Maison >interface Web >Tutoriel H5 >Utilisez HTML5 pour implémenter un algorithme de tri de sélection simple et une démonstration, avec le code joint
Utilisez HTML5 pour implémenter un algorithme de tri de sélection simple et une démonstration, avec le code joint
- PHPzoriginal
- 2017-03-05 11:31:583165parcourir
Tri par sélection simple est un type d'algorithme de tri par sélection. Idée de base : à chaque passage, l'enregistrement avec le plus petit mot-clé est sélectionné parmi les enregistrements à trier, et l'ordre est placé à la fin de la séquence d'enregistrements triés jusqu'à ce que tout le tri soit terminé. Puisque dans chaque boucle, les positions des éléments de valeurs égales changeront, il s'agit d'un tri instable.
------------------------------------------------------ ------ --------------------------
Comme indiqué ci-dessous :
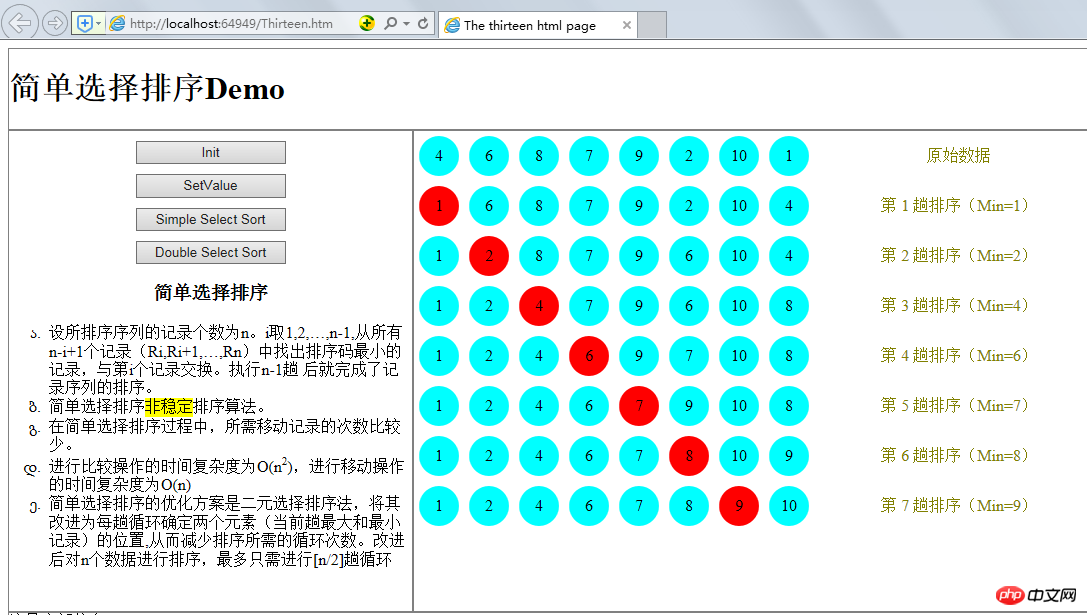
La solution d'optimisation pour le tri par sélection simple consiste à utiliser le tri par sélection binaire, qui est amélioré pour déterminer les positions de deux éléments (les enregistrements les plus grands et les plus petits de la passe en cours) dans chaque cycle, réduisant ainsi le nombre de cycles nécessaires au tri. Après l'amélioration, pour trier n données, seules [n/2] boucles sont nécessaires au maximum.
