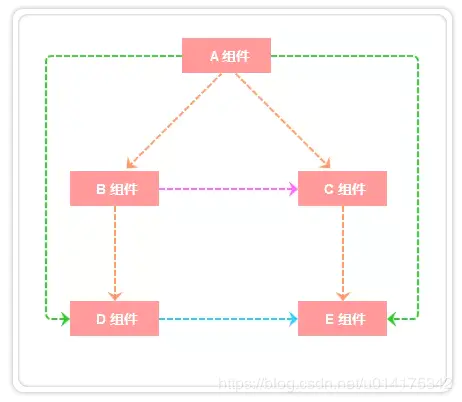
위 그림과 같이 A와 B, A와 C, B와 D, C와 E 컴포넌트의 관계는 부모-자식 관계입니다. B와 C의 관계는 형제, A와 E는 세대 간 관계, D와 E는 사촌 관계(비직계 친척)입니다. Components
아버지와 아들이 아닌 컴포넌트 간 통신(형제 컴포넌트, 세대간 관계 컴포넌트 등)
- 1. props / $emit
부모 컴포넌트는 다음을 통해 자식 컴포넌트에 데이터를 전달합니다. props 및 하위 구성 요소는 $emit를 하위 구성 요소 통신에 전달할 수 있습니다.
1. 상위 구성 요소가 하위 구성 요소에 값을 전달합니다상위 구성 요소가 하위 구성 요소에 데이터를 전달하는 방법: 하위 구성 요소의 상위 구성 요소 section.vue에서 데이터를 가져오는 방법 기사.vue 기사// section父组件
<template>
<p class="section">
<com-article :articles="articleList"></com-article>
</p>
</template>
<script>
import comArticle from './test/article.vue'
export default {
name: 'HelloWorld',
components: { comArticle },
data() {
return {
articleList: ['one', 'two', 'three','four','fives']
}
}
}
</script>
// 子组件 article.vue
<template>
<p>
<span v-for="(item, index) in articles" :key="index">{{item}}</span>
</p>
</template>
<script>
export default {
props: ['articles']
}
</script>요약 : prop만 상위 컴포넌트에서 하위 컴포넌트(부모-자식 컴포넌트)로 전달하는 것이 소위 단방향 데이터 흐름입니다. 또한 prop은 읽기 전용이므로 수정할 수 없습니다. 모든 수정 사항이 유효하지 않으며 경고가 표시됩니다.
2. 하위 구성 요소는 값을 상위 구성 요소에 전달합니다.
$emit에 대한 제가 이해한 바는 $emit가 사용자 정의 이벤트를 바인딩하고 이 명령문이 실행될 때 매개 변수 arg가 상위 구성 요소에 전달된다는 것입니다. 구성 요소인 경우 상위 구성 요소는 v-on을 통해 매개변수를 수신하고 수신합니다. 예를 통해 하위 구성 요소가 상위 구성 요소에 데이터를 전달하는 방법을 설명하세요. 이전 예를 기반으로 페이지에서 렌더링된 항목 항목을 클릭합니다. 상위 구성 요소
// 父组件中
<template>
<p class="section">
<com-article :articles="articleList" @onEmitIndex="onEmitIndex"></com-article>
<p>{{currentIndex}}</p>
</p>
</template>
<script>
import comArticle from './test/article.vue'
export default {
name: 'HelloWorld',
components: { comArticle },
data() {
return {
currentIndex: -1,
articleList: ['one', 'two', 'three','four','fives']
}
},
methods: {
onEmitIndex(idx) {
this.currentIndex = idx
}
}
}
</script>
<template>
<p>
<p v-for="(item, index) in articles" :key="index" @click="emitIndex(index)">{{item}}</p>
</p>
</template>
<script>
export default {
props: ['articles'],
methods: {
emitIndex(index) {
this.$emit('onEmitIndex', index)
}
}
}
</script>// 父组件中
<template>
<p class="hello_world">
<p>{{msg}}</p>
<com-a></com-a>
<button @click="changeA">点击改变子组件值</button>
</p>
</template>
<script>
import ComA from './test/comA.vue'
export default {
name: 'HelloWorld',
components: { ComA },
data() {
return {
msg: 'Welcome'
}
},
methods: {
changeA() {
// 获取到子组件A
this.$children[0].messageA = 'this is new value'
