Maison >Java >javaDidacticiel >Java résume les principes des flux IO et la classification des flux
Java résume les principes des flux IO et la classification des flux
- WBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBavant
- 2022-06-28 15:21:071331parcourir
Cet article vous apporte des connaissances pertinentes sur java, qui organise principalement les problèmes liés aux principes du flux O et à la classification des flux, y compris le flux de nœuds, le flux de tampon, le flux de conversion, le flux de sortie, etc., comme suit Jetons un coup d'œil, j'espère cela sera utile à tout le monde.

Étude recommandée : "Tutoriel vidéo Java"
1. Présentation
I/Oest l'abréviation deEntrée/Sortie, la technologieE/Sest une technologie très pratique utilisée pour gérer la transmission de données entre appareils. Tels que la lecture/écriture de fichiers, la communication réseau, etc.I/O是Input/Output的缩写,I/O技术是非常实用的技术,用于处理设备之间的数据传输。如读/写文件,网络通讯等。
- 输入
input:读取外部数据(磁 盘、光盘等存储设备的数据)到程序(内存)中。- 输出
output:将程序(内存)数据输出到磁盘、光盘等存储设 备中。
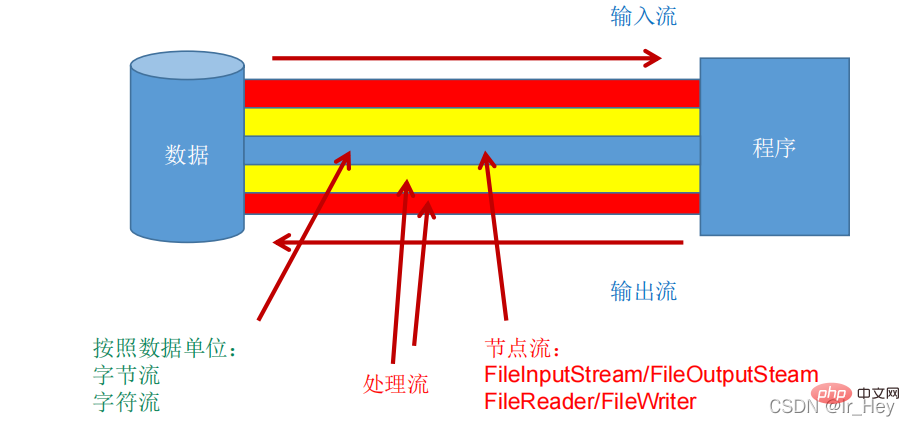
Java程序中,对于数据的输入/输出操作以“流(
stream)” 的方式进行。
java.io包下提供了各种“流”类和接口,用以获取不种类的数据,并通过标准的方法输入或输出数据。
二、流的分类
1. 概述
按操作数据单位不同分为:字节流(8
bit),字符流(16bit)
按数据流的流向不同分为:输入流,输出流
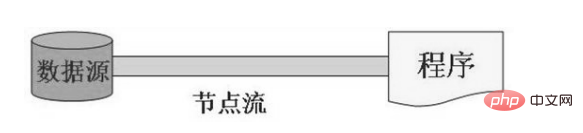
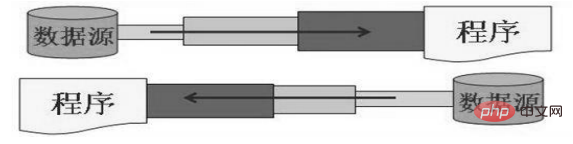
按流的角色的不同分为:节点流,处理流
节点流:直接从数据源或目的地读写数据
处理流:不直接连接到数据源或目的地,而是“连接”在已存在的流(节点流或处理流)之上,通过对数据的处理为程序提供更为强大的读写功能。
Java的IO流共涉及40多个类,实际上非常规则,都是从以上4个抽象基类派生的,由这4个类派生出来的子类名称都是以其父类名作为子类名后缀。
| (抽象基类) | 字节流 | 字符流 |
|---|---|---|
| 输入流 | InputStream |
Reader |
| 输出流 | OutputStream |
Writer |
IO 流体系体系: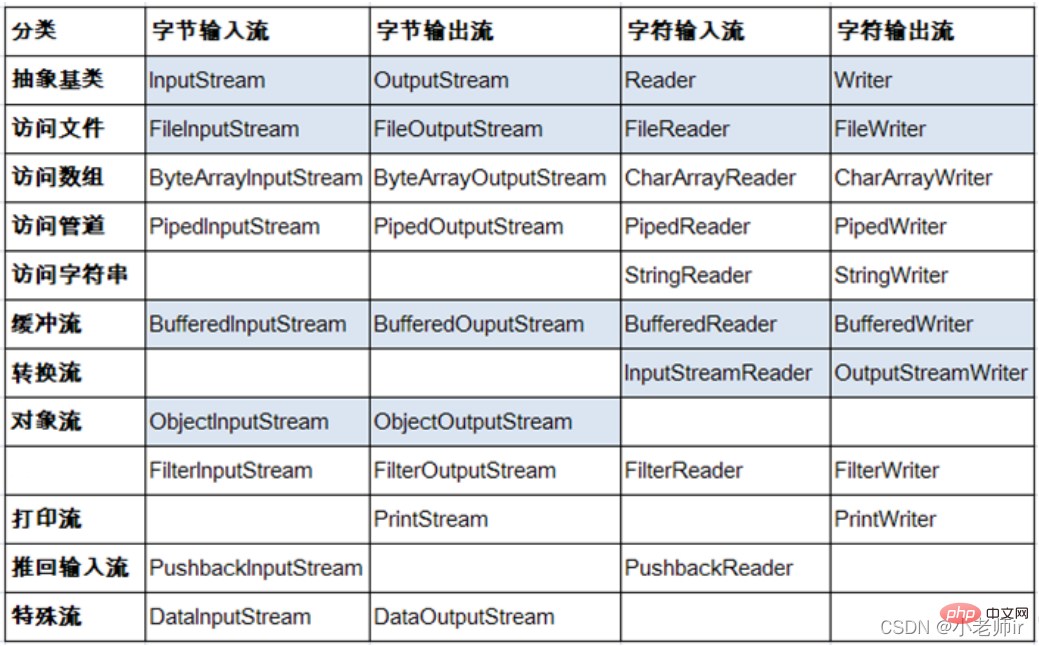
2. InputStream
概述
典型实现:
FileInputStream
方法
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
int read() |
从输入流中读取数据的下一个字节。返回 0 到 255 范围内的 int 字节值。如果因为已经到达流末尾而没有可用的字节,则返回值 -1。 |
int read(byte[] b) |
从此输入流中将最多 b.length 个字节的数据读入一个 byte 数组中。如果因为已经到达流末尾而没有可用的字节,则返回值 -1。否则以整数形式返回实际读取的字节数。 |
int read(byte[] b, int off,int len) |
将输入流中最多 len 个数据字节读入 byte 数组。尝试读取 len 个字节,但读取的字节也可能小于该值。以整数形式返回实际读取的字节数。如果因为流位于文件末尾而没有可用的字节,则返回值 -1。 |
public void close() throws IOException
|
Dans les programmes Java, les opérations d'entrée/sortie de données sont effectuées sous la forme de "stream (stream)". |
 🎜🎜 2 . Classification des flux🎜
🎜🎜 2 . Classification des flux🎜1. Présentation
🎜🎜 Selon les différentes unités de données d'exploitation, ils sont divisés en : flux d'octets (8bit), flux de caractères (16 ). bit)🎜🎜🎜 Selon les différentes directions d'écoulement du flux de données, il est divisé en : flux d'entrée, flux de sortie🎜🎜🎜 Selon les différents rôles du flux, il est divisé en : flux de nœuds, flux de traitement🎜<ul> <li>🎜Flux de nœuds : lire et écrire des données directement à partir de la source de données ou de la destination<br><img src="https://img.php.cn%20/upload/article/000/000/067/2303dcd820fa8efec736198a8887cf17-1.%20png" alt="Insérer la description de l'image ici">🎜</li>