Comme le montre la figure ci-dessous :

Le principe de l'algorithme ne sera pas décrit en détail. Utilisez Html5 pour implémenter une sélection simple. l'algorithme de tri et le code de démonstration est le suivant :


<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>The thirteen html page</title>
<style type="text/css">
ul li
{
list-style-type:georgian;
text-align:left;
}
.mark
{
width:280px;
height:40px;
color:Olive;
text-align:center;
line-height:40px;
margin:5px;
float:left;
}
.redball
{
width:40px;
height:40px;
border-radius:20px;
background-color:Red;
text-align:center;
line-height:40px;
margin:5px;
float:left;
}
.ball
{
width:40px;
height:40px;
border-radius:20px;
background-color:Aqua;
text-align:center;
line-height:40px;
margin:5px;
float:left;
}
.line
{
clear:left;
}
header
{
height:80px;
border:1px solid gray;
}
.left
{
border:1px solid gray;
float:left;
width:30%;
height:480px;
margin-left:0px;
margin-right:0px;
}
aside
{
text-align:center;
}
section
{
width:69.5%;
float:left;
height:480px;
border:1px solid gray;
margin-left:0px;
margin-right:0px;
}
footer
{
clear:left;
height:60px;
border:1px solid gray;
}
input[type="button"]
{
width:150px;
text-align:center;
margin-top:10px;
}
</style>
<script type="text/javascript">
function initDiv() {
var mainArea = document.getElementById("mainArea");
var childs = mainArea.childNodes;
//添加节点之前先删除,应该从后往前删除,否则节点移动,只能删除一半
for (var i = childs.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
mainArea.removeChild(childs[i]);
}
for (var i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
var newDivLine = document.createElement("div");
newDivLine.setAttribute("class", "line");
newDivLine.setAttribute("id", i);
mainArea.appendChild(newDivLine);
for (var j = 0; j < 9; j++) {
var newDiv = document.createElement("div");
var id = i.toString() + j.toString();
newDiv.setAttribute("id", id);
if (j < 8) {
newDiv.setAttribute("class", "ball");
} else {
newDiv.setAttribute("class", "mark");
}
newDivLine.appendChild(newDiv);
}
}
}
//初始元素赋值
function setElementsValue() {
var arrTmp = [4, 6, 8, 7, 9, 2, 10, 1];
for (var i = 0; i < arrTmp.length; i++) {
document.getElementById("0" + i.toString()).innerText = arrTmp[i];
}
document.getElementById("08").innerText = "原始数据";
}
//简单选择排序
function setSimpleSortValue() {
var arrTmp = [4, 6, 8, 7, 9, 2, 10, 1];
var m = 0;//表示要交换的最小坐标
for (var i = 0; i < arrTmp.length-1; i++) {
m = i;
for (var j = i + 1; j < arrTmp.length; j++) {
if (arrTmp[m] > arrTmp[j]) {
m = j;
}
}
if (arrTmp[i] > arrTmp[m]) {
var tmp = arrTmp[m];
arrTmp[m] = arrTmp[i];
arrTmp[i] = tmp;
}
//显示出来
for (var k = 0; k < arrTmp.length; k++) {
document.getElementById((i+1).toString() + k.toString()).innerText = arrTmp[k];
if (i == k) {
document.getElementById((i + 1).toString() + (k).toString()).setAttribute("class", "redball");
} else {
document.getElementById((i + 1).toString() + (k).toString()).attributes["class"].nodeValue="ball";;
}
}
document.getElementById((i+1).toString() + "8").innerText = "第 " + (i+1).toString() + " 趟排序(Min=" + arrTmp[i] + ")";
}
}
//二元选择排序
function setDoubleSelectSort() {
var arrTmp = [4, 6, 8, 7, 9, 2, 10, 1];
selectSortB(arrTmp);
var len=arrTmp.length;
for (var i = (len / 2)+1; i < len; i++) {
for (var j = 0; j < 8; j++) {
document.getElementById((i).toString() + (j).toString()).innerText = "";
document.getElementById((i).toString() + (j).toString()).className="ball";
}
document.getElementById(i.toString() + "8").innerText = "";