}
}
}
</script>
// 子组件中
<template>
<p class="com_a">
<span>{{messageA}}</span>
<p>获取父组件的值为: {{parentVal}}</p>
</p>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data() {
return {
messageA: 'this is old'
}
},
computed:{
parentVal(){
return this.$parent.msg;
}
}
}
</script>의 배열에 표시된 아래 첨자는 경계 조건에 주의해야 합니다. 예를 들어 #app에서 $parent를 가져오는 경우 새로운 Vue( ) 인스턴스를 얻게 됩니다. 이 인스턴스에서 $parent를 가져오면 정의되지 않은 상태가 되며, 맨 아래 하위 구성 요소에서 $children을 가져오면 빈 배열이 됩니다. 또한 $parent와 $children의 값이 다르다는 점에 유의하세요. $children의 값은 배열이고 $parent는 객체입니다. 요약: 위의 두 가지 방법은 부모와 자식 구성 요소 간의 통신에 사용되며, 부모와 자식 구성 요소 간의 통신을 위한 props가 더 편리합니다. 부모-자식 구성 요소가 아닌 구성 요소 간의 통신에는 둘 다 사용할 수 없습니다. 3. Provide/ inject
개념: provide/ inject 는 vue2.2.0의 새로운 API입니다. 간단히 말해서 상위 컴포넌트에서 제공을 통해 변수를 제공한 다음 하위 컴포넌트에 주입합니다. 변수를 주입합니다. 참고: 하위 구성 요소가 여기에 아무리 깊게 중첩되어 있어도 주입이 호출되는 한 제공되는 데이터를 주입할 수 있으며 현재 상위 구성 요소의 props 속성에서 데이터를 반환하는 것으로 제한되지 않습니다
예제 검증다음 예제를 사용하여 위의 설명을 검증해 보겠습니다. A.vue, B.vue, C.vue의 세 가지 구성 요소가 있다고 가정합니다. 여기서 C는 B의 하위 구성 요소이고 B는 A// A.vue
<template>
<p>
<comB></comB>
</p>
</template>
<script>
import comB from '../components/test/comB.vue'
export default {
name: "A",
provide: {
for: "demo"
},
components:{
comB
}
}
</script>
// B.vue
<template>
<p>
{{demo}}
<comC></comC>
</p>
</template>
<script>
import comC from '../components/test/comC.vue'
export default {
name: "B",
inject: ['for'],
data() {
return {
demo: this.for
}
},
components: {
comC
}
}
</script>
// C.vue
<template>
<p>
{{demo}}
</p>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "C",
inject: ['for'],
data() {
return {
demo: this.for
}
}
}
</script>의 하위 구성 요소입니다. 4. ref / refs
ref: 일반 DOM 요소에 사용되는 경우 참조는 DOM 요소를 가리키고, 하위 구성 요소에 사용되는 경우 참조는 구성 요소 인스턴스를 직접 호출할 수 있습니다. ref를 사용하여 컴포넌트에 액세스하는 예: // 子组件 A.vue
export default {
data () {
return {
name: 'Vue.js'
}
},
methods: {
sayHello () {
console.log('hello')
}
}
}
// 父组件 app.vue
<template>
<component-a ref="comA"></component-a>
</template>
<script>
export default {
mounted () {
const comA = this.$refs.comA;
console.log(comA.name); // Vue.js
comA.sayHello(); // hello
}
}
</script>
eventBus는 이벤트 버스라고도 합니다. vue의 개념은 모든 구성 요소가 동일한 이벤트 센터를 공유하는 것처럼 센터에 등록하여 이벤트를 보내거나 이벤트를 받을 수 있으므로 구성 요소가 다른 구성 요소에 알릴 수 있습니다. eventBus도 불편함이 있습니다. 프로젝트가 커지면 유지 관리가 어려운 재해가 발생하기 쉽습니다. Vue 프로젝트에서 구성 요소 간 데이터 통신을 위해 eventBus를 사용하는 방법은 무엇입니까?
