What are edge artificial intelligence and edge computing?

Edge artificial intelligence is one of the most noteworthy new areas in artificial intelligence. It is allowing people to run artificial intelligence processes without having to worry about privacy or data transmission. The speed slows down. Edge AI is making the use of artificial intelligence wider and more widespread, allowing smart devices to respond quickly to input without accessing the cloud. While this is a quick definition of edge AI, let’s take a moment to better understand edge AI by exploring some use cases. First, edge AI has widespread applications in the healthcare industry. For example, integrating edge AI on monitoring devices can more accurately monitor and analyze patients’ vital signs and respond immediately when needed. This capability can make healthcare more efficient while also reliably handling sensitive personal data. In addition, edge artificial intelligence can also be applied to smart homes. By integrating artificial intelligence into home devices, such as smart speakers and smart TVs, users can interact with smart devices more widely and conveniently. The existence of edge artificial intelligence makes these devices no longer need to rely on the cloud.
What is edge computing?
In order to truly understand edge artificial intelligence, we first need to understand edge computing and understand the most important aspects of edge computing. The best way is to compare it to cloud computing. Cloud computing is the provision of computing services over the Internet. In contrast, edge computing systems do not connect to the cloud but run on local devices. These local devices can be dedicated edge computing servers, local devices, or Internet of Things (IoT). There are many advantages to using edge computing. For example, Internet/cloud-based computing is limited by latency and bandwidth, while edge computing is not limited by these parameters.
What is edge artificial intelligence?
Now that we understand edge computing, we can look at edge artificial intelligence. Edge AI combines artificial intelligence and edge computing. Artificial intelligence algorithms run on devices with edge computing capabilities. The benefit of this is that the data can be processed in real time without the need to connect to the cloud.
Most cutting-edge artificial intelligence processes are performed in the cloud because they require large amounts of computing power. The result is that these AI processes are prone to downtime. Because edge AI systems run on edge computing devices, required data operations can be performed locally, sent when an Internet connection is established, and save time. Deep learning algorithms can run on the device itself (the point of origin of the data).
Edge AI is becoming increasingly important as more and more devices require AI without access to the cloud. Think about how many factory robots or cars are now equipped with computer vision algorithms. In this case, data transfer lag time can be fatal. Because fast response times are so important, the device itself must have an edge AI system that enables it to analyze and classify images without relying on a cloud connection.
When information processing tasks performed in the cloud are delegated to edge computers, the result is real-time latency, real-time processing. Furthermore, by limiting data transfer to the most important information, the data volume itself is reduced and communication interruptions are minimized.
Edge AI and IoT
Edge AI is combined with other digital technologies such as 5G and the Internet of Things (IoT). The IoT can generate data for use by edge AI systems, and 5G technology is critical to the continued development of edge AI and IoT.
The Internet of Things refers to various smart devices that are connected to each other through the Internet. All of these devices generate data that can be fed into an edge AI device, which also serves as a temporary storage unit for the data until synchronized with the cloud. This method of data processing allows for greater flexibility.
The fifth generation mobile network 5G is crucial to the development of edge computing intelligence and the Internet of Things. 5G can transmit data at higher speeds, up to 20Gbps, while 4G can only transmit data at 1Gbps. 5G also supports simultaneous connections (1,000,000 per square kilometer) supporting better latency speeds (1ms to 10ms). These advantages over 4G are important because as the Internet of Things develops, the amount of data will grow and transmission speeds will be affected. 5G enables more interactions between a wider range of devices, many of which can be equipped with edge computing intelligence.
USE CASES FOR EDGE AI
Use cases for edge AI include almost any situation where data processing can be done more efficiently on a local device than through the cloud. However, some of the most common use cases for edge AI include self-driving cars, autonomous drones, facial recognition, and digital assistants.
Self-driving cars are one of the most relevant use cases for edge artificial intelligence. Self-driving cars must constantly scan their surroundings and assess the situation, making corrections to their trajectory based on nearby events. Real-time data processing is critical for these situations, so its on-board edge artificial intelligence system is responsible for data storage, operation and analysis. Edge AI systems are necessary to bring Level 3 and 4 (fully autonomous) vehicles to market.