}
}
//二元选择排序(升序)
function selectSortB(a) {
var len = a.length;
var temp, min, max;
for (var i = 0; i < len / 2; i++) {
min = i; max = i;
for (var j = i + 1; j <= len - 1 - i; j++) {
max = (a[j] > a[max]) ? j : max;//每一趟取出当前最大和最小的数组下标
min = (a[j] < a[min]) ? j : min;
};
temp = a[i];//先放小的
a[i] = a[min];
if (i == max) { //最大数在数组头部
if ((len - i - 1) !== min) {//最大数在头部,最小数在尾部
a[min] = a[len - i - 1];
}
a[len - i - 1] = temp;
}
else if ((len - i - 1) === min) {//最大数不在头部,最小数在尾部
a[len - i - 1] = a[max];
a[max] = temp
}
else {
//如果最大数在尾部,也是成立的,不用特殊讨论
a[min] = temp;
temp = a[len - i - 1];
a[len - i - 1] = a[max];
a[max] = temp;
}
//显示出来
for (var k = 0; k < a.length; k++) {
document.getElementById((i + 1).toString() + k.toString()).innerText = a[k];
if (i == k || len - i - 1 == k) {
document.getElementById((i + 1).toString() + (k).toString()).setAttribute("class", "redball");
} else {
document.getElementById((i + 1).toString() + (k).toString()).className = "ball";
}
}
document.getElementById((i + 1).toString() + "8").innerText = "第 " + (i + 1).toString() + " 趟排序(Min=" + a[i] + ",Max=" + a[len-i-1] + ")";
}
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<header>
<h1>简单选择排序Demo</h1>
</header>
<aside class="left">
<input type="button" id="btnInit" value="Init" onclick="initDiv();" />
<br />
<input type="button" id="btnSetValue" value="SetValue" onclick="setElementsValue();" />
<br />
<input type="button" id="btnSimpleSort" value="Simple Select Sort" onclick="setSimpleSortValue();" />
<br />
<input type="button" id="btnDoubleSelect" value="Double Select Sort" onclick="setDoubleSelectSort();" />
<br />
<h3>简单选择排序</h3>
<ul>
<li>设所排序序列的记录个数为n。i取1,2,…,n-1,从所有n-i+1个记录(Ri,Ri+1,…,Rn)中找出排序码最小的记录,与第i个记录交换。执行n-1趟 后就完成了记录序列的排序。</li>
<li>简单选择排序<mark>非稳定</mark>排序算法。</li>
<li>在简单选择排序过程中,所需移动记录的次数比较少。</li>
<li>进行比较操作的时间复杂度为O(n<sup>2</sup>),进行移动操作的时间复杂度为O(n)</li>
<li>简单选择排序的优化方案是二元选择排序法,将其改进为每趟循环确定两个元素(当前趟最大和最小记录)的位置,从而减少排序所需的循环次数。改进后对n个数据进行排序,最多只需进行[n/2]趟循环</li>
</ul>
</aside>
<section id="mainArea"></section>
<footer>
这是底部信息
</footer>
</body>
</html>
Voir Code
À propos de 2 Traitement particulier du tri par méta-sélection :
En général, un simple échange suffit.
Des cas particuliers se produisent lorsque quatre valeurs sont identiques, comme a[i]=a[max], a[len-1-i]=a[min].
Dans le code, j'ai choisi d'attribuer d'abord la valeur minimale min à a[i], et en même temps de retirer la valeur de a[i], puis j'ai discuté de trois situations dans le code
① : Lorsque max est Lorsque la tête du tableau est en tête du tableau, la situation de savoir si min est à la queue du tableau est discutée sous la condition ①
② : Lorsque min est à la queue du tableau ; (et max n'est pas en tête du tableau)
③ : En général, la même chose s'applique à [min est en tête du tableau, max est à la queue du tableau]
Pour Pour plus d'articles sur l'utilisation de HTML5 pour implémenter des algorithmes de tri de sélection simples et des démonstrations, veuillez faire attention au site Web PHP chinois !
Articles Liés
Voir plus- Le plug-in de défilement plein écran AlloyTouch crée une page H5 fluide en 30 secondes
- Combat réel HTML5 et analyse des événements tactiles (touchstart, touchmove et touchend)
- Explication détaillée des exemples de dessin d'images dans le canevas HTML5 9
- Expressions régulières et nouveaux éléments HTML5
- Comment combiner NodeJS et HTML5 pour glisser-déposer plusieurs fichiers à télécharger sur le serveur