1 . 초기화먼저 이벤트 버스를 생성하고 다른 모듈이 이를 사용하거나 모니터링할 수 있도록 내보내야 합니다.
// event-bus.js import Vue from 'vue' export const EventBus = new Vue()
2. 이벤트 보내기
두 가지 구성 요소가 있다고 가정합니다. 구성요소는 형제 구성요소이거나 상위-하위 구성요소일 수 있습니다. 여기서는 형제 구성요소를 예로 들어 보겠습니다.
<template>
<p>
<show-num-com></show-num-com>
<addition-num-com></addition-num-com>
</p>
</template>
<script>
import showNumCom from './showNum.vue'
import additionNumCom from './additionNum.vue'
export default {
components: { showNumCom, additionNumCom }
}
</script>
// addtionNum.vue 中发送事件
<template>
<p>
<button @click="additionHandle">+加法器</button>
</p>
</template>
<script>
import {EventBus} from './event-bus.js'
console.log(EventBus)
export default {
data(){
return{
num:1
}
},
methods:{
additionHandle(){
EventBus.$emit('addition', {
num:this.num++
})
}
}
}
</script>3. 이 방법으로 구성요소 addtionNum에서 추가 버튼을 클릭합니다. vue.showNum.vue는 전달된 숫자를 사용하여 합계 결과를 표시합니다.
4. 이벤트 리스너를 제거합니다.
이벤트 리스너를 제거하려면 다음과 같이 하세요.
// showNum.vue 中接收事件
<template>
<p>计算和: {{count}}</p>
</template>
<script>
import { EventBus } from './event-bus.js'
export default {
data() {
return {
count: 0
}
},
mounted() {
EventBus.$on('addition', param => {
this.count = this.count + param.num;
})
}
}
</script>6. Vuex
1. Vuex 소개
Vuex 是一个专为 Vue.js 应用程序开发的状态管理模式。它采用集中式存储管理应用的所有组件的状态,并以相应的规则保证状态以一种可预测的方式发生变化. Vuex 解决了多个视图依赖于同一状态和来自不同视图的行为需要变更同一状态的问题,将开发者的精力聚焦于数据的更新而不是数据在组件之间的传递上
2、Vuex各个模块
state:用于数据的存储,是store中的唯一数据源
getters:如vue中的计算属性一样,基于state数据的二次包装,常用于数据的筛选和多个数据的相关性计算
mutations:类似函数,改变state数据的唯一途径,且不能用于处理异步事件
actions:类似于mutation,用于提交mutation来改变状态,而不直接变更状态,可以包含任意异步操作
modules:类似于命名空间,用于项目中将各个模块的状态分开定义和操作,便于维护
3、Vuex实例应用
// 父组件
<template>
<p id="app">
<ChildA/>
<ChildB/>
</p>
</template>
<script>
import ChildA from './components/ChildA' // 导入A组件
import ChildB from './components/ChildB' // 导入B组件
export default {
name: 'App',
components: {ChildA, ChildB} // 注册A、B组件
}
</script>
// 子组件childA
<template>
<p id="childA">
<h1>我是A组件</h1>
<button @click="transform">点我让B组件接收到数据</button>
<p>因为你点了B,所以我的信息发生了变化:{{BMessage}}</p>
</p>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data() {
return {
AMessage: 'Hello,B组件,我是A组件'
}
},
computed: {
BMessage() {
// 这里存储从store里获取的B组件的数据
return this.$store.state.BMsg
}
},
methods: {
transform() {
// 触发receiveAMsg,将A组件的数据存放到store里去
this.$store.commit('receiveAMsg', {
AMsg: this.AMessage
})
}
}
}
</script>
// 子组件 childB
<template>
<p id="childB">
<h1>我是B组件</h1>
<button @click="transform">点我让A组件接收到数据</button>
<p>因为你点了A,所以我的信息发生了变化:{{AMessage}}</p>
</p>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data() {
return {
BMessage: 'Hello,A组件,我是B组件'
}
},
computed: {
AMessage() {