<li>🎜Flux de traitement : non directement connecté à la source ou à la destination des données, mais "connecté" à un flux existant (flux de nœuds ou traitement au-dessus du flux), il offre au programme des fonctions de lecture et d'écriture plus puissantes en traitant les données. <br><img src="https://img.php.cn/upload/article/000/000/067/0a7881848e79bce34e3884eeac3bd014-2.png" alt="Insérer la description de l'image ici">🎜</li> </ul>🎜<strong>Le flux IO de Java implique plus de 40 classes. En fait, elles sont toutes dérivées des 4 classes de base abstraites ci-dessus. Les sous-classes dérivées de ces 4 classes. sont suffixés avec le nom de la classe parent comme nom de sous-classe. </strong>🎜<table>
<thead><tr class="firstRow">
<th>(Classe de base abstraite)</th>
<th>Flux d'octets</th>
<th>Flux de caractères</th> 🎜 </tr></thead>
<tbody>
<tr>🎜<strong>InputStream</strong>🎜🎜<code>InputStream🎜🎜Reader🎜🎜
OutputStream🎜🎜Writer🎜🎜🎜🎜🎜
Système de flux IO :
 🎜
🎜2. InputStream
🎜 Présentation🎜🎜 🎜Implémentation typique :FileInputStream🎜🎜 Méthode🎜| Méthode | Description🎜||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
int read() |
读取单个字符。作为整数读取的字符,范围在 0 到 65535 之间 (0x00-0xffff)(2个字节的Unicode码),如果已到达流的末尾,则返回 -1 |
int read(char[] cbuf) |
将字符读入数组。如果已到达流的末尾,则返回 -1。否则返回本次读取的字符数。 |
int read(char[] cbuf,int off,int len) |
将字符读入数组的某一部分。存到数组cbuf中,从off处开始存储,最多读len个字符。如果已到达流的末尾,则返回 -1。否则返回本次读取的字符数。 |
public void close() throws IOException |
关闭此输入流并释放与该流关联的所有系统资源。 |
典型实现类:FileReader
@Test
public void testFileReader(){
FileReader fr = null;
try {
//1.实例化File类的对象,指明要操作的文件
File file = new File("hello.txt");//相较于当前Module
//2.提供具体的流
fr = new FileReader(file);
//3.数据的读入
//read():返回读入的一个字符。如果达到文件末尾,返回-1
//方式一:// int data = fr.read();// while(data != -1){// System.out.print((char)data);// data = fr.read();// }
//方式二:语法上针对于方式一的修改
int data;
while((data = fr.read()) != -1){
System.out.print((char)data);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//4.流的关闭操作// try {// if(fr != null)// fr.close();// } catch (IOException e) {// e.printStackTrace();// }
//或
if(fr != null){
try {
fr.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
//对read()操作升级:使用read的重载方法
@Test
public void testFileReader1() {
FileReader fr = null;
try {
//1.File类的实例化
File file = new File("hello.txt");
//2.FileReader流的实例化
