ホームページ >ウェブフロントエンド >jsチュートリアル >Angular 変更検出における DOM 更新メカニズムの簡単な分析
Angular 変更検出における DOM 更新メカニズムの簡単な分析
- 青灯夜游転載
- 2022-12-12 19:44:582623ブラウズ

変更検出は Angular の重要な部分であり、モデルとビュー間の同期を維持します。日々の開発プロセスでは、変更検出について知る必要はありません。Angular がこの部分の作業を完了するのに役立ち、開発者はビジネスの実装により集中できるようになり、開発効率と開発エクスペリエンスが向上します。ただし、フレームワークを詳しく使用したい場合、または単に関数を実装するのではなく高パフォーマンスのコードを作成したい場合は、変更検出について理解する必要があります。これは、フレームワークの理解を深め、エラーをデバッグし、パフォーマンスを向上させるのに役立ちます。 [関連チュートリアルの推奨事項: "angular チュートリアル "]
Angular の DOM 更新メカニズム
最初に小さな例を見てみましょう。
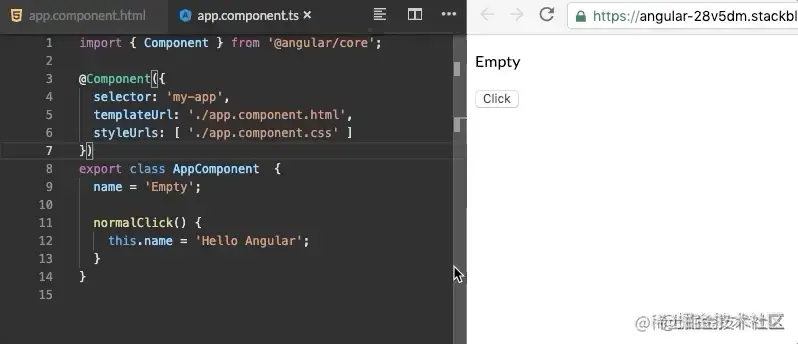
#ボタンをクリックすると、name 属性が変更され、DOM が新しい name 値で自動的に更新されます。
ここで質問ですが、name の値を変更して DOM に innerText を出力すると、どのような値になりますか?
import { Component, ViewChild, ElementRef } from '@angular/core';
@Component({
selector: 'my-app',
templateUrl: './app.component.html',
styleUrls: [ './app.component.css' ]
})
export class AppComponent {
name = 'Empty';
@ViewChild('textContainer') textContainer: ElementRef;
normalClick(): void {
this.name = 'Hello Angular';
console.log(this.textContainer.nativeElement.innerText);
}
}正解できましたか?
では、これら 2 つのコードでは一体何が起こったのでしょうか?
ネイティブ JS を使用してこのコードを記述する場合、ボタンをクリックしてもビューは絶対に変わりませんが、Angular ではビューが変更されるのに、なぜ自動的にビューが更新されるのでしょうか? 毛糸?これはzone.jsというライブラリと切り離せないもので、簡単に言うと値が変化するイベントの処理を行うもので、これについては次のセクションで詳しく説明しますので、今はこれだけ知っていれば十分です。
このライブラリにこの処理を実行させたくない場合、Angular にはzone.js を無効にする方法も用意されています。
main.ts でzone.js を無効にすることができます。
import { enableProdMode } from '@angular/core';
import { platformBrowserDynamic } from '@angular/platform-browser-dynamic';
import { AppModule } from './app/app.module';
import { environment } from './environments/environment';
if (environment.production) {
enableProdMode();
}
platformBrowserDynamic().bootstrapModule(AppModule, {
ngZone: 'noop'
})
.catch(err => console.error(err));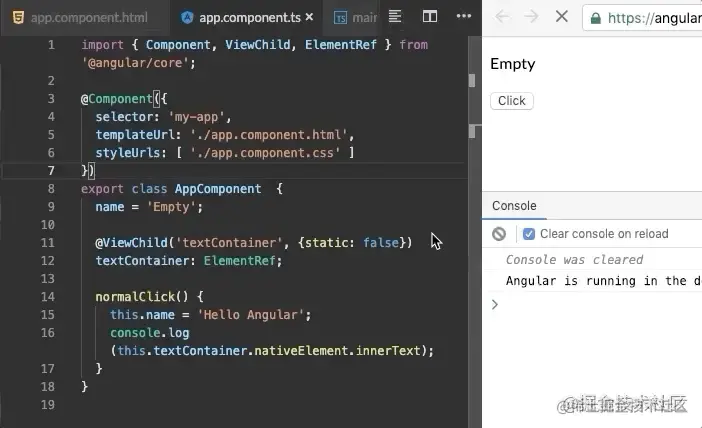
zone.js を無効にすると、ビューは更新されません。ソース コードに移動して、ビューの更新に関連するコードを見つけます。
*/
class ApplicationRef {
/** @internal */
constructor(_zone, _injector, _exceptionHandler, _initStatus) {
this._zone = _zone;
this._injector = _injector;
this._exceptionHandler = _exceptionHandler;
this._initStatus = _initStatus;
/** @internal */
this._bootstrapListeners = [];
this._views = [];
this._runningTick = false;
this._stable = true;
this._destroyed = false;
this._destroyListeners = [];
/**
* Get a list of component types registered to this application.