// 这里存储从store里获取的A组件的数据
return this.$store.state.AMsg
}
},
methods: {
transform() {
// 触发receiveBMsg,将B组件的数据存放到store里去
this.$store.commit('receiveBMsg', {
BMsg: this.BMessage
})
}
}
}
</script>
vuex的store,js
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
const state = {
// 初始化A和B组件的数据,等待获取
AMsg: '',
BMsg: ''
}
const mutations = {
receiveAMsg(state, payload) {
// 将A组件的数据存放于state
state.AMsg = payload.AMsg
},
receiveBMsg(state, payload) {
// 将B组件的数据存放于state
state.BMsg = payload.BMsg
}
}
export default new Vuex.Store({
state,
mutations
})七、localStorage / sessionStorage
这种通信比较简单,缺点是数据和状态比较混乱,不太容易维护。 通过window.localStorage.getItem(key)获取数据 通过window.localStorage.setItem(key,value)存储数据
注意用JSON.parse() / JSON.stringify() 做数据格式转换 localStorage / sessionStorage可以结合vuex, 实现数据的持久保存,同时使用vuex解决数据和状态混乱问题.
八 $attrs与 $listeners
现在我们来讨论一种情况, 我们一开始给出的组件关系图中A组件与D组件是隔代关系, 那它们之前进行通信有哪些方式呢?
使用props绑定来进行一级一级的信息传递, 如果D组件中状态改变需要传递数据给A, 使用事件系统一级级往上传递
使用eventBus,这种情况下还是比较适合使用, 但是碰到多人合作开发时, 代码维护性较低, 可读性也低
使用Vuex来进行数据管理, 但是如果仅仅是传递数据, 而不做中间处理,使用Vuex处理感觉有点大材小用了.
在vue2.4中,为了解决该需求,引入了$attrs 和$listeners , 新增了inheritAttrs 选项。 在版本2.4以前,默认情况下,父作用域中不作为 prop 被识别 (且获取) 的特性绑定 (class 和 style 除外),将会“回退”且作为普通的HTML特性应用在子组件的根元素上。接下来看一个跨级通信的例子:
// app.vue
// index.vue
<template>
<p>
<child-com1
:name="name"
:age="age"
:gender="gender"
:height="height"
title="程序员成长"
></child-com1>
</p>
</template>
<script>
const childCom1 = () => import("./childCom1.vue");
export default {
components: { childCom1 },
data() {
return {
name: "zhang",
age: "18",
gender: "女",
height: "158"
};
}
};
</script>
// childCom1.vue
<template class="border">
<p>
<p>name: {{ name}}</p>
<p>childCom1的$attrs: {{ $attrs }}</p>
<child-com2 v-bind="$attrs"></child-com2>
</p>
</template>
<script>
const childCom2 = () => import("./childCom2.vue");
export default {
components: {
childCom2
},
inheritAttrs: false, // 可以关闭自动挂载到组件根元素上的没有在props声明的属性
props: {
name: String // name作为props属性绑定
},
created() {
console.log(this.$attrs);
// { "age": "18", "gender": "女", "height": "158", "title": "程序员成长" }
}
};
</script>
// childCom2.vue
<template>
<p class="border">
<p>age: {{ age}}</p>
<p>childCom2: {{ $attrs }}</p>
</p>
</template>
<script>
export default {
inheritAttrs: false,
props: {
age: String
},
created() {
console.log(this.$attrs);
// { "gender": "女", "height": "158", "title": "程序员成长指北" }
}
};
</script>总结
常见使用场景可以分为三类:
父子组件通信: props; $parent / $children; provide / inject ; ref ; $attrs / $listeners
兄弟组件通信: eventBus ; vuex
跨级通信: eventBus;Vuex;provide / inject 、$attrs / $listeners
위 내용은 Vue 구성 요소와 통신하는 8가지 방법 소개(컬렉션)의 상세 내용입니다. 자세한 내용은 PHP 중국어 웹사이트의 기타 관련 기사를 참조하세요!