fr = new FileReader(file);
//3.读入的操作
//read(char[] cbuf):返回每次读入cbuf数组中的字符的个数。如果达到文件末尾,返回-1
char[] cbuf = new char[5];
int len;
while((len = fr.read(cbuf)) != -1){
//方式一:
//错误的写法// for(int i = 0;i <h3>4. OutputStream</h3><p><strong> 概述</strong></p><blockquote><p>典型实现:<code>FileOutputStream</code></p></blockquote><p><strong> 方法</strong></p>
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
void write(int b) |
将指定的字节写入此输出流。write 的常规协定是:向输出流写入一个字节。要写入的字节是参数 b 的八个低位。b 的 24 个高位将被忽略。 即写入0~255范围的。 |
void write(byte[] b) |
将 b.length 个字节从指定的 byte 数组写入此输出流。write(b) 的常规协定是:应该与调用 write(b, 0, b.length) 的效果完全相同。 |
void write(byte[] b,int off,int len) |
将指定 byte 数组中从偏移量 off 开始的 len 个字节写入此输出流。 |
public void flush()throws IOException |
刷新此输出流并强制写出所有缓冲的输出字节,调用此方法指示应将这些字节立即写入它们预期的目标。 |
public void close() throws IOException |
关闭此输出流并释放与该流关联的所有系统资源。 |
主要实现类:FileInputOutputStream
/*
实现对图片的复制操作
*/
@Test
public void testFileInputOutputStream() {
FileInputStream fis = null;
FileOutputStream fos = null;
try {
//
File srcFile = new File("爱情与友情.jpg");
File destFile = new File("爱情与友情2.jpg");
//
fis = new FileInputStream(srcFile);
fos = new FileOutputStream(destFile);
//复制的过程
byte[] buffer = new byte[5];
int len;
while((len = fis.read(buffer)) != -1){
fos.write(buffer,0,len);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if(fos != null){
//
try {
fos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(fis != null){
try {
fis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
5. Writer
概述
典型实现:
FileWriter
方法
| 方法 | 描述 | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
void write(int c) |
写入单个字符。要写入的字符包含在给定整数值的 16 个低位中,16 高位被忽略。 即写入0 到 65535 之间的Unicode码。 | |||||||||||||||||||
void write(char[] cbuf) |
写入字符数组。 | |||||||||||||||||||
void write(char[] cbuf,int off,int len) |
写入字符数组的某一部分。从off开始,写入len个字符 | |||||||||||||||||||
void write(String str) |
写入字符串。 | |||||||||||||||||||
void write(String str,int off,int len) |
写入字符串的某一部分。 | |||||||||||||||||||
void flush() |
刷新该流的缓冲,则立即将它们写入预期目标。 | |||||||||||||||||||
public void close() throws IOException |
méthode. |
| Méthode | Description |
|---|---|
int read() 🎜🎜Lisez un seul caractère. Caractère lu sous forme d'entier compris entre 0 et 65535 (0x00-0xffff) (code Unicode sur 2 octets), ou -1 si la fin du flux a été atteinte 🎜🎜int read(char[ ] cbuf)🎜🎜Lire les caractères dans un tableau. Si la fin du flux a été atteinte, -1 est renvoyé. Sinon, renvoie le nombre de caractères lus cette fois. 🎜🎜int read(char[] cbuf,int off,int len)🎜🎜Lire les caractères dans une certaine partie du tableau. Stockez-le dans le tableau cbuf, en commençant par off, et lisez jusqu'aux caractères len. Si la fin du flux a été atteinte, -1 est renvoyé. Sinon, renvoie le nombre de caractères lus cette fois. 🎜🎜public void close() lance IOException🎜🎜Ferme ce flux d'entrée et libère toutes les ressources système associées au flux. 🎜🎜🎜🎜🎜🎜 Classe d'implémentation typique : FileReader🎜🎜//从内存中写出数据到硬盘的文件里。