* This list is populated even before the component is created.
*/
this.componentTypes = [];
/**
* Get a list of components registered to this application.
*/
this.components = [];
this._onMicrotaskEmptySubscription = this._zone.onMicrotaskEmpty.subscribe({
next: () => {
this._zone.run(() => {
this.tick();
});
}
});
...
}
/**
* Invoke this method to explicitly process change detection and its side-effects.
*
* In development mode, `tick()` also performs a second change detection cycle to ensure that no
* further changes are detected. If additional changes are picked up during this second cycle,
* bindings in the app have side-effects that cannot be resolved in a single change detection
* pass.
* In this case, Angular throws an error, since an Angular application can only have one change
* detection pass during which all change detection must complete.
*/
tick() {
NG_DEV_MODE && this.warnIfDestroyed();
if (this._runningTick) {
const errorMessage = (typeof ngDevMode === 'undefined' || ngDevMode) ?
'ApplicationRef.tick is called recursively' :
'';
throw new RuntimeError(101 /* RuntimeErrorCode.RECURSIVE_APPLICATION_REF_TICK */, errorMessage);
}
try {
this._runningTick = true;
for (let view of this._views) {
view.detectChanges();
}
if (typeof ngDevMode === 'undefined' || ngDevMode) {
for (let view of this._views) {
view.checkNoChanges();
}
}
}
catch (e) {
// Attention: Don't rethrow as it could cancel subscriptions to Observables!
this._zone.runOutsideAngular(() => this._exceptionHandler.handleError(e));
}
finally {
this._runningTick = false;
}
}
}広い解釈では、この ApplicationRef は Angular アプリケーション全体のインスタンスです。コンストラクターでは、zone (ゾーン ライブラリ) onMicrotaskEmpty (名前から察するにマイクロタスクをクリアする科目です) サブスクライブしました。サブスクリプションでは、tick() が呼び出されます。tick では何が行われるのでしょうか?
感想: 前回、コンストラクター内でサブスクライブしない方が良いと言いましたが、なぜここでこれほど不規則になるのでしょうか。
もちろんそうではありません。前回は、Angular コンポーネントのどの部分を constructor に配置する必要があり、どの部分を ngOnInit に配置する必要があるかについて説明しました。ただし、ここでは ApplicationRef はサービスであるため、初期化コードは constructor にのみ配置できます。
tick 関数では、tick 関数が実行中であることが判明した場合、これはアプリケーション全体のインスタンスであり、再帰的に呼び出すことができないため、例外がスローされます。次に、すべてのビューを走査し、各ビューで detectChanges() が実行され、変更検出が実行されます。変更検出については後で詳しく説明します。その直後、devMode の場合、すべてのビューが再度走査され、各ビューが checkNoChanges() を実行して変更があるかどうかを確認します。変更がある場合は、エラーがスローされます ( Thisこの問題については後で詳しく説明します)。ここでは をスキップしてください)。
さて、これで更新方法がわかりました。つまり、ApplicationRef の tick メソッドを呼び出すことです。
import { Component, ViewChild, ElementRef, ApplicationRef } from '@angular/core';
@Component({
selector: 'app-root',
templateUrl: './app.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./app.component.scss']
})
export class AppComponent {
name = 'Empty';
@ViewChild('textContainer') textContainer: ElementRef = {} as any;
constructor(private app: ApplicationRef){}
normalClick(): void {
this.name = 'Hello Angular';
console.log(this.textContainer.nativeElement.innerText);
this.app.tick();
}
}案の定、ビューは正常に更新できます。
簡単に整理しましょう。DOM の更新は tick() のトリガーに依存しています。zone.js は、開発者がこの操作を手動でトリガーすることを回避するのに役立ちます。さて、これでzone.jsを有効にすることができます。
それでは、変化検出とは何でしょうか?次回の記事もお楽しみに。
プログラミング関連の知識について詳しくは、プログラミング教育をご覧ください。 !
以上がAngular 変更検出における DOM 更新メカニズムの簡単な分析の詳細内容です。詳細については、PHP 中国語 Web サイトの他の関連記事を参照してください。