Because autonomous drones are not flown by human operators, their requirements for self-driving cars are very similar. If a drone loses control or malfunctions during flight, it could crash and cause damage to property or life. Drones may fly beyond the range of internet access points, and they must have edge AI capabilities. For services like Amazon Prime Air, which aims to deliver packages via drones, edge AI systems will be integral.
Another use case for edge AI is facial recognition systems. Facial recognition systems rely on computer vision algorithms to analyze data collected by cameras. Facial recognition applications used for tasks such as security need to run reliably even when not connected to the cloud.
Digital assistants are another common use case for edge AI. Digital assistants like Google Assistant, Alexa and Siri must be able to run on smartphones and other digital devices even when not connected to the internet. When data is processed on the device, it does not need to be transferred to the cloud, which helps reduce traffic and ensure privacy.
The above is the detailed content of What are edge artificial intelligence and edge computing?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Are You At Risk Of AI Agency Decay? Take The Test To Find OutApr 21, 2025 am 11:31 AM
Are You At Risk Of AI Agency Decay? Take The Test To Find OutApr 21, 2025 am 11:31 AMThis article explores the growing concern of "AI agency decay"—the gradual decline in our ability to think and decide independently. This is especially crucial for business leaders navigating the increasingly automated world while retainin
 How to Build an AI Agent from Scratch? - Analytics VidhyaApr 21, 2025 am 11:30 AM
How to Build an AI Agent from Scratch? - Analytics VidhyaApr 21, 2025 am 11:30 AMEver wondered how AI agents like Siri and Alexa work? These intelligent systems are becoming more important in our daily lives. This article introduces the ReAct pattern, a method that enhances AI agents by combining reasoning an
 Revisiting The Humanities In The Age Of AIApr 21, 2025 am 11:28 AM
Revisiting The Humanities In The Age Of AIApr 21, 2025 am 11:28 AM"I think AI tools are changing the learning opportunities for college students. We believe in developing students in core courses, but more and more people also want to get a perspective of computational and statistical thinking," said University of Chicago President Paul Alivisatos in an interview with Deloitte Nitin Mittal at the Davos Forum in January. He believes that people will have to become creators and co-creators of AI, which means that learning and other aspects need to adapt to some major changes. Digital intelligence and critical thinking Professor Alexa Joubin of George Washington University described artificial intelligence as a “heuristic tool” in the humanities and explores how it changes
 Understanding LangChain Agent FrameworkApr 21, 2025 am 11:25 AM
Understanding LangChain Agent FrameworkApr 21, 2025 am 11:25 AMLangChain is a powerful toolkit for building sophisticated AI applications. Its agent architecture is particularly noteworthy, allowing developers to create intelligent systems capable of independent reasoning, decision-making, and action. This expl
 What are the Radial Basis Functions Neural Networks?Apr 21, 2025 am 11:13 AM
What are the Radial Basis Functions Neural Networks?Apr 21, 2025 am 11:13 AMRadial Basis Function Neural Networks (RBFNNs): A Comprehensive Guide Radial Basis Function Neural Networks (RBFNNs) are a powerful type of neural network architecture that leverages radial basis functions for activation. Their unique structure make
 The Meshing Of Minds And Machines Has ArrivedApr 21, 2025 am 11:11 AM
The Meshing Of Minds And Machines Has ArrivedApr 21, 2025 am 11:11 AMBrain-computer interfaces (BCIs) directly link the brain to external devices, translating brain impulses into actions without physical movement. This technology utilizes implanted sensors to capture brain signals, converting them into digital comman
 Insights on spaCy, Prodigy and Generative AI from Ines MontaniApr 21, 2025 am 11:01 AM
Insights on spaCy, Prodigy and Generative AI from Ines MontaniApr 21, 2025 am 11:01 AMThis "Leading with Data" episode features Ines Montani, co-founder and CEO of Explosion AI, and co-developer of spaCy and Prodigy. Ines offers expert insights into the evolution of these tools, Explosion's unique business model, and the tr
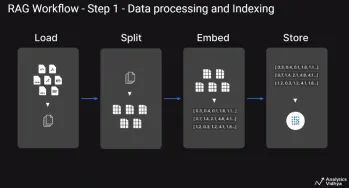 A Guide to Building Agentic RAG Systems with LangGraphApr 21, 2025 am 11:00 AM
A Guide to Building Agentic RAG Systems with LangGraphApr 21, 2025 am 11:00 AMThis article explores Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) systems and how AI agents can enhance their capabilities. Traditional RAG systems, while useful for leveraging custom enterprise data, suffer from limitations such as a lack of real-time dat


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

MantisBT
Mantis is an easy-to-deploy web-based defect tracking tool designed to aid in product defect tracking. It requires PHP, MySQL and a web server. Check out our demo and hosting services.

Dreamweaver Mac version
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

PhpStorm Mac version
The latest (2018.2.1) professional PHP integrated development tool

WebStorm Mac version
Useful JavaScript development tools