@Test
public void testFileWriter() {
FileWriter fw = null;
try {
//1.提供File类的对象,指明写出到的文件
File file = new File("hello1.txt");
//2.提供FileWriter的对象,用于数据的写出
fw = new FileWriter(file,false);
//3.写出的操作
fw.write("I have a dream!\n");
fw.write("you need to have a dream!");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//4.流资源的关闭
if(fw != null){
try {
fw.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}🎜4. OutputStream🎜🎜🎜 Présentation🎜🎜🎜🎜Implémentation typique : FileOutputStream🎜🎜🎜 Méthode🎜 🎜| Méthode | Description | 🎜|||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Méthode | Description | 🎜|||||||||||||||||
public InputStreamReader(InputStream in) |
public InputSreamReader(InputStream in,String charsetName) |
3. OutputStreamWriter
概述
- 实现将字符的输出流按指定字符集转换为字节的输出流。
- 需要和
OutputStream“套接”。
(2)构造器
public OutputStreamWriter(OutputStream out) |
public OutputSreamWriter(OutputStream out,String charsetName) |
4. 代码演示
代码演示1:
@Test
public void test1() throws IOException {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("dbcp.txt");// InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(fis);//使用系统默认的字符集
//参数2指明了字符集,具体使用哪个字符集,取决于文件dbcp.txt保存时使用的字符集
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(fis,"UTF-8");//使用系统默认的字符集
char[] cbuf = new char[20];
int len;
while((len = isr.read(cbuf)) != -1){
String str = new String(cbuf,0,len);
System.out.print(str);
}
isr.close();
}
代码演示2:
@Test
public void test2() throws Exception {
//1.造文件、造流
File file1 = new File("dbcp.txt");
File file2 = new File("dbcp_gbk.txt");
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file1);
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(file2);
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(fis,"utf-8");
OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(fos,"gbk");
//2.读写过程
char[] cbuf = new char[20];
int len;
while((len = isr.read(cbuf)) != -1){
osw.write(cbuf,0,len);
}
//3.关闭资源
isr.close();
osw.close();
}}
六、标准输入、输出流
1. 概述
System.in和System.out分别代表了系统标准的输入和输出设备
默认输入设备是:键盘,输出设备是:显示器
System.in的类型是InputStream,System.out的类型是PrintStream,其是OutputStream的子类,FilterOutputStream的子类
重定向:通过System类的setIn,setOut方法对默认设备进行改变。
public static void setIn(InputStream in)public static void setOut(PrintStream out)
2. 代码演示
/*
从键盘输入字符串,要求将读取到的整行字符串转成大写输出。然后继续进行输入操作,
直至当输入“e”或者“exit”时,退出程序。
方法一:使用Scanner实现,调用next()返回一个字符串
方法二:使用System.in实现。System.in ---> 转换流 ---> BufferedReader的readLine()
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
BufferedReader br = null;
try {
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(System.in);
br = new BufferedReader(isr);
while (true) {
System.out.println("请输入字符串:");
String data = br.readLine();
if ("e".equalsIgnoreCase(data) || "exit".equalsIgnoreCase(data)) {
System.out.println("程序结束");
break;
}
String upperCase = data.toUpperCase();
System.out.println(upperCase);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (br != null) {
try {
br.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
七. 打印流
1. 概述
实现将基本数据类型的数据格式转化为字符串输出
打印流:
PrintStream和PrintWriter
提供了一系列重载的
print()和println()方法,用于多种数据类型的输出
PrintStream和PrintWriter的输出不会抛出IOException异常
PrintStream和PrintWriter有自动flush功能
PrintStream打印的所有字符都使用平台的默认字符编码转换为字节。 在需要写入字符而不是写入字节的情况下,应该使用PrintWriter类。
System.out返回的是PrintStream的实例
2. 代码演示
/*
2. 打印流:PrintStream 和PrintWriter
2.1 提供了一系列重载的print() 和 println()
2.2 练习:
*/
@Test
public void test2() {
PrintStream ps = null;
try {
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(new File("D:\\IO\\text.txt"));
// 创建打印输出流,设置为自动刷新模式(写入换行符或字节 '\n' 时都会刷新输出缓冲区)
ps = new PrintStream(fos, true);
if (ps != null) {// 把标准输出流(控制台输出)改成文件
System.setOut(ps);
}
for (int i = 0; i <h2>八、数据流</h2><blockquote><p> 为了方便地操作Java语言的基本数据类型和String的数据,可以使用数据流。</p></blockquote><blockquote>
<p> 数据流有两个类:(用于读取和写出基本数据类型、String类的数据)</p>
<ol>
<li><code>DataInputStream</code></li>
<li><code>DataOutputStream</code></li>
</ol>
<p>分别“套接”在 <code>InputStream</code> 和 <code>OutputStream</code> 子类的流上</p>
</blockquote><blockquote><p><code>DataInputStream</code>中的方法:</p></blockquote>
boolean readBoolean() |
byte readByte() char |
readChar() |
float readFloat() |
double readDouble() |
long readLong() |
int readInt() |
short readShort() |
String readUTF() |
void readFully(byte[] b) |
Supplément : Méthode dans DataOutputStream : Remplacez la lecture de la méthode ci-dessus par l'écriture correspondante
Apprentissage recommandé : "Tutoriel vidéo Java"
Ce qui précède est le contenu détaillé de. pour plus d'informations, suivez d'autres articles connexes sur le site Web de PHP en chinois!
Articles Liés
Voir plus- Qu'est-ce que la dénomination des cas de chameaux en javascript
- Parlez brièvement de la surveillance des événements en JavaScript
- Un article pour maîtriser le concept et l'utilisation de Stream, une nouvelle fonctionnalité de Java 8
- Un article pour vous présenter les piles et files d'attente Java
- Objet de date JavaScript Date (partage du résumé)